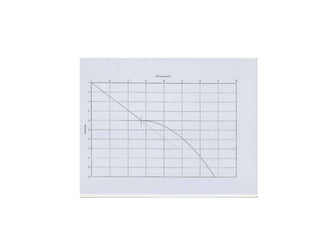
The Mackintosh Probe is a lightweight penetrometer that is faster and cheaper than boring equipment, especially for moderate depths in soft or loose soils. It consists of 16mm steel rods connected by couplings that prevent buckling during driving with a 5kg hammer from 30cm above. The number of blows to penetrate 30cm is recorded and used to evaluate soil consistency, density, and parameters. It allows disturbed soil sampling and subsurface stratigraphy identification. Advantages include being light, easy to use, economical, and faster than other tools, while disadvantages include potential for human error, limited depth, and inability to penetrate medium-strength soils. The procedure involves assembling the probe, driving it with blows counted for 30cm intervals, until 15