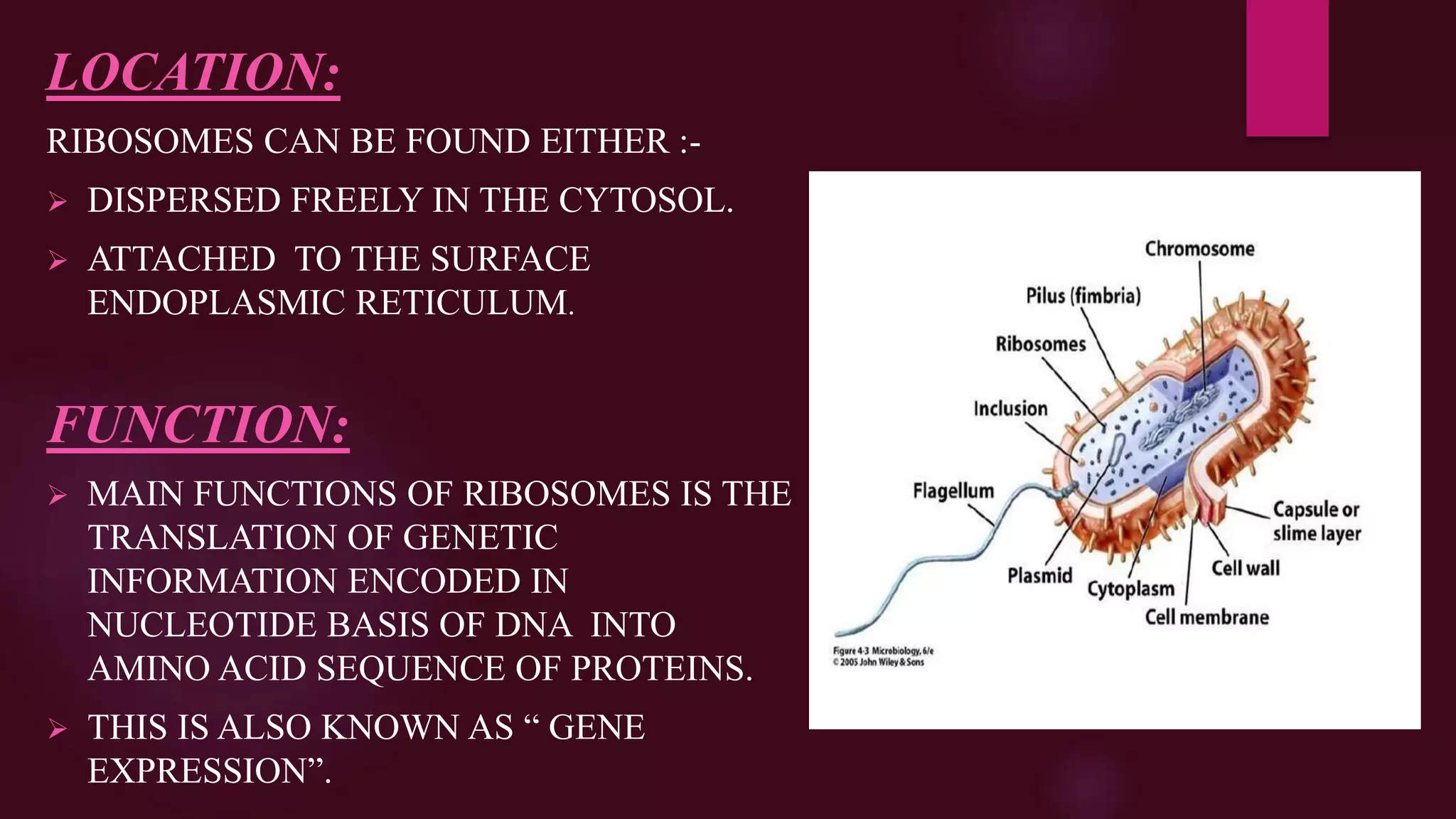
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and have no nucleus. They contain genetic material in the form of a single circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 micrometers in diameter. The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that encloses prokaryotic cells and is composed of phospholipids and proteins arranged in a fluid mosaic structure. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis in prokaryotes and are composed of RNA and protein. Inclusion bodies are insoluble protein aggregates that form in bacteria when they are forced to overproduce foreign proteins.