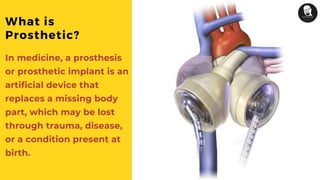
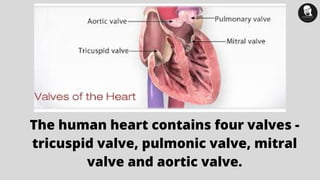
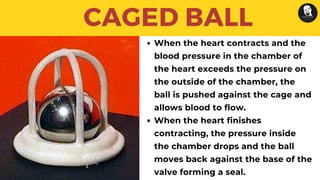
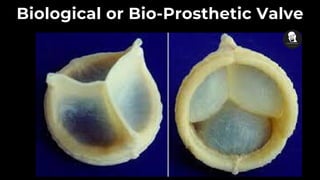
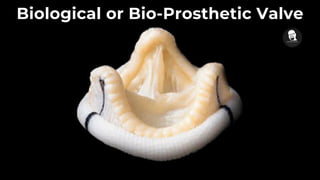
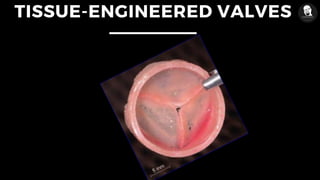
The document discusses prosthetic heart valves, including their definition, types, and functionalities in addressing heart valve malfunctions. It categorizes heart valves into mechanical, biological, and tissue-engineered types, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. The overview also highlights the materials used and the potential lifespans of different valve types.