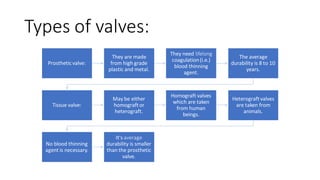
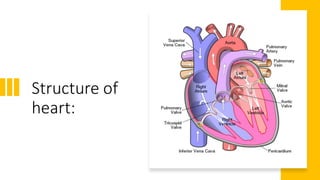
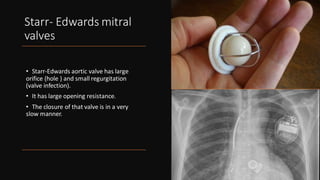
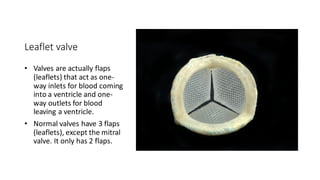
The document explains the function and structure of the heart, including common causes of heart malfunction and types of heart valves. It details artificial heart valves, their materials, benefits, and potential complications during and after implantation. Additionally, it covers the design requirements for artificial valves to avoid issues such as hemolysis and thrombosis.