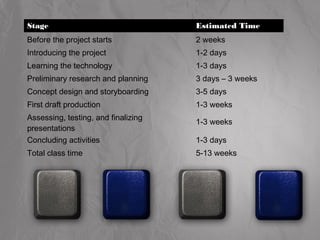
The document outlines the various phases of a project-based multimedia learning strategy, including preparing resources and materials, introducing the project to students, having students learn the necessary technologies, conducting preliminary research and planning, developing concept designs and storyboards, producing drafts and finalizing the project, and concluding with presentations. It provides details on activities and considerations for each phase to help structure and implement the multimedia learning projects.