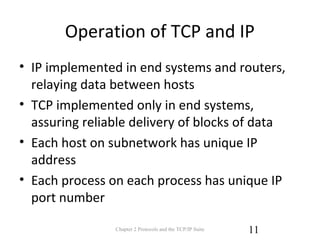
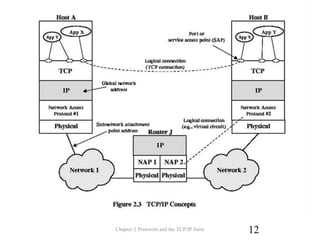
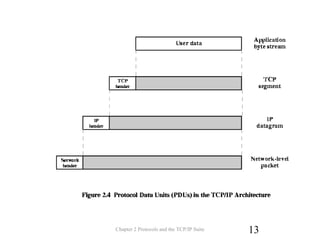
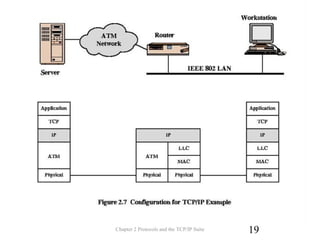
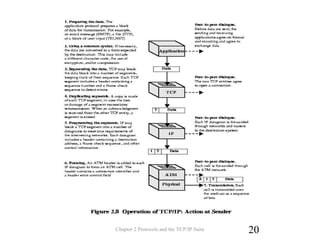
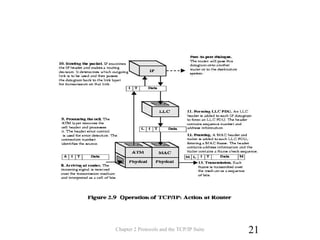
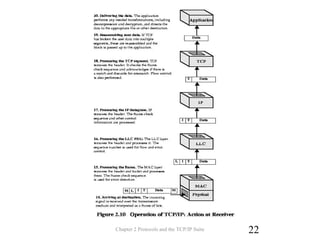
The document discusses protocols and the TCP/IP protocol suite. It introduces the layered protocol architecture and describes the need for coordination between communicating systems. It explains key aspects of protocols including syntax, semantics, and timing. The TCP/IP protocol suite is presented including the layers of physical, network access, internet, and transport. TCP and UDP are described as transport layer protocols, with TCP providing reliable connection-oriented delivery and UDP being unreliable and connectionless. The OSI reference model layers and concepts of internetworking such as routers are also summarized.