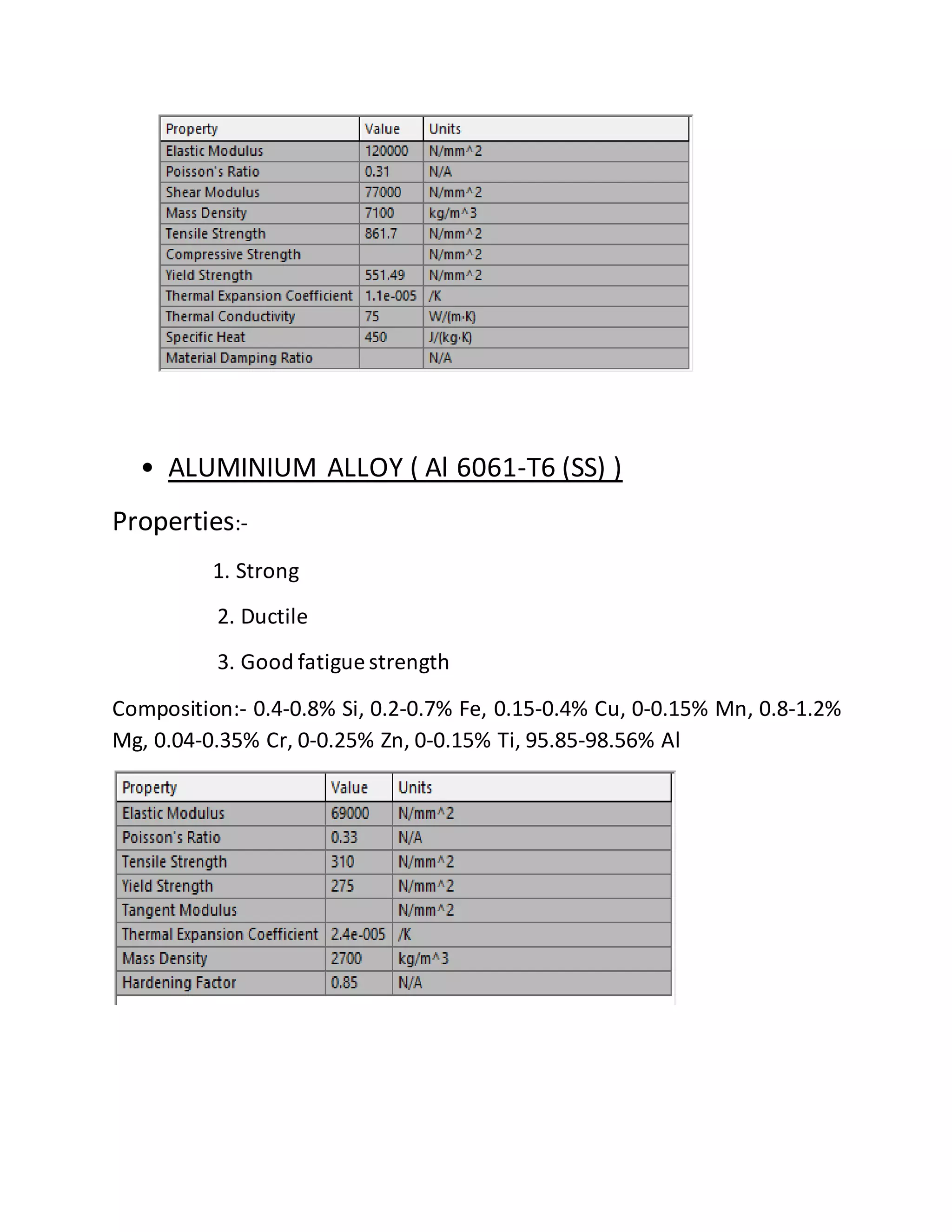
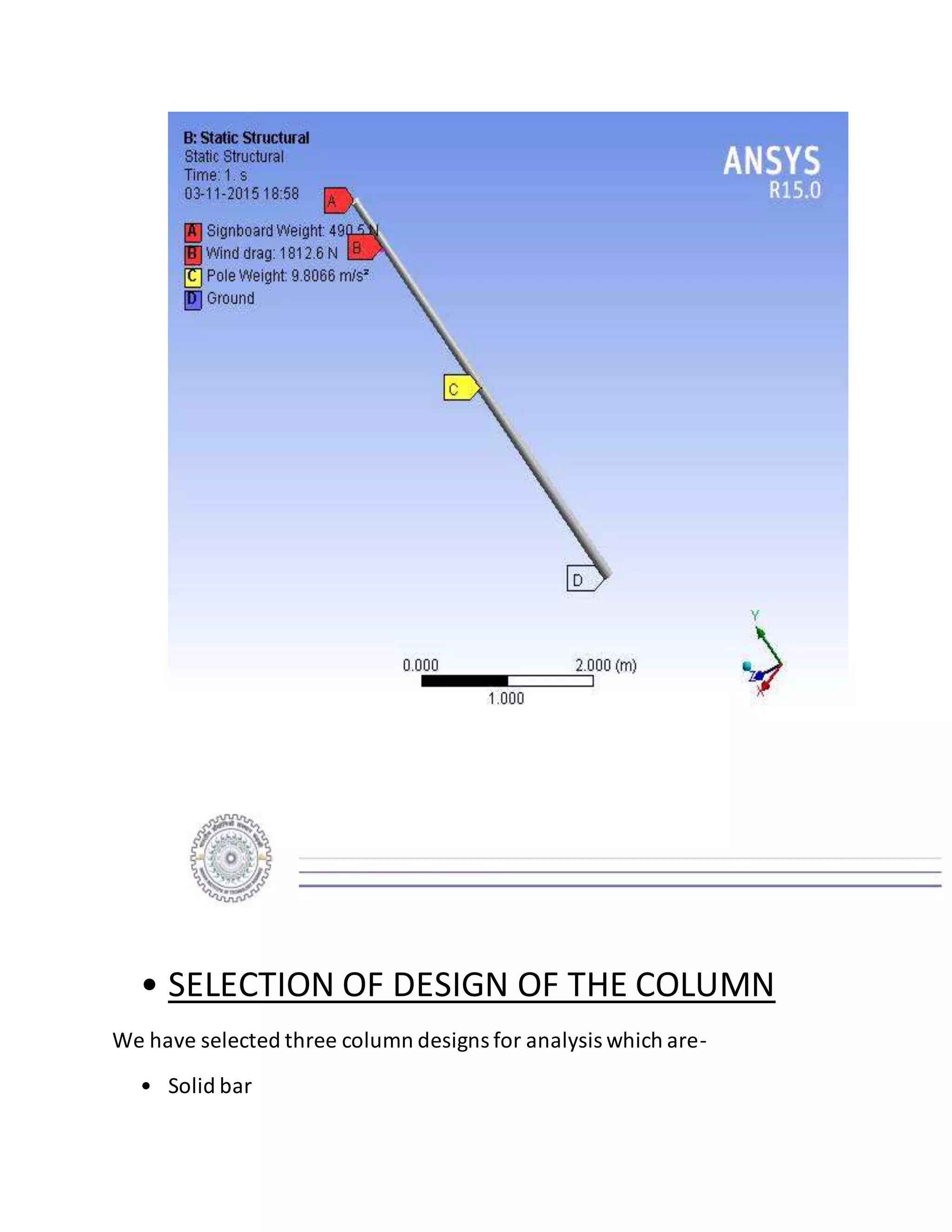
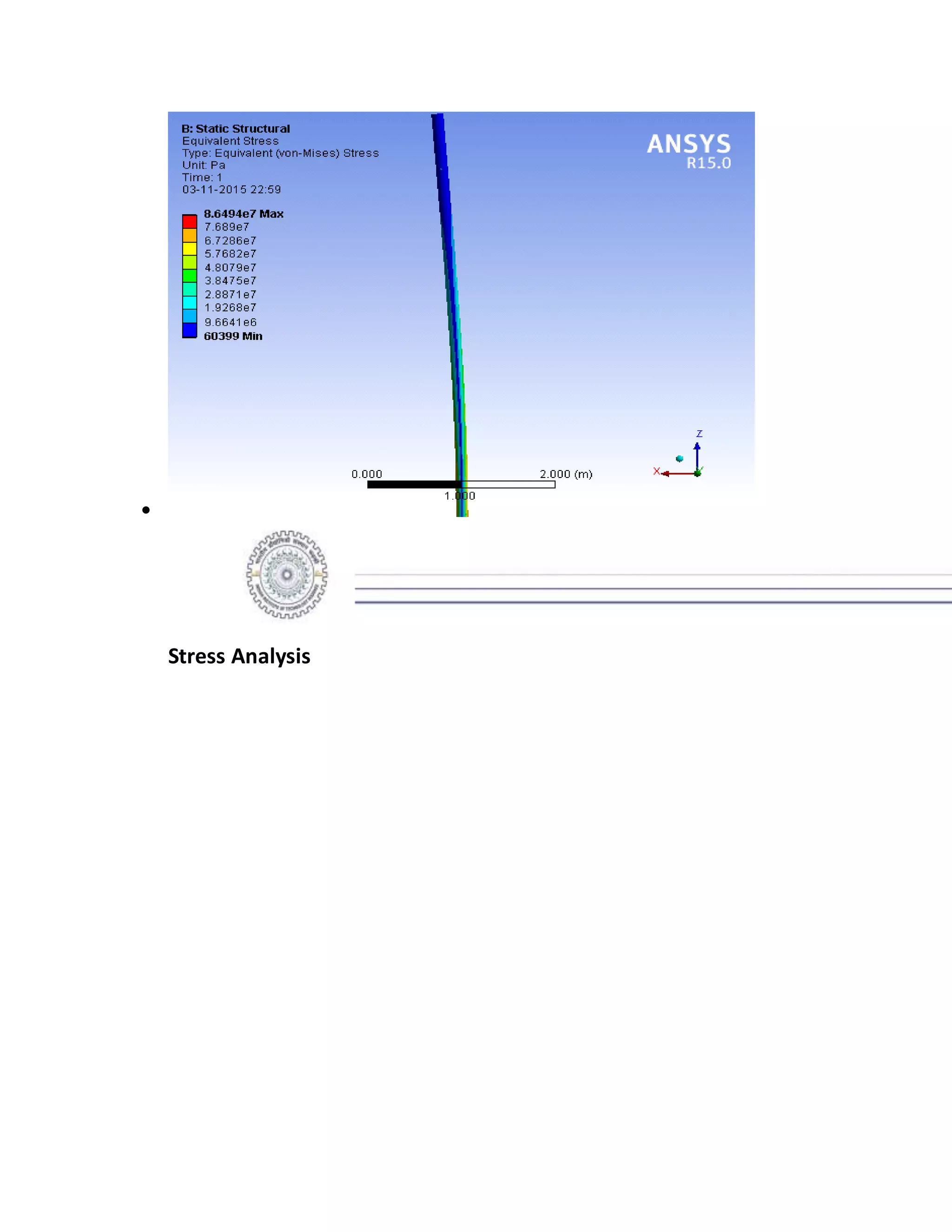
