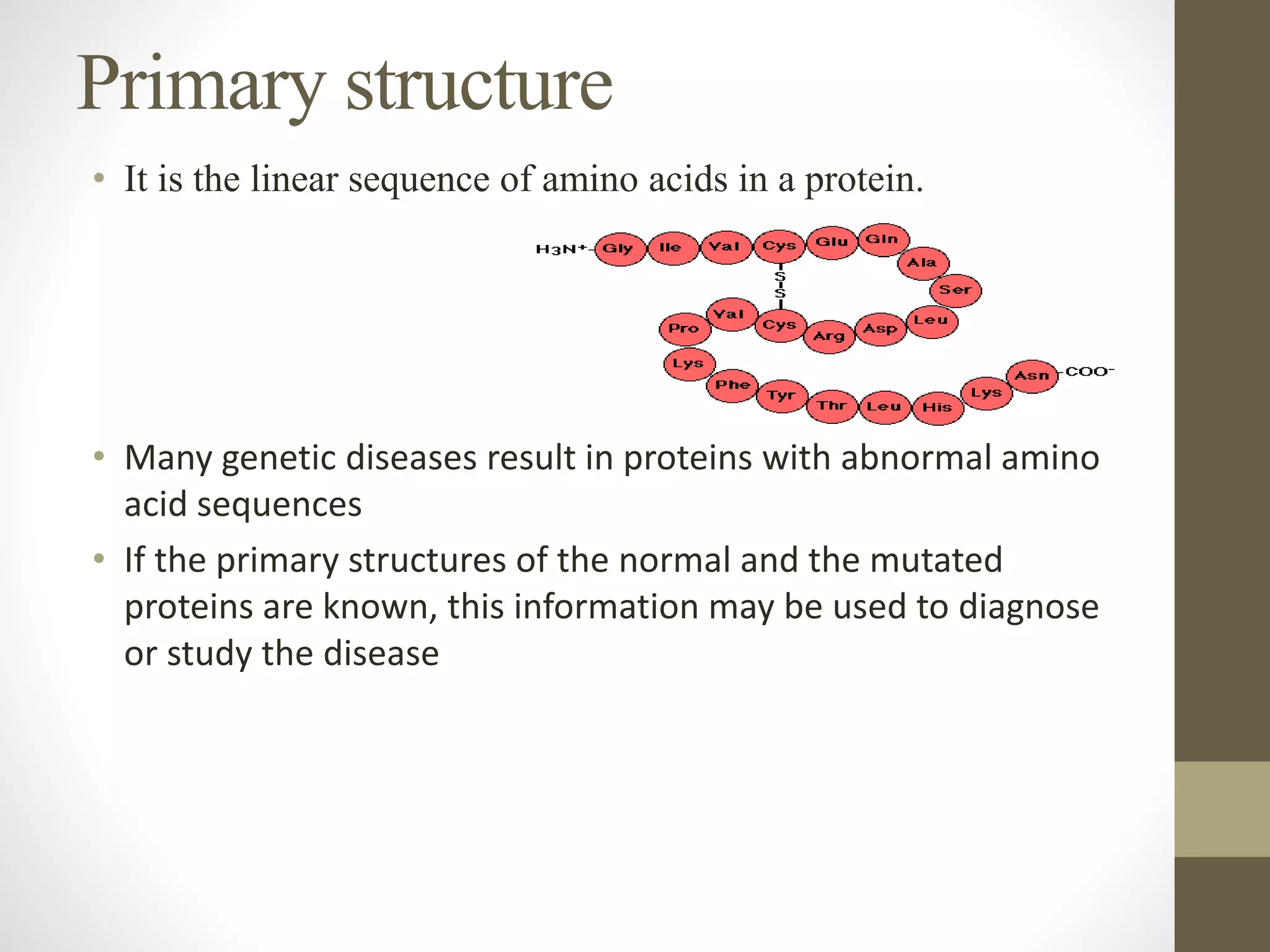
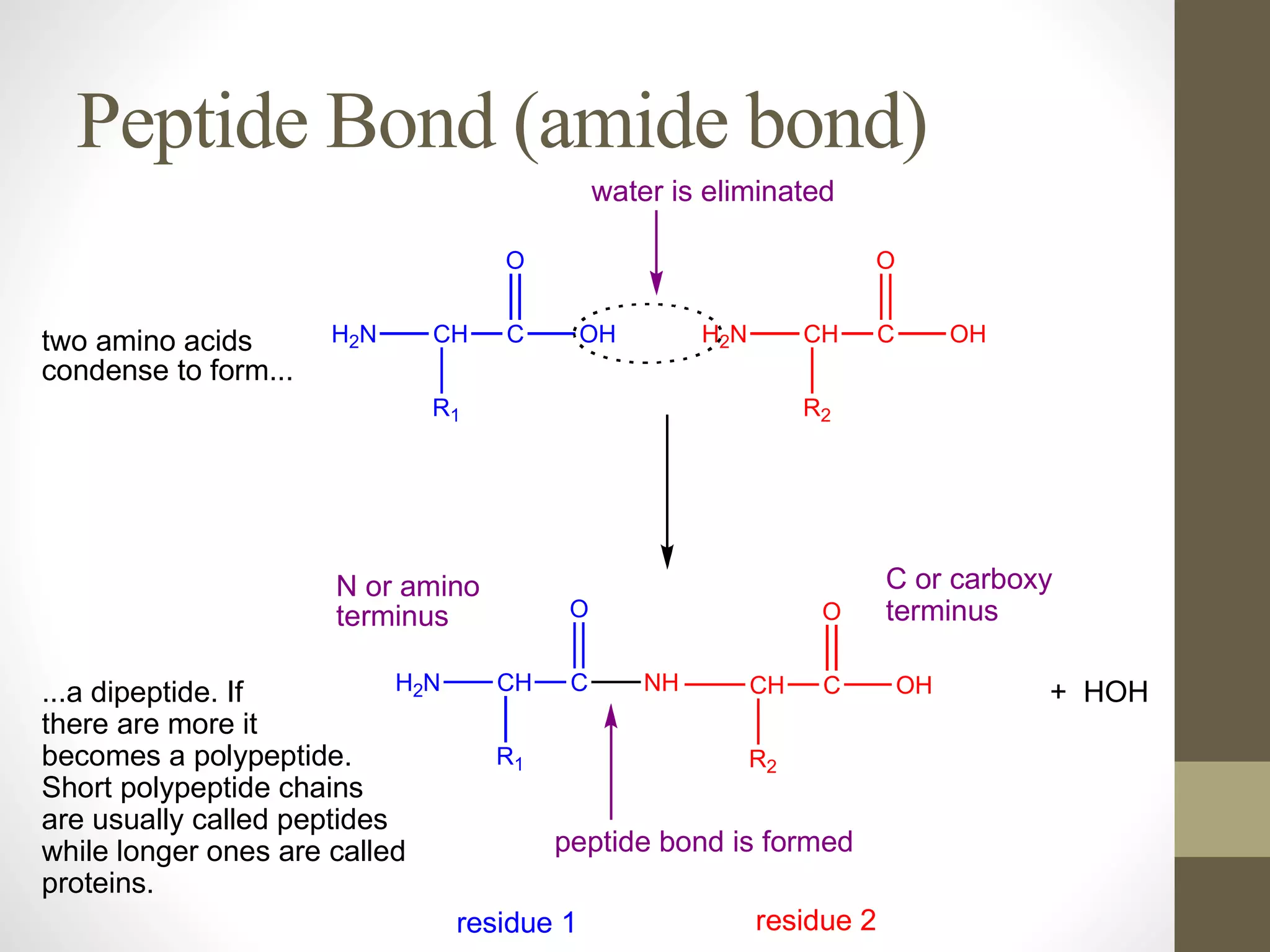
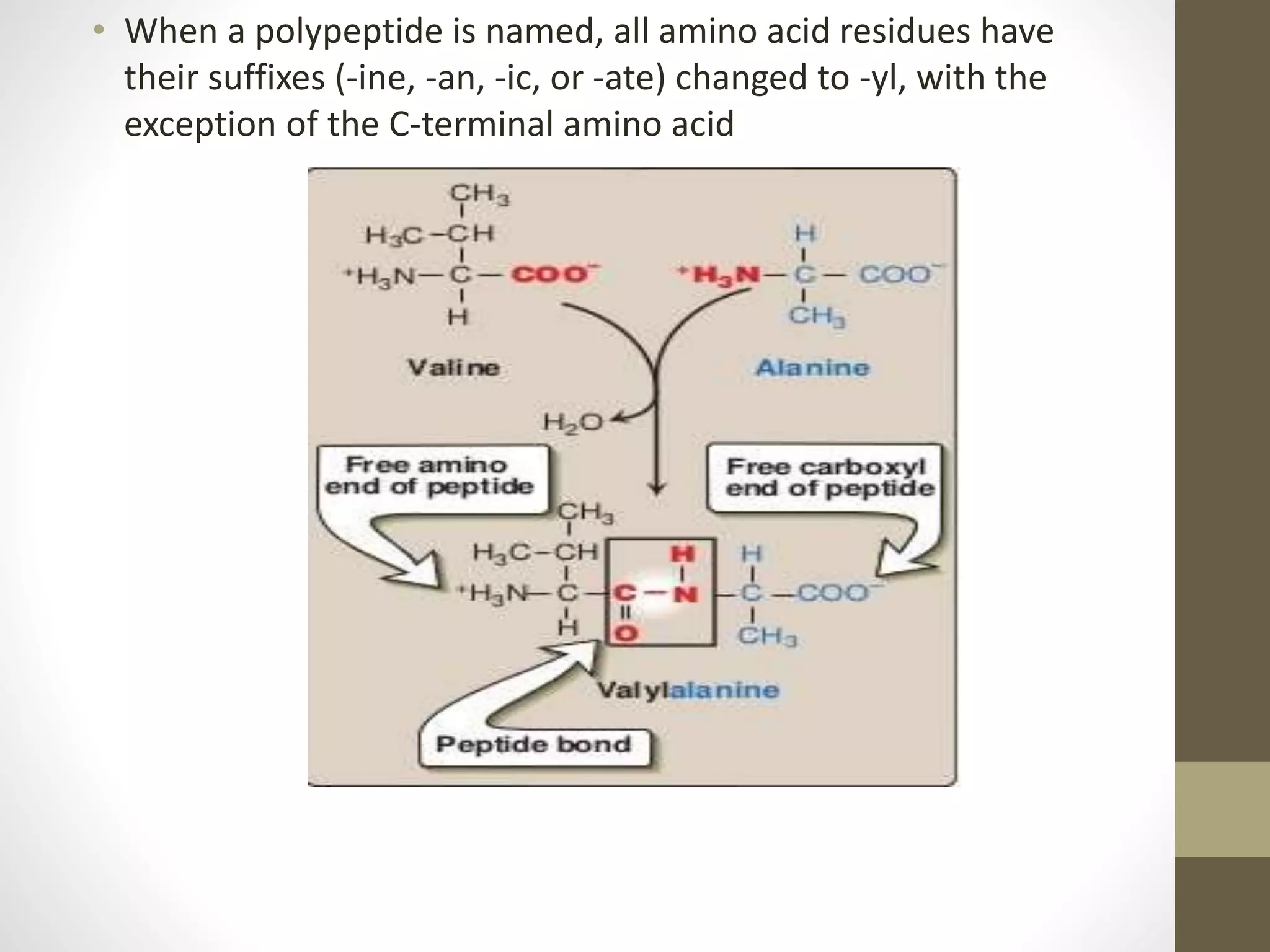
