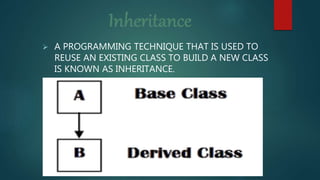
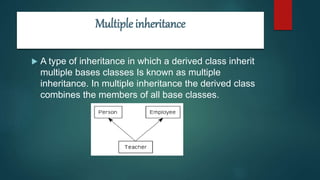
