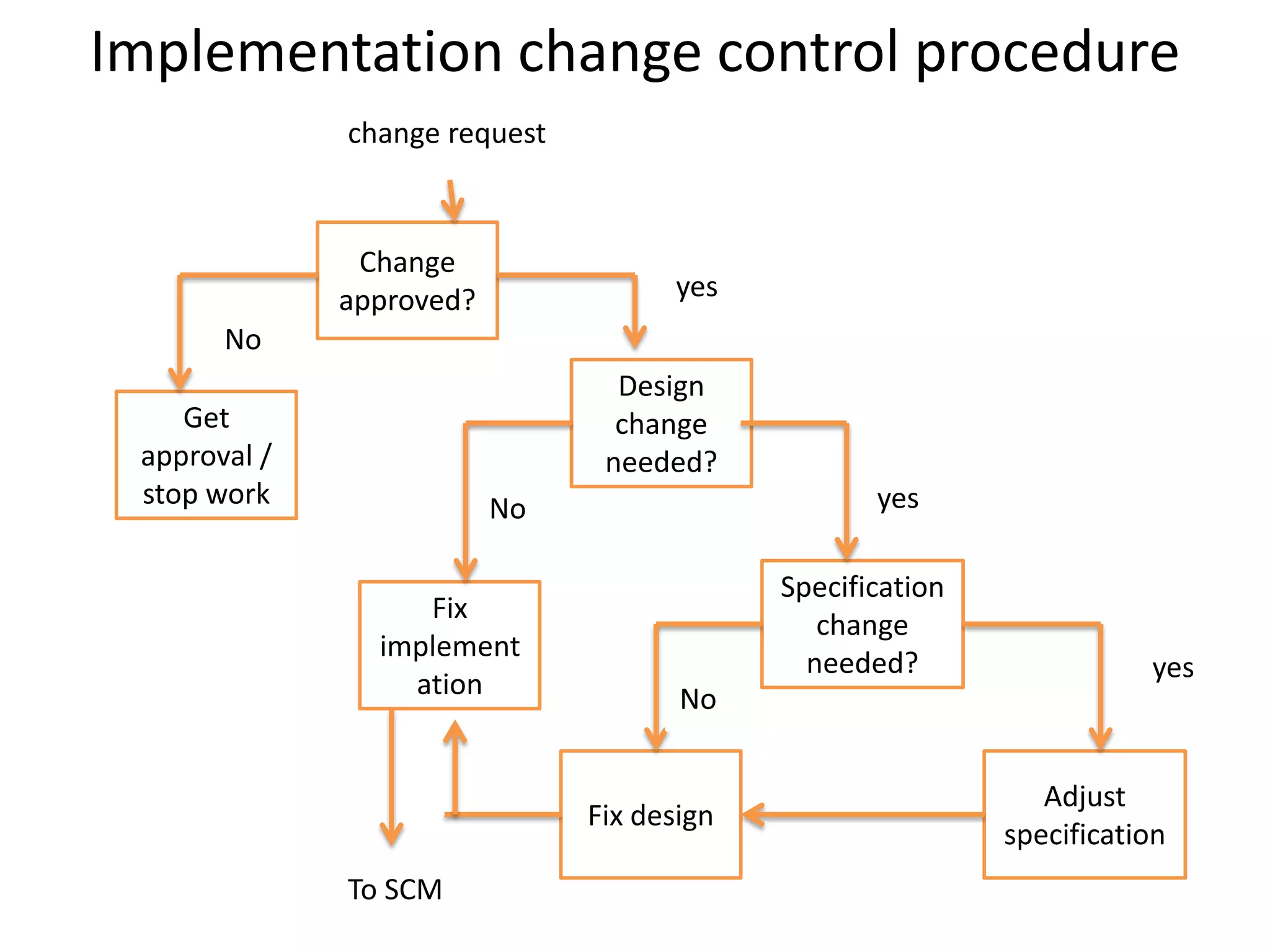
This document outlines a software configuration management plan, including its objectives to define responsibilities, approaches, and methods used. It describes the contents of the plan such as baselines, identification systems, change control procedures, implementation checkpoints, and tools to support configuration management. The document also provides examples of questions to consider in requirements, design, implementation, and testing phases and discusses configuration auditing.