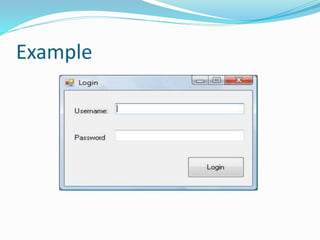
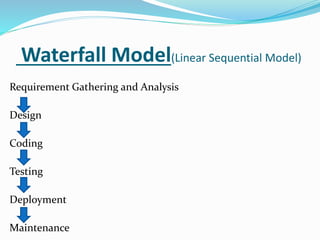
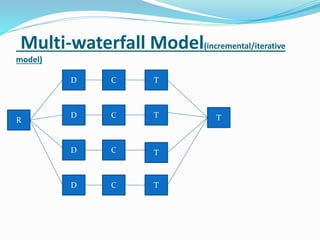
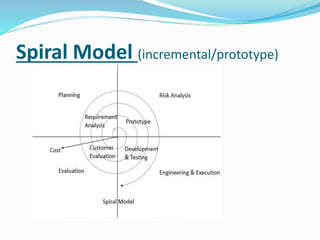
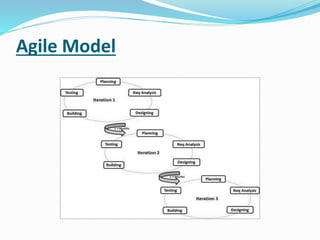
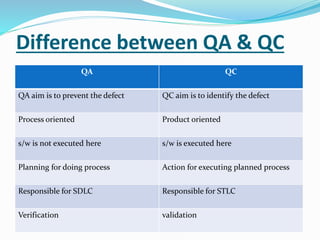
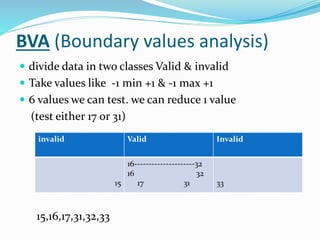
The document provides information on software testing and the software testing life cycle. It defines software, testing, and software testing. It describes why software testing is important and discusses manual testing. It covers the software development life cycle (SDLC) process and different testing models like waterfall, spiral, and agile. It also defines quality management systems, the roles of testers, and different testing techniques like black box and white box testing.