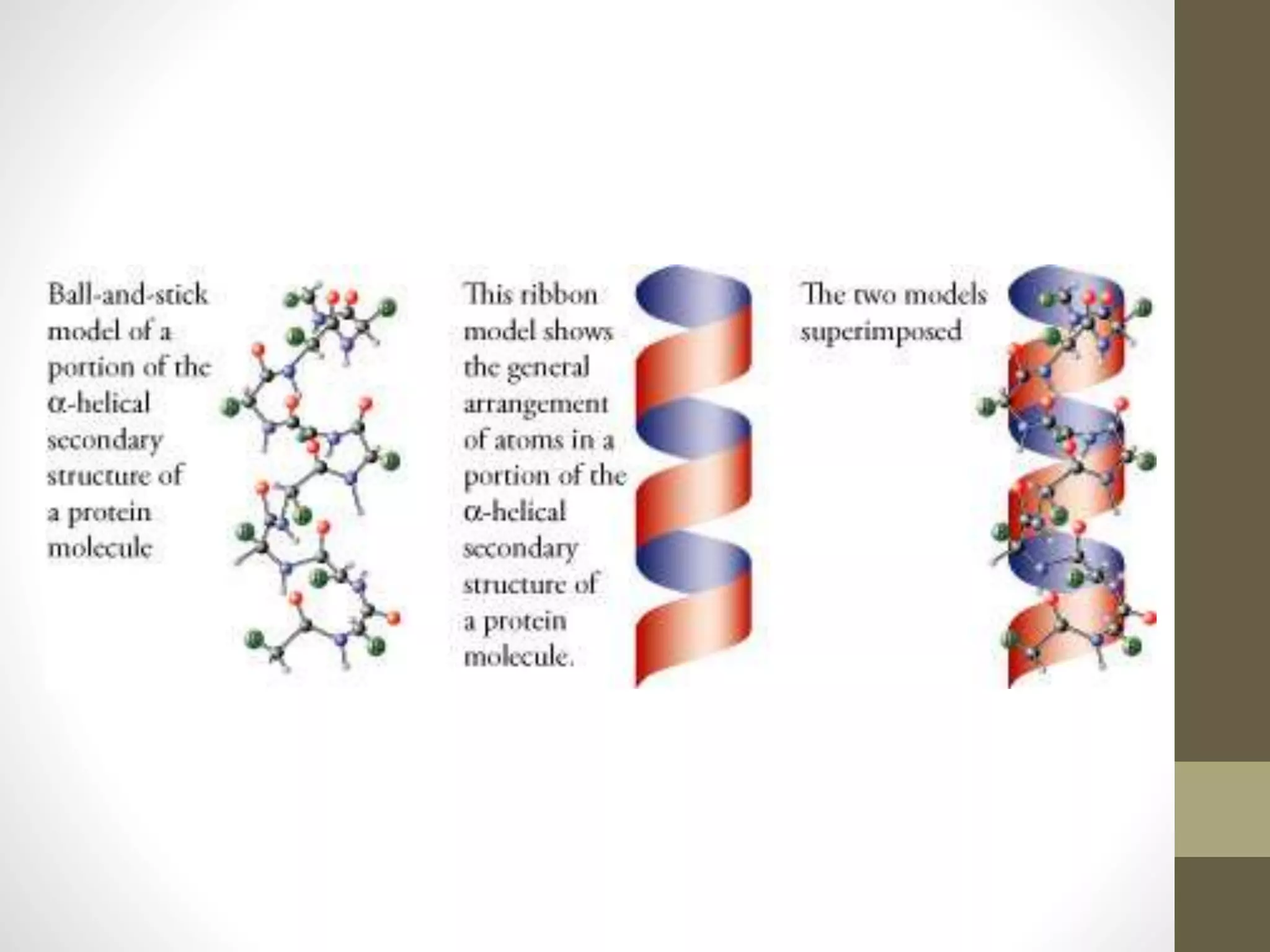
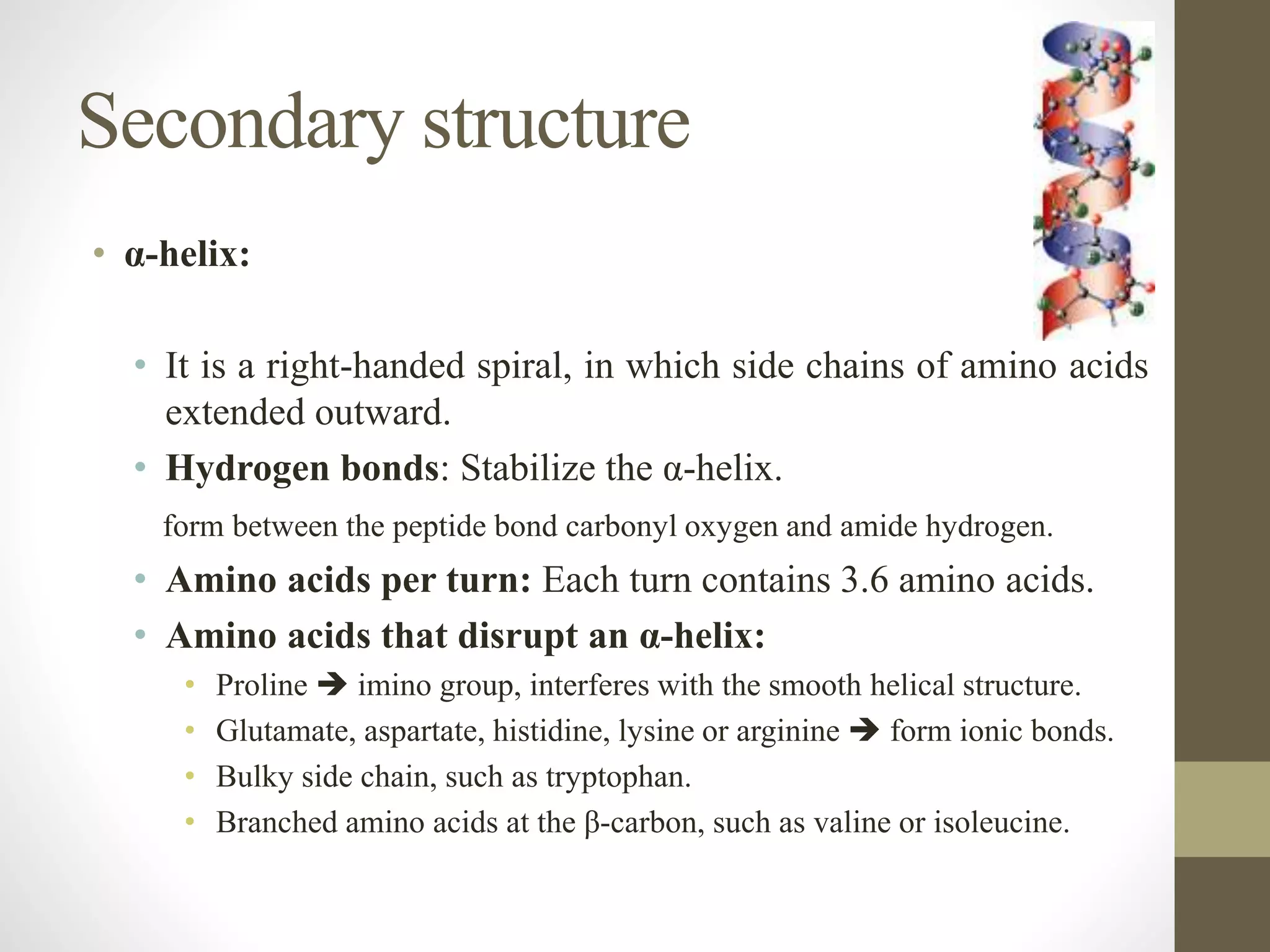
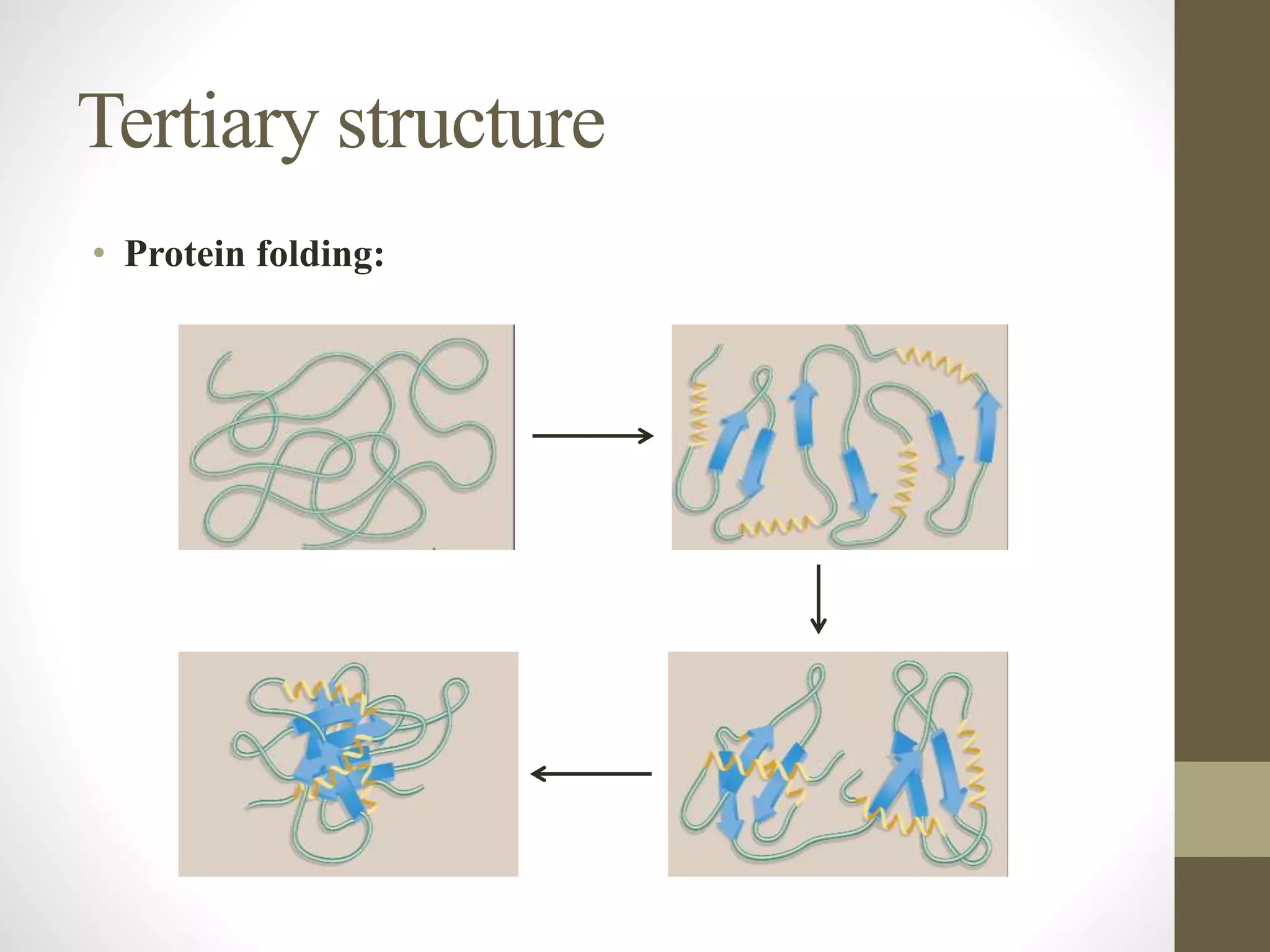
