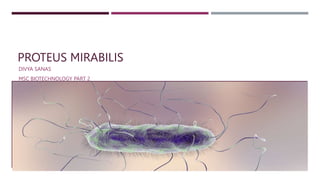
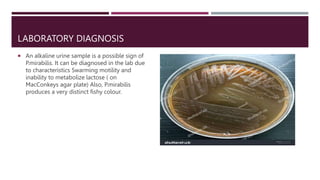
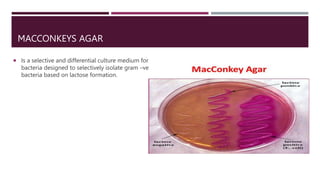
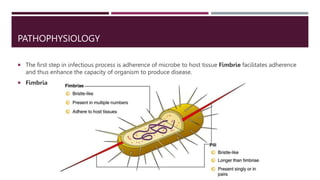
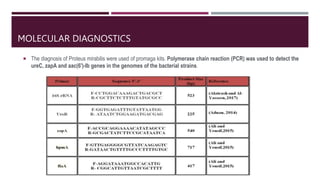
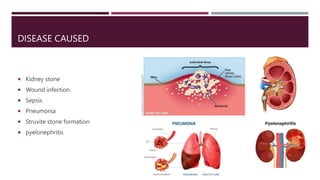
Proteus mirabilis is a gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the human intestinal tract. It can cause urinary tract infections when it enters the urinary system, where it produces an enzyme called urease that breaks down urea into ammonia, raising the pH of urine. P. mirabilis is responsible for 90% of Proteus infections and can lead to sepsis, abdominal infections, and secondary infections of wounds and ears. It is diagnosed through laboratory tests detecting its unique swarming motility, inability to metabolize lactose, and distinctive fishy odor. Treatment involves antibiotics like beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and fluoroquinolones to which P. mirabilis