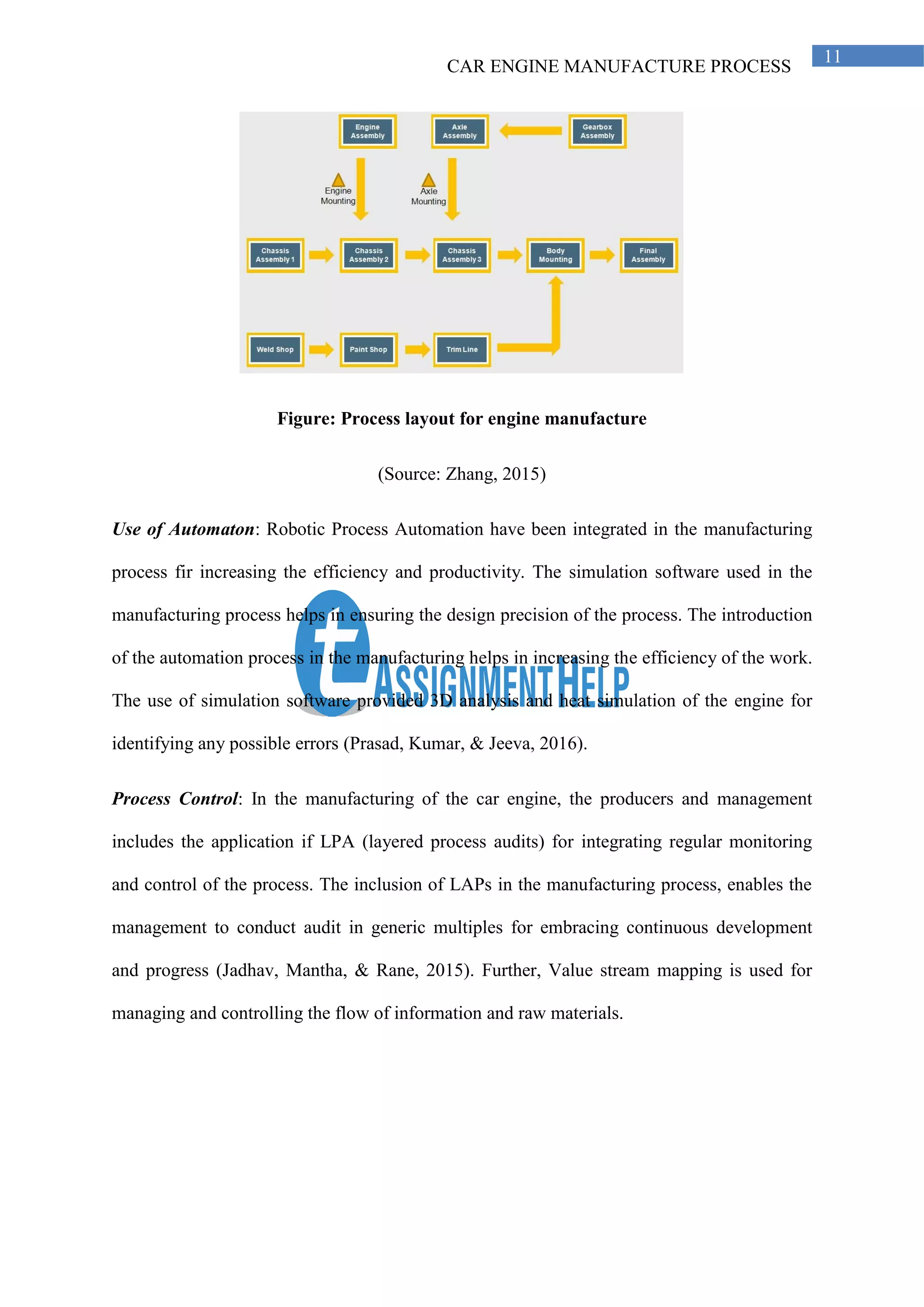
This document outlines the project management process for evaluating car engine manufacturing, emphasizing parameters such as health and safety, sustainability, and stakeholder involvement. It discusses the use of lean manufacturing principles, advanced technologies, and compliance with regulatory standards to optimize production, ensure quality, and mitigate environmental impacts. The assessment covers materials, processes, and maintenance practices to enhance manufacturability and maintainability in engine production.