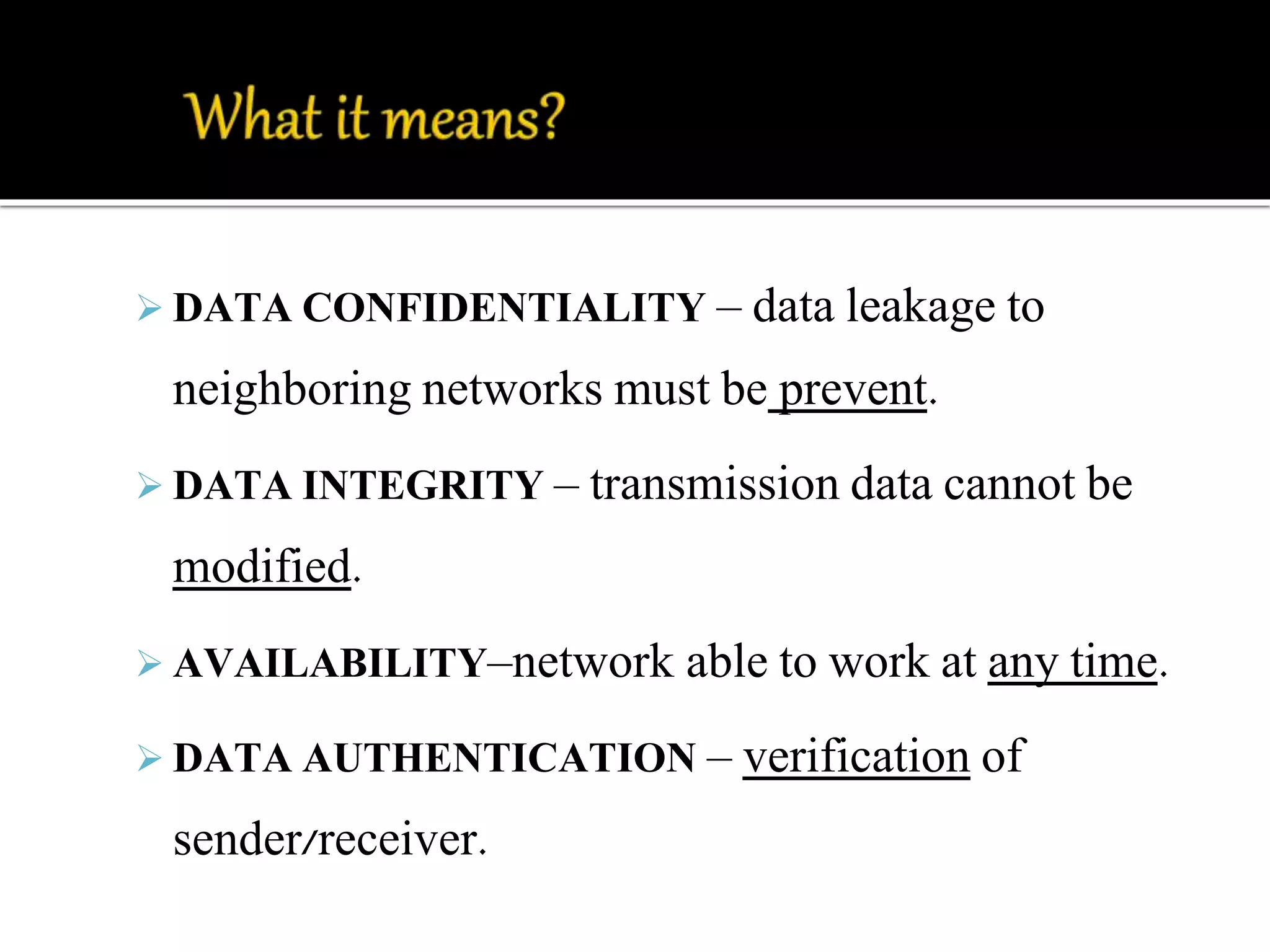
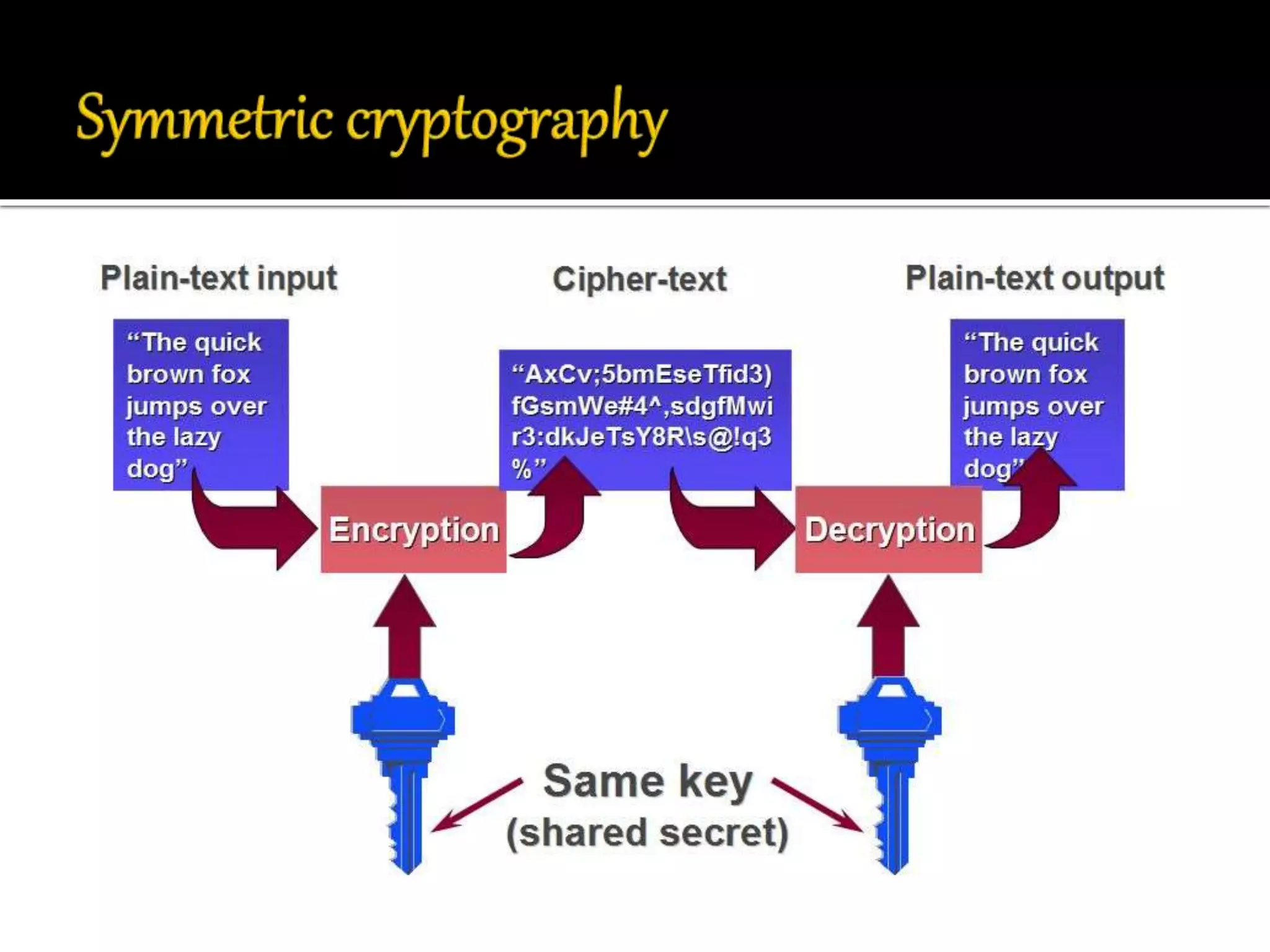
This document discusses wireless sensor networks and network security. It defines what a wireless sensor network is and common applications. It then discusses protocols used for communication between nodes, including what they are, how they perform tasks, and their role in security. The document outlines various security threats like denial of service attacks, and mechanisms to protect against them, including cryptography, key management protocols, and encryption protocols. It emphasizes the importance of security protocols for wireless sensor networks.