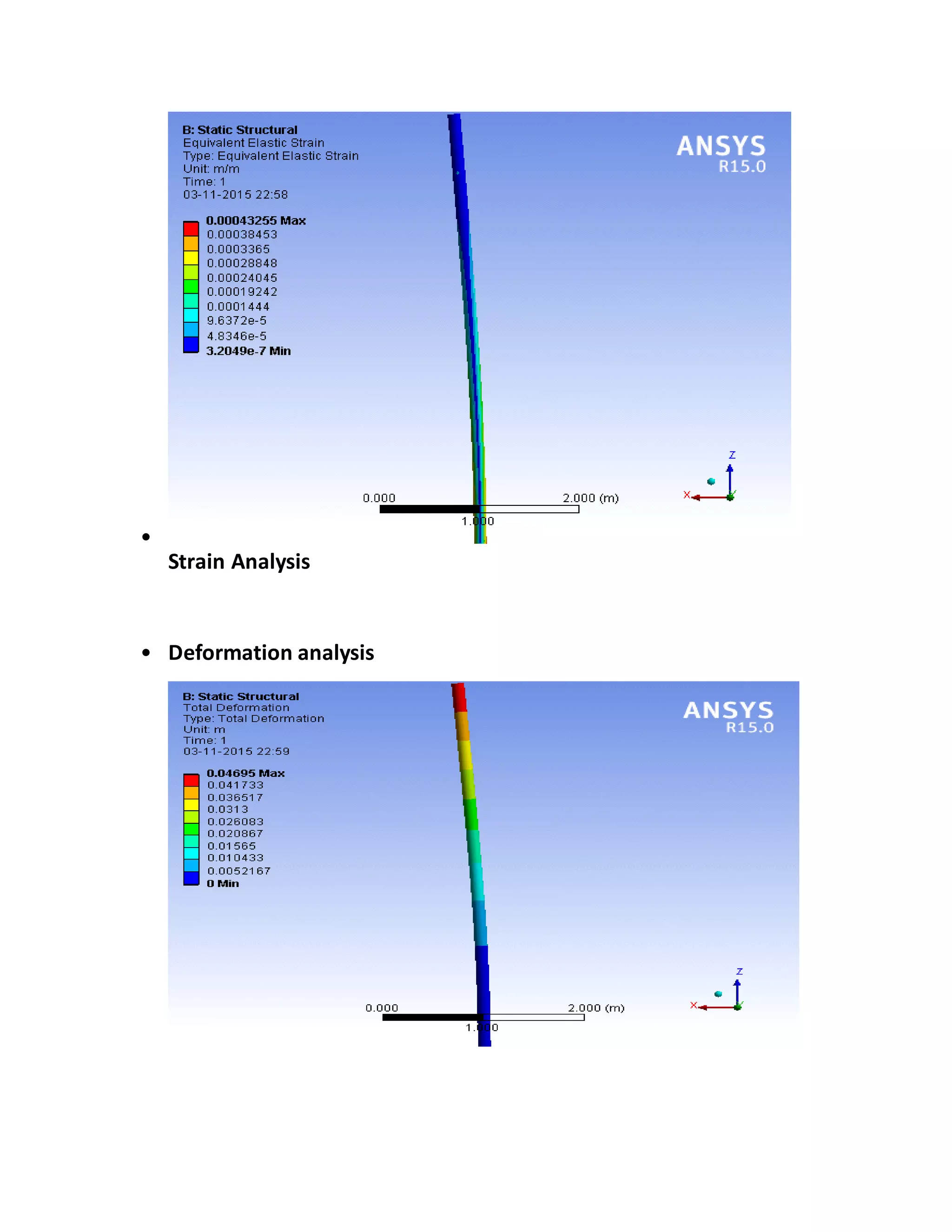
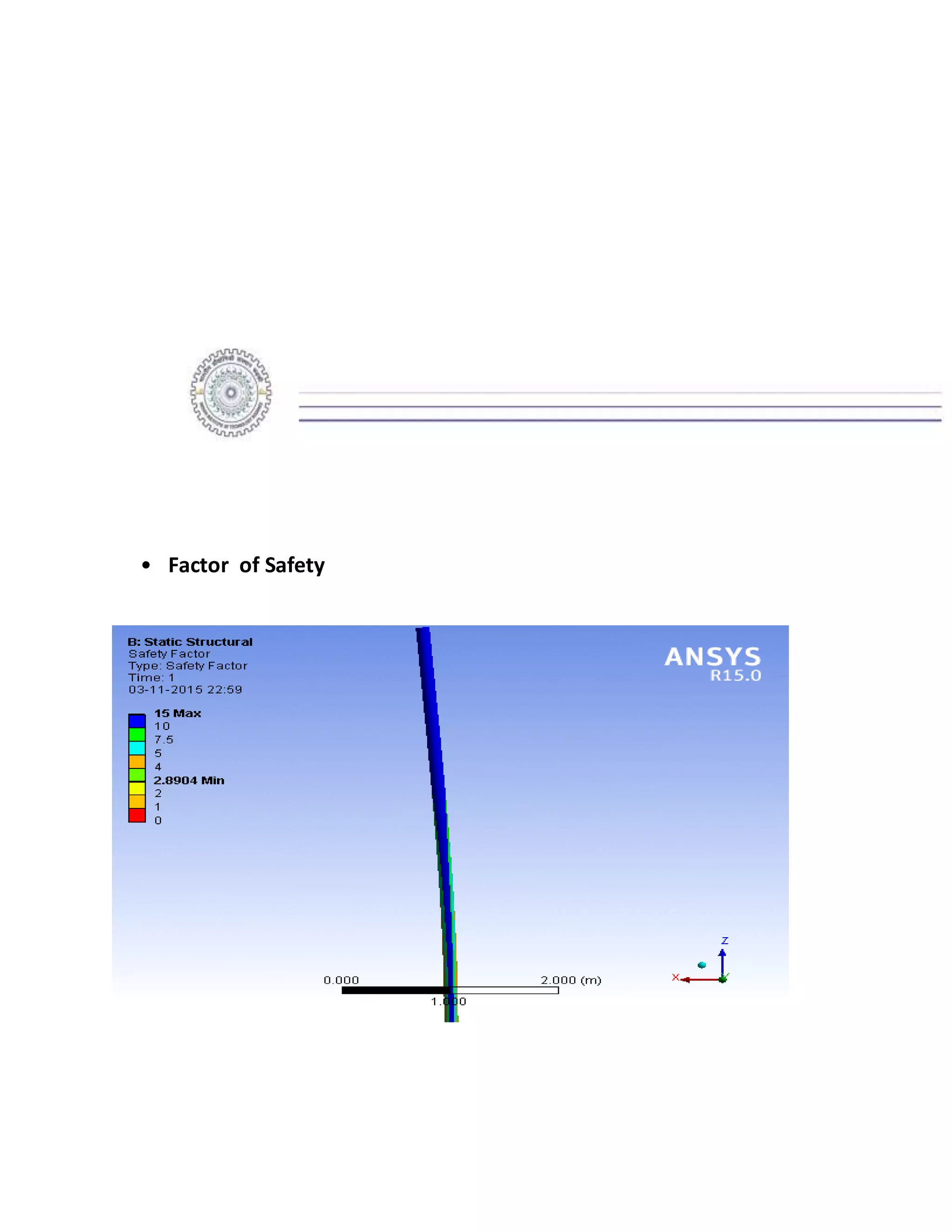
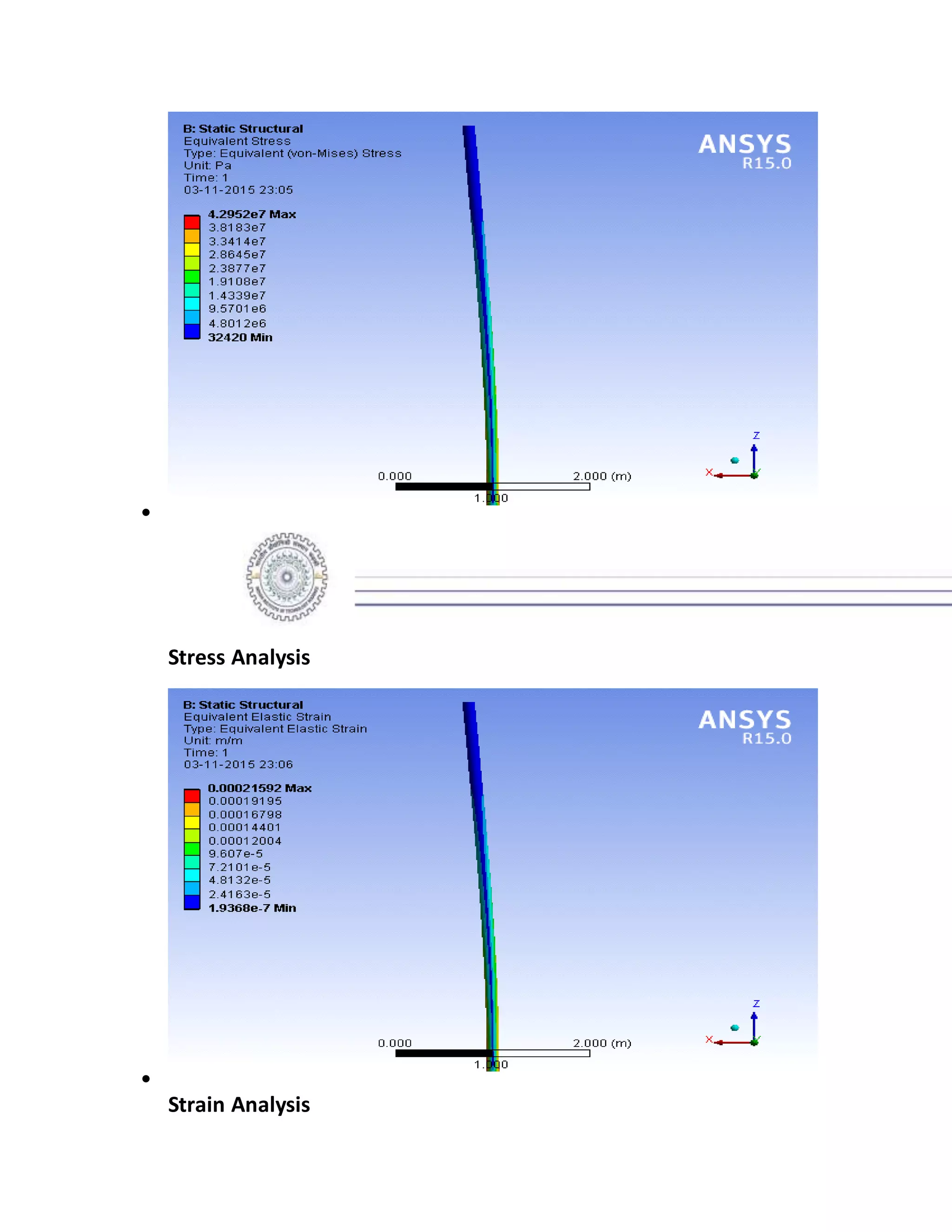
