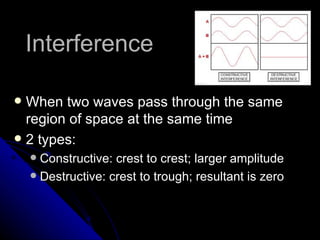
The document discusses several optics concepts including interference, diffraction, dispersion of light, the electromagnetic spectrum, reflection, refraction, mirrors, lenses, and important formulas. Interference can be constructive or destructive. Diffraction refers to how waves bend around obstacles. Dispersion of light occurs when the index of refraction varies with wavelength. Reflection and refraction describe how waves interact with surfaces and change speed when passing between substances. Mirrors and lenses have focal points determined by their curvature and distance from the lens.