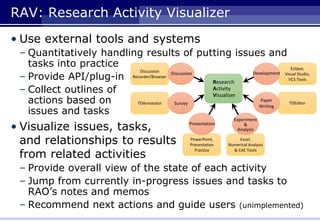
The document proposes a gamification framework aimed at enhancing motivation in research activities at Nagoya University. It outlines a prototype system called 'research activity concierge,' which organizes, visualizes, and monitors research tasks while incorporating game design elements to improve student engagement. Future work includes verifying the framework's effectiveness through practical use and comparing activity levels with and without the system.








![e.g.) Discussion (main activity)
Main activity
Sub-activities
Actions
Results
• [Discussion]→[Ask question at seminar]
– Actions: Ask <*> questions
– Results: Asked <*> questions,
Cumulative question number has topped <**> times
Discussion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ohirateem201514-151216125018/85/Proposed-framework-for-Gamifying-Research-Activities-9-320.jpg)
![e.g.) Programming
Actions
Results
Implementation
Main activity
Sub-activities
Programming
• [Gaining expertise],[Implementation]→[Programming]
– Actions: Write server/client program, Write I/O process of DB
– Results: Committed <*> times, Wrote <**> lines of code,
Cumulative total of code has topped <***> lines, …
Gaining expertise
(sub-activity of Gaining expertise
and Implementation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ohirateem201514-151216125018/85/Proposed-framework-for-Gamifying-Research-Activities-10-320.jpg)



![RAC MyPage
Use Case and Ongoing Data Collection
You should create API
for paper writing.
[Note]
“Development tasks”
[Memo]
Editor hook
RAV
Run action
“Create script”
Summarize work,
describe memo,
make self-assessment
RAW
Send notification
Evaluate results
of activity
Feedback
Organize statements
Create note/memo
Discussion
User
Others
Commit to server
・ Seminar content
・ Notes, memos
・ Source code
・ Logs
- Action
- Evaluation
- UI operation
Select action
“Write server program”
Check stats/badges,
use items
Check progress
and feedback
RAO
RAO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ohirateem201514-151216125018/85/Proposed-framework-for-Gamifying-Research-Activities-15-320.jpg)




