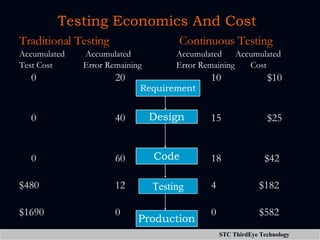
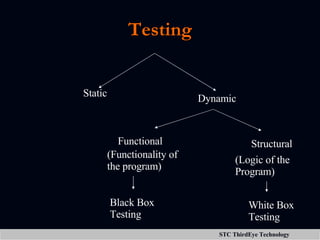
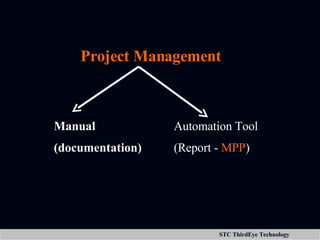
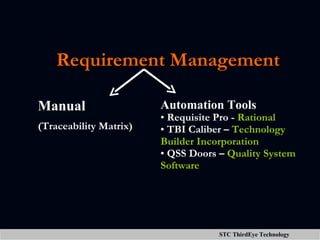
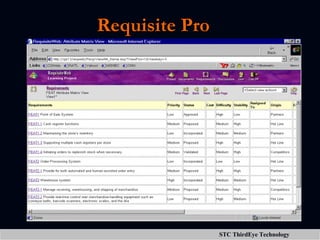
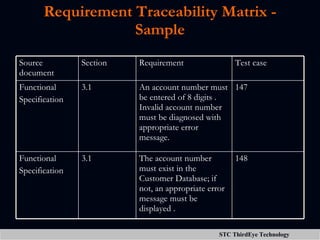
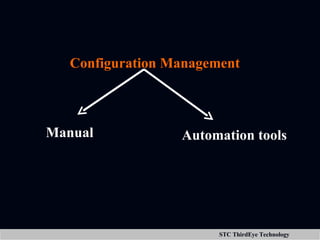
The document discusses various aspects of project management including planning, scheduling, costing, and monitoring software projects. It also discusses requirement management which involves managing changes to software requirements and using tools like requirement traceability matrices. Configuration management is also covered which deals with version control and tools to manage changes made during a project. Finally, the document discusses software testing including test plans, test cases, classifications of defects, and testing principles.



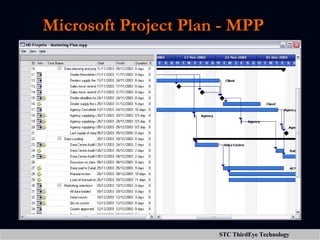




![Automation Tools(CM) Types Of Tools : VSS =>Visual Source Safe(Microsoft Product) Rational Clear Case =>(Rational Corporation Product) CVS =>Concurrent Version System.(free tool - Open Source) [wincvs.org]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-management-1223618448278211-9/85/Project-Management-14-320.jpg)