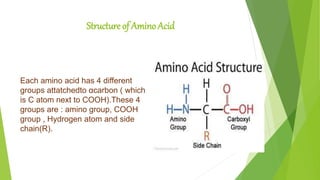
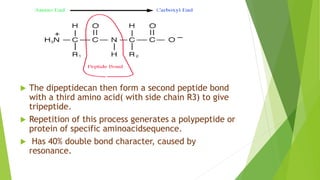
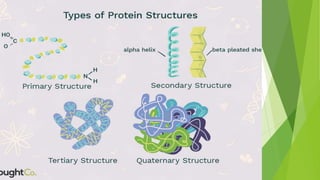
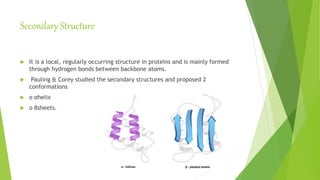
The document discusses the structure and biological significance of proteins. It describes the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. The secondary structure involves hydrogen bonding that forms alpha helices or beta sheets. Tertiary structure defines the overall 3D shape formed by interactions between amino acid side chains. Quaternary structure refers to the clustering of multiple peptide chains through various bonds. Proteins are essential to life and constitute 50% of cellular material.




![Amino Acids
Amino acids are a group of organic compounds
containing two functional groups –amino and
carboxyl.
The amino group[ -NH2] is basic while the
carboxyl group [COOH] is acidic in nature.
There are about 300 aminocids occur in nature.
Only 20 of them occur in proteins.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinanditsstructureandfunctions-200705065651/85/Protein-and-it-s-structure-and-functions-5-320.jpg)