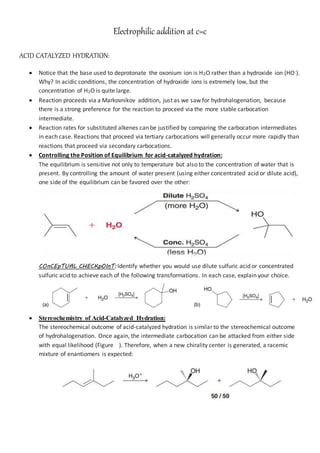
The document discusses electrophilic addition at C=C through acid-catalyzed hydration, emphasizing the role of water over hydroxide ions due to concentration differences in acidic conditions. It highlights the Markovnikov addition preference for more stable carbocation intermediates and how reaction rates differ based on the carbocation type. The stereochemical outcomes resemble those of hydrohalogenation, producing a racemic mixture of enantiomers due to possible attacks from either side of the planar carbocation intermediate.