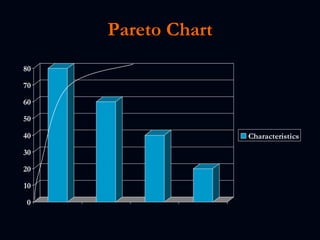
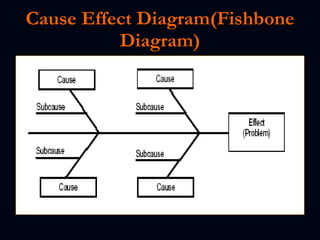
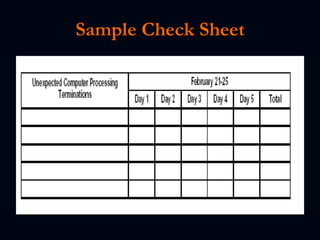
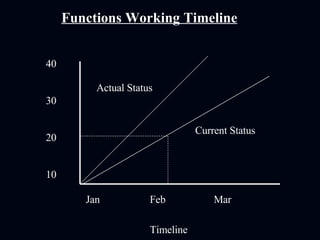
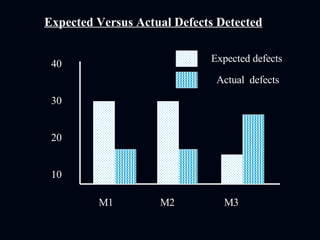
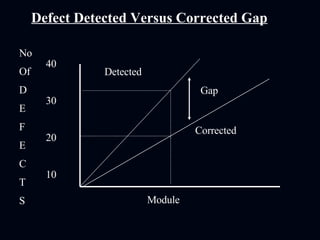
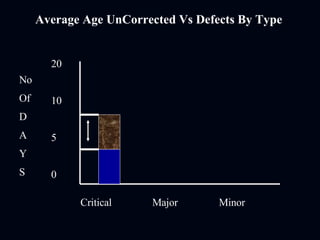
The document discusses various test reporting tools that testers use such as Pareto charts, cause-effect diagrams, and check sheets. It then provides examples of eight interim test reports that provide status updates on functional testing, defects uncovered versus corrected, and average age of uncorrected defects. The summaries provide testing metrics to analyze progress and identify issues.