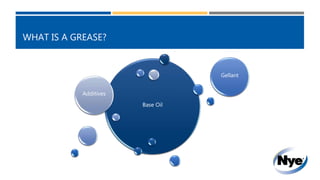
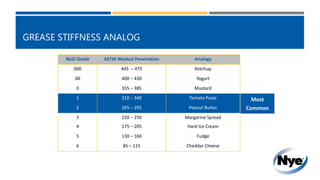
The document provides a technical reference on the properties of grease lubricants, detailing various base oil chemistries, their temperature ranges, and viscosity indexes. It highlights the benefits of greases, such as load handling, oil retention, and noise control, as well as key physical properties like flash point and evaporation. Additionally, it includes a comparison of NLGI grades with common food analogs to illustrate grease stiffness.