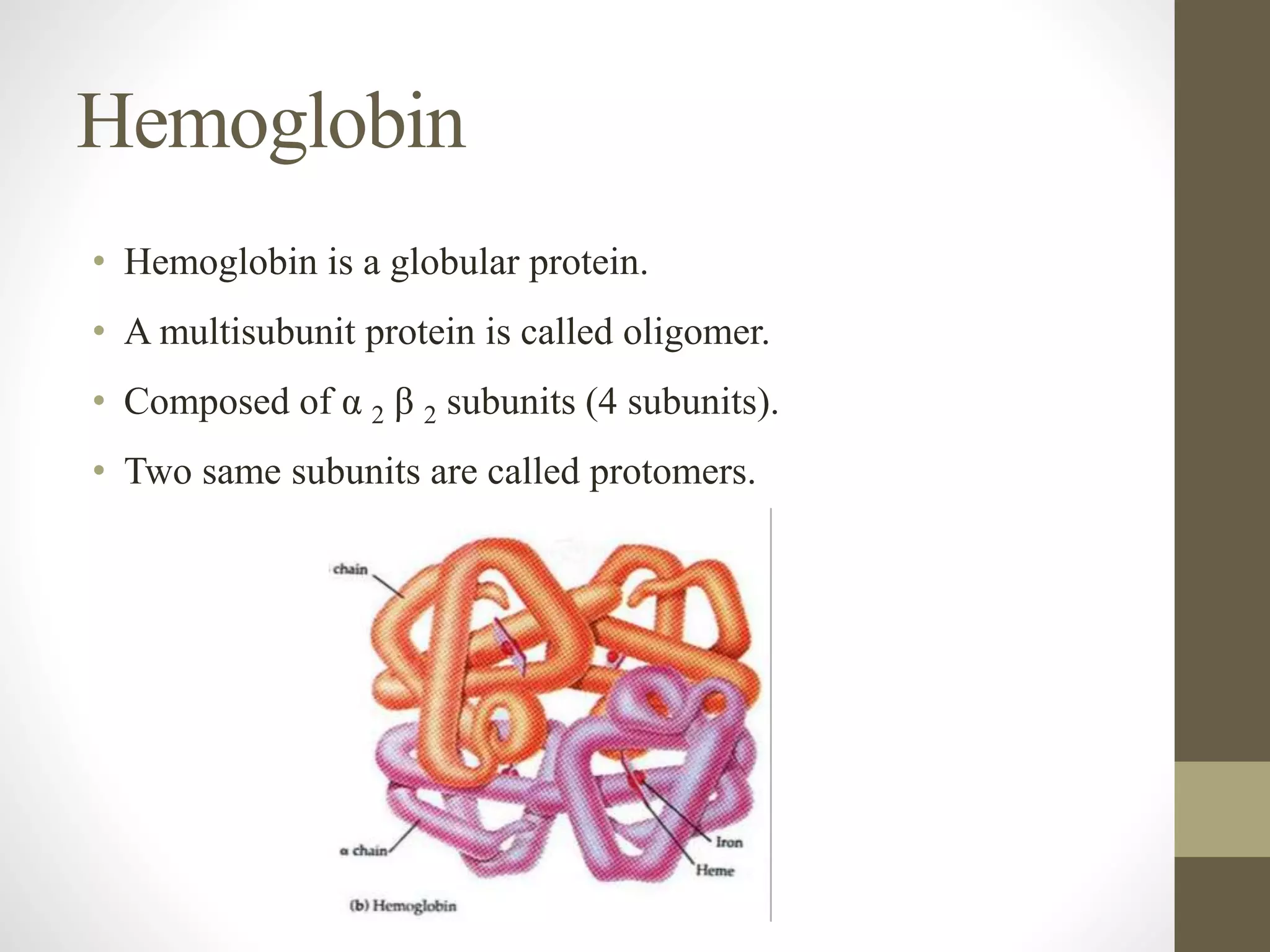
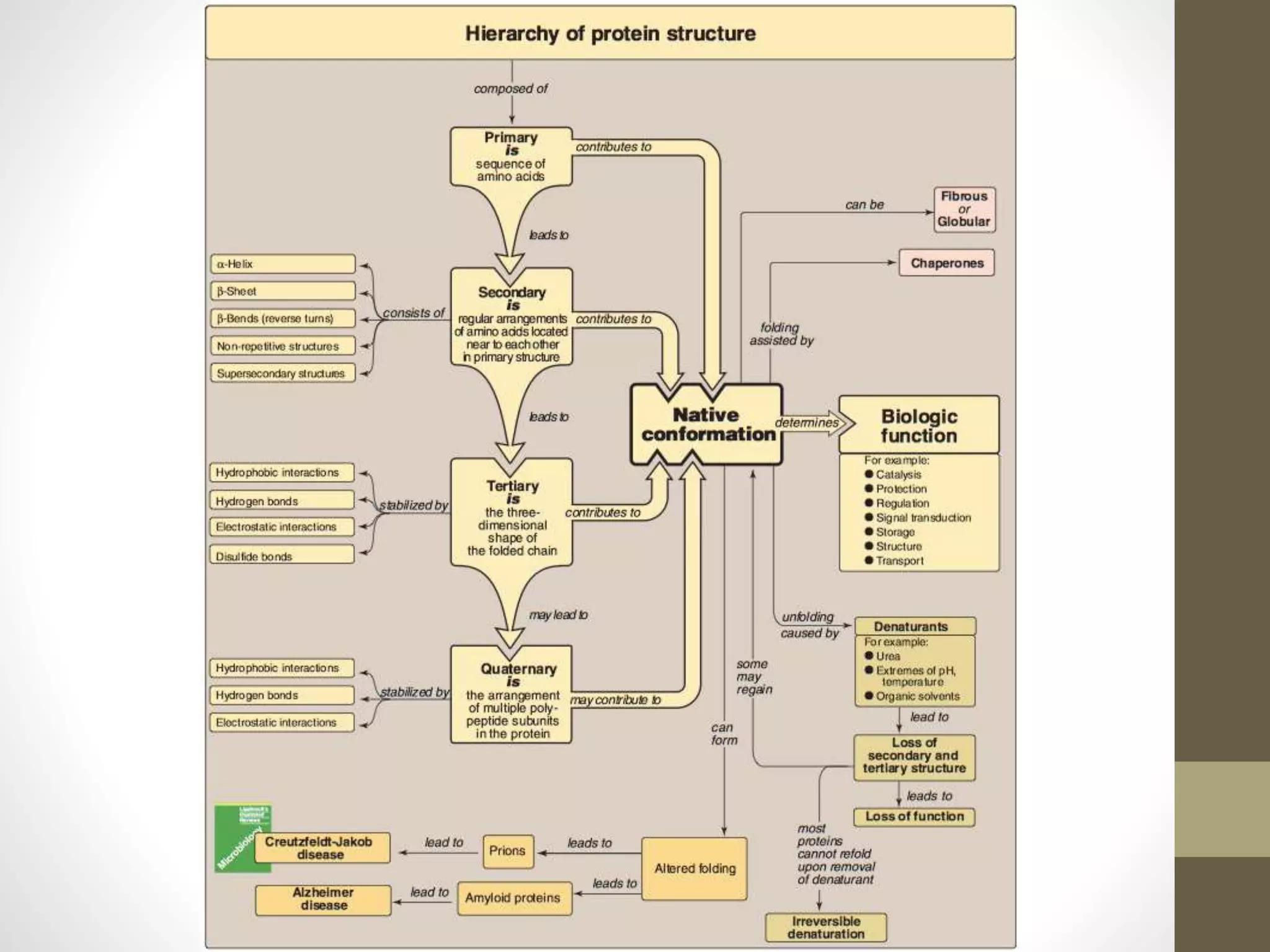
Proteins are made of amino acid chains that fold into complex 3D structures which determine their function. There are four levels of protein structure: primary structure is the amino acid sequence; secondary structures include alpha helices and beta sheets formed by hydrogen bonds between nearby amino acids in the sequence. Tertiary structure is the 3D structure of the whole chain, stabilized by interactions between amino acid side chains. Quaternary structure involves the interaction of multiple polypeptide chains to form a multi-subunit protein complex like hemoglobin. Misfolded proteins can aggregate abnormally and lead to diseases such as Alzheimer's and prion diseases.