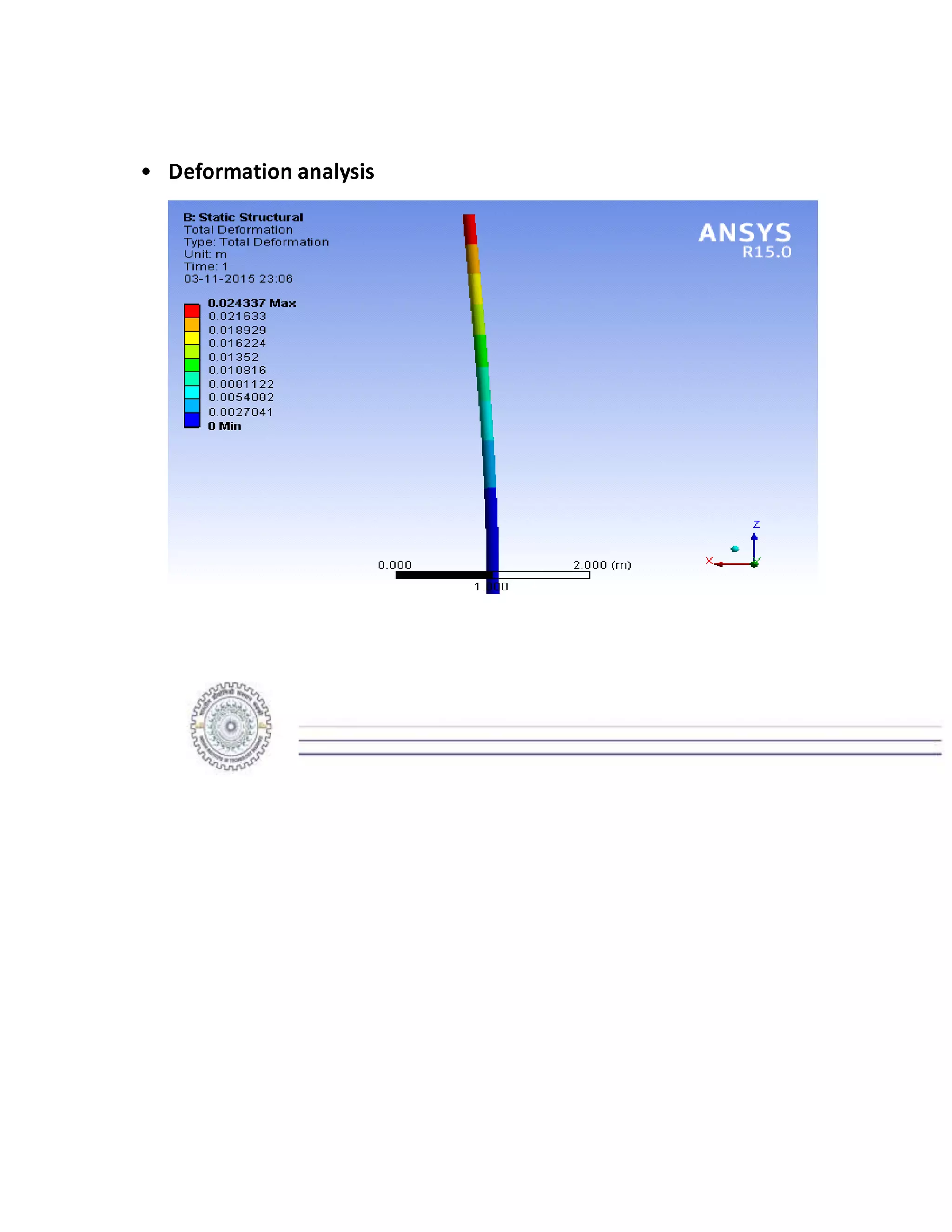
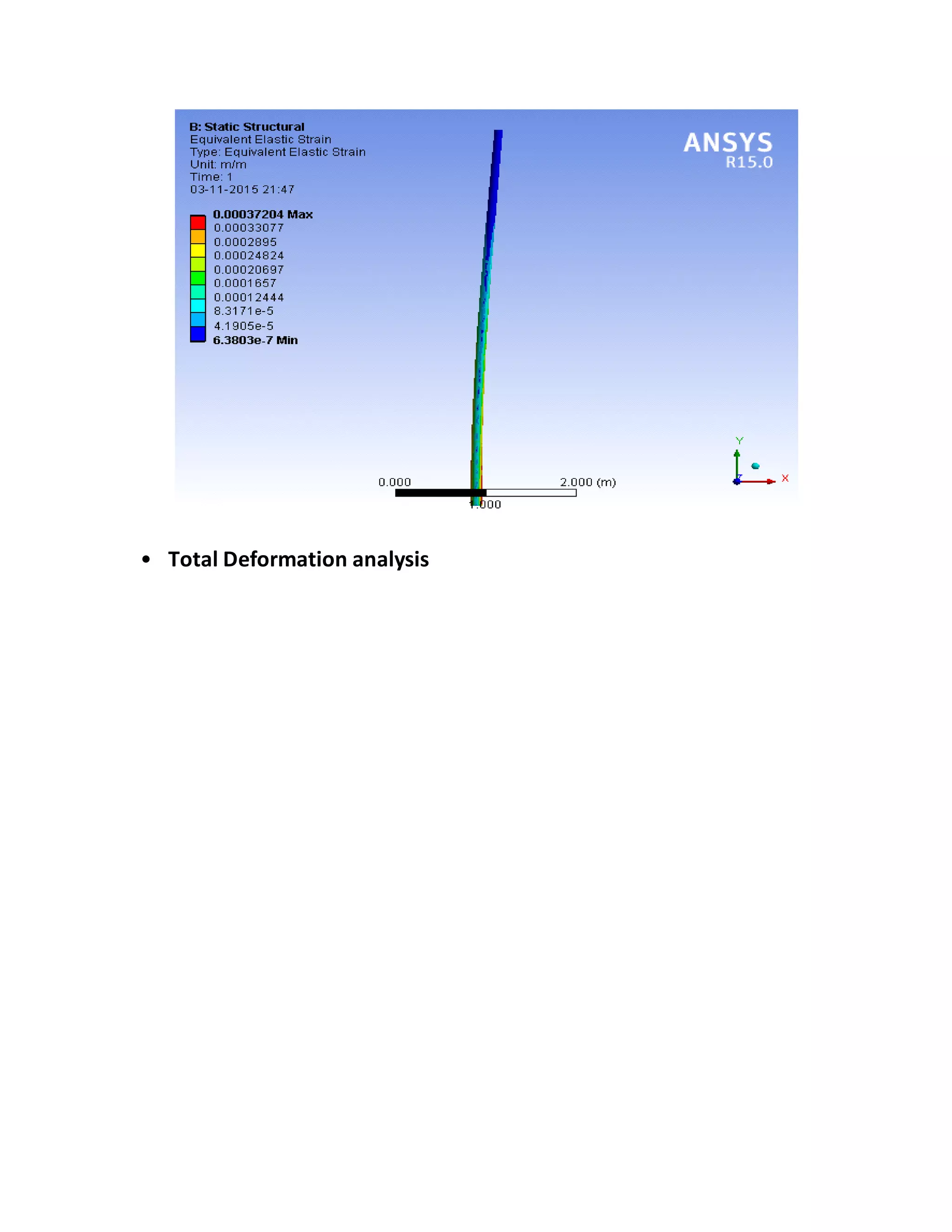
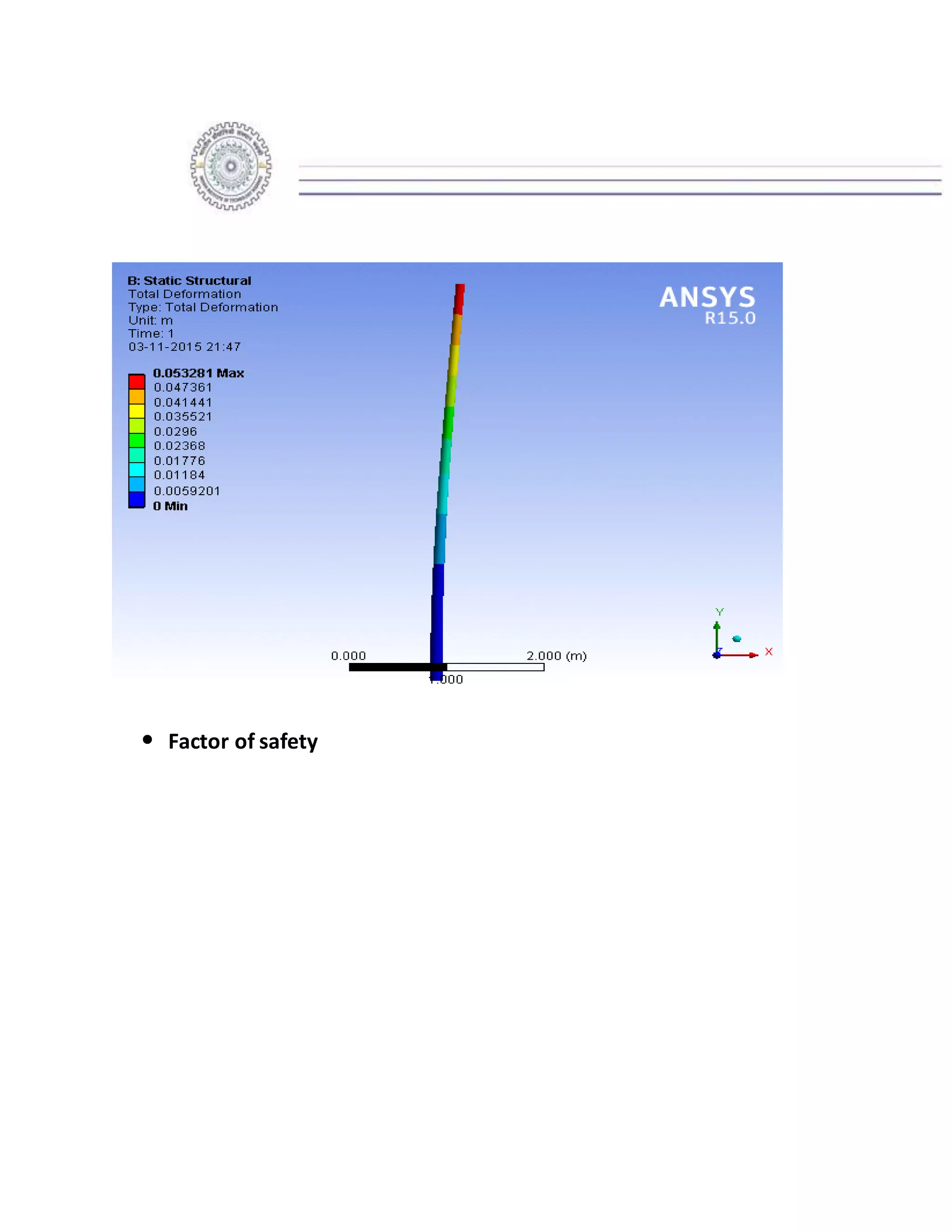
