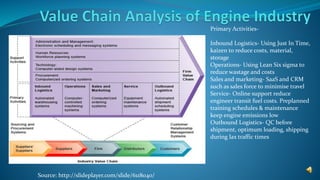
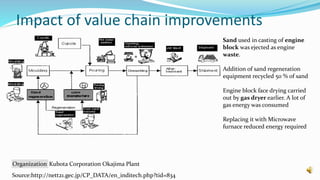
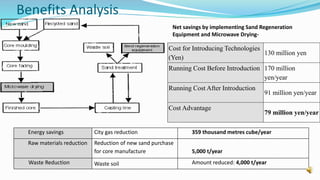
This document discusses sustainability practices in the engine manufacturing industry. It outlines how just-in-time production and reducing inventory impacts suppliers. It also describes the types of engines produced and their environmental and social impacts, including pollution effects. The document then discusses primary business activities and examples of value chain improvements from companies like reducing waste and increasing efficiency. Finally, it outlines best practices adopted by various engine companies focused on sustainability.