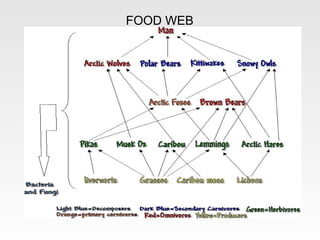
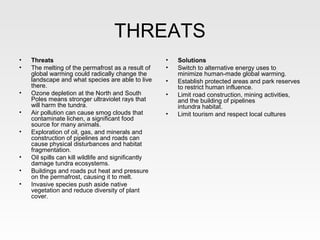
The tundra biome is the coldest of all biomes, with extremely low temperatures averaging between -20°F to -30°F. It has a short growing season and receives little precipitation annually. Plants grow slowly due to the cold and include various mosses, shrubs, grasses, and willows. Fauna includes herbivores like caribou and lemmings, and carnivores such as arctic foxes and polar bears. Threats to the tundra include melting permafrost from climate change and human disturbances from resource extraction and infrastructure development. The tundra plays an important role in global climate regulation and biodiversity.