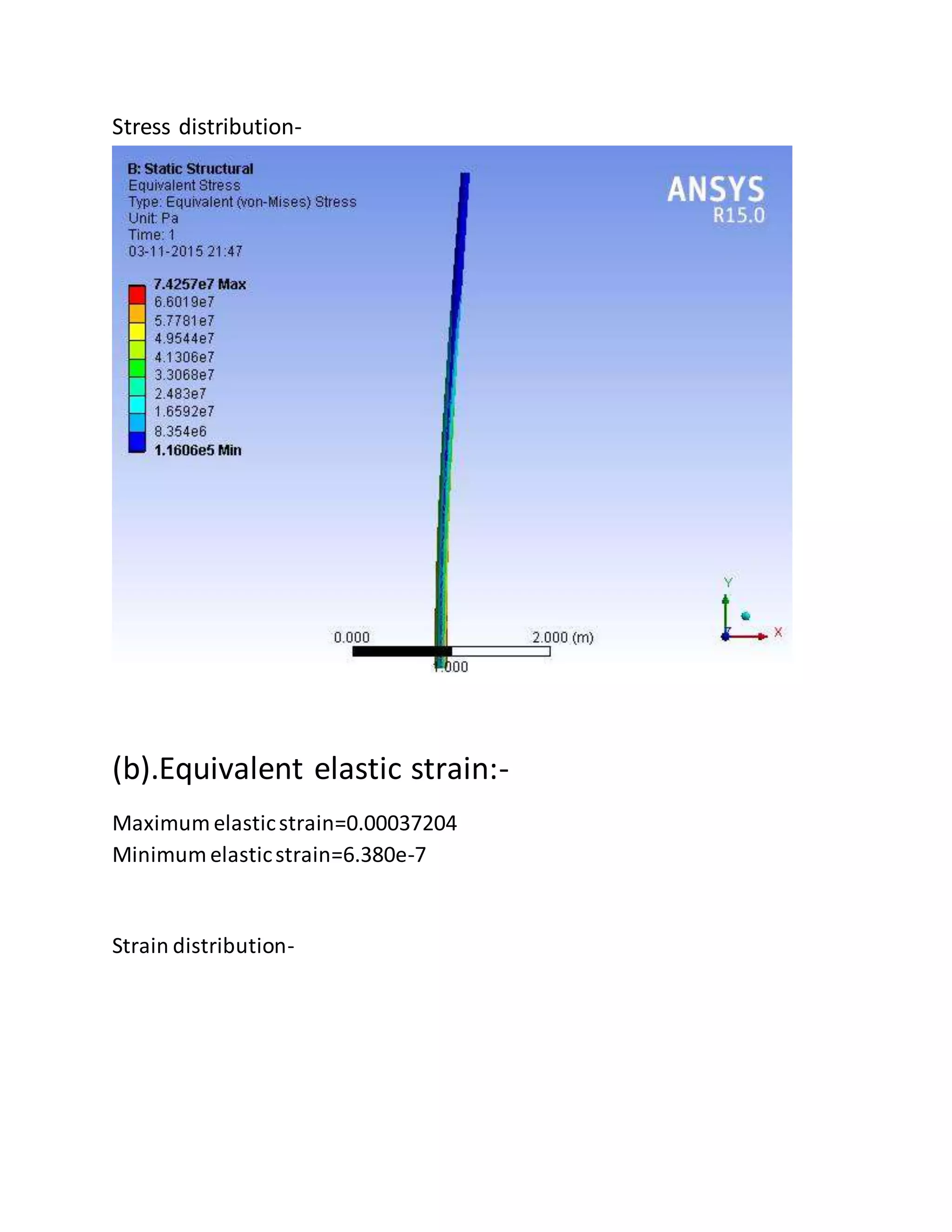
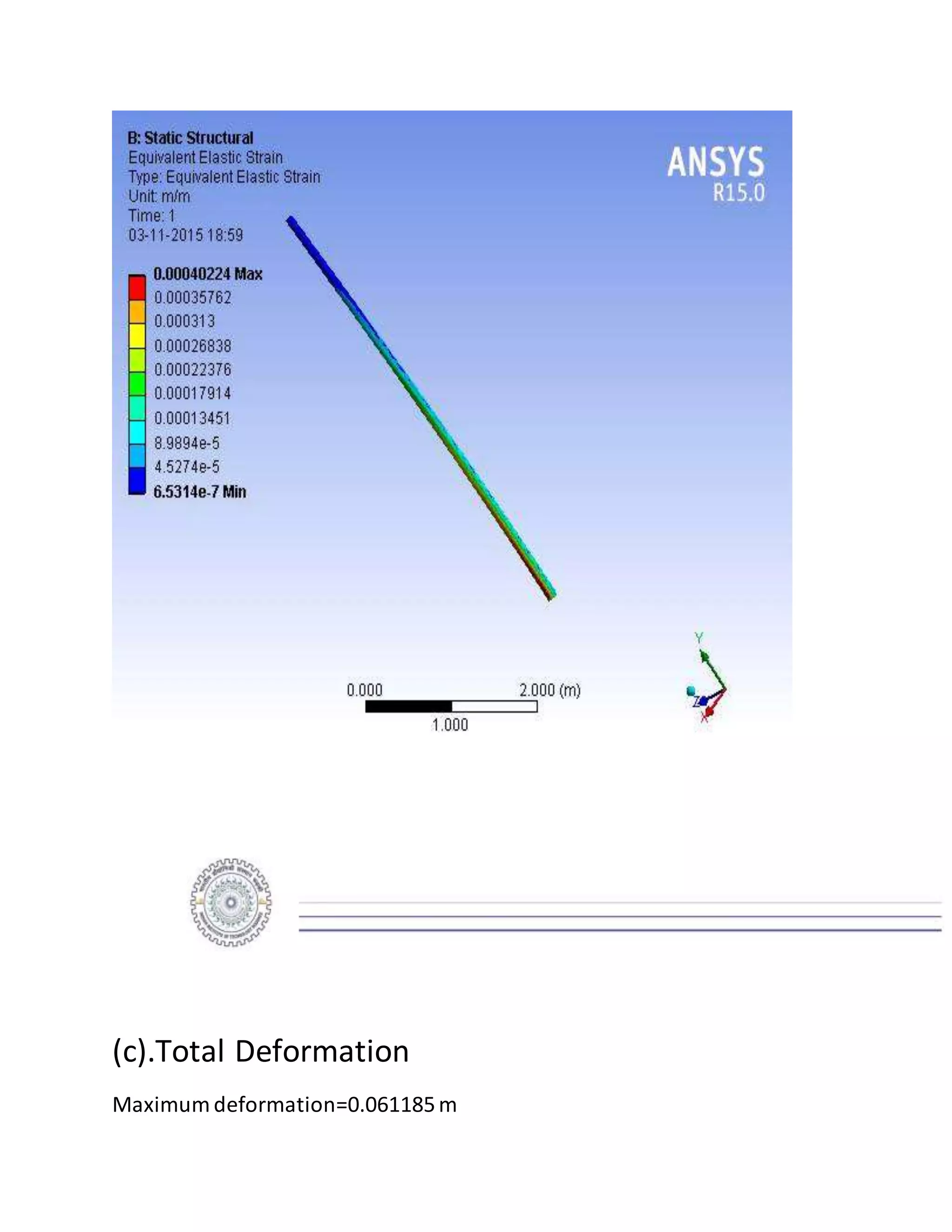
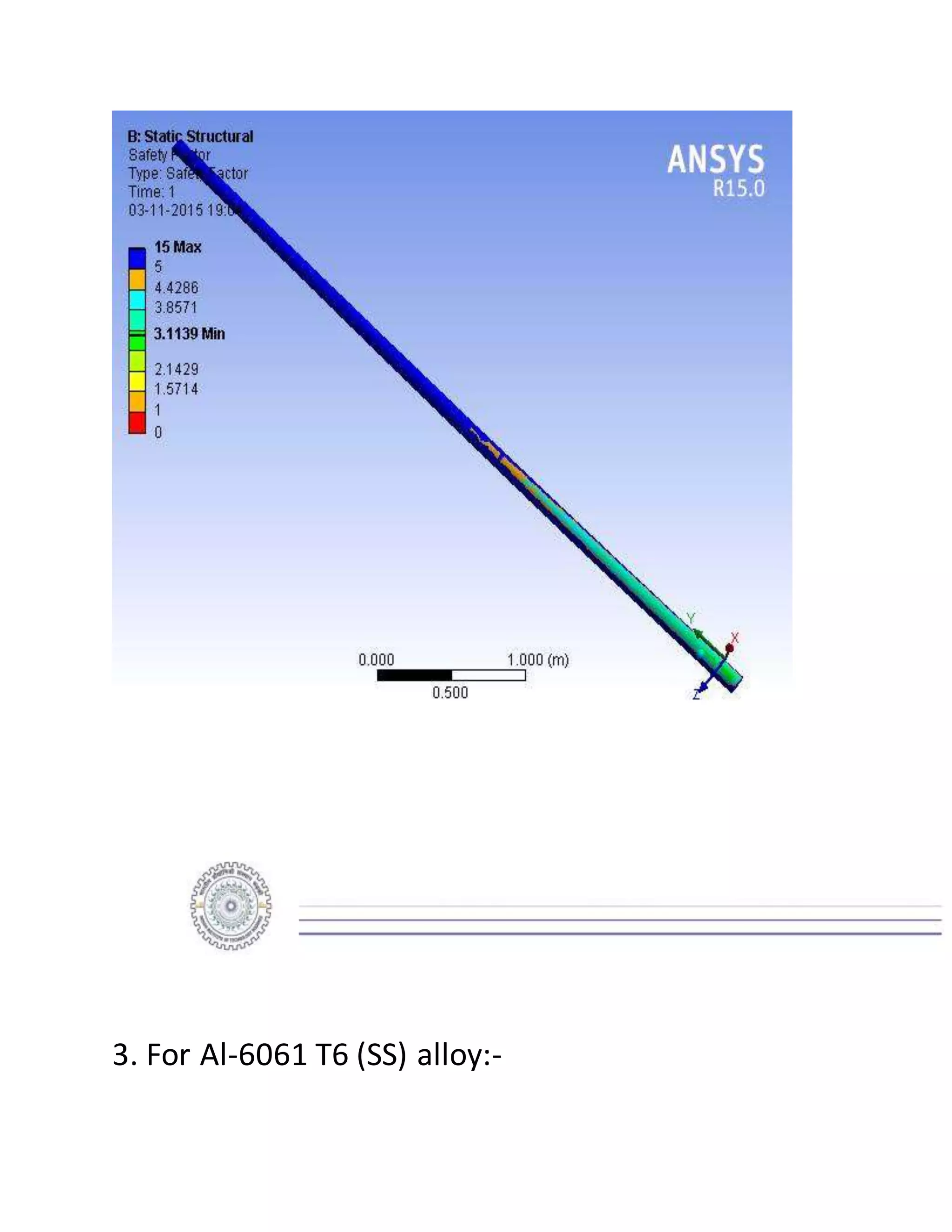
