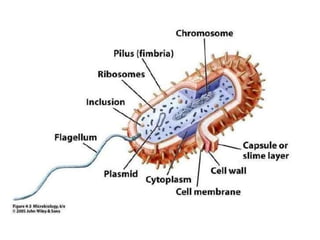
Bacteria have a simple cellular structure compared to eukaryotes. They lack internal membrane-bound organelles. Their cellular components include a cytoplasm containing a nucleoid, plasmids, ribosomes and other structures. The cell envelope includes a plasma membrane, cell wall, and in some cases an outer membrane. Some bacteria have external structures like flagella, fimbriae or pili that allow movement or attachment. Gram staining distinguishes bacteria based on differences in their cell wall composition and thickness.