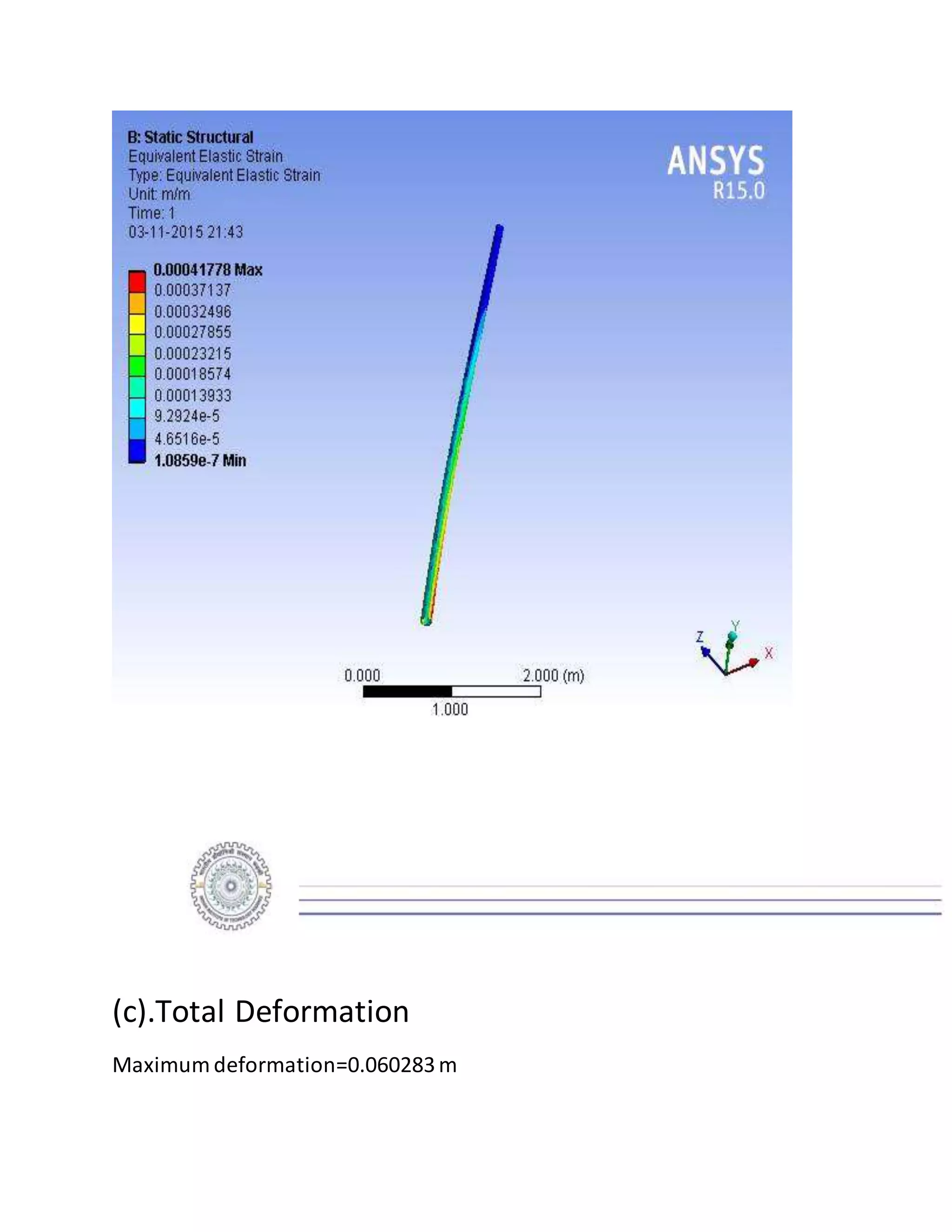
The report details the design of a column for a signboard at IIT Roorkee, including calculations for material selection, stress analysis, and cost estimation. Using SolidWorks and Ansys software, the analysis compares various materials, ultimately determining that aluminum alloy Al 7075 offers the best balance of safety factor and cost. The findings indicate that the most optimal design is a tapered column, with a safety factor of 3.3667 and an estimated cost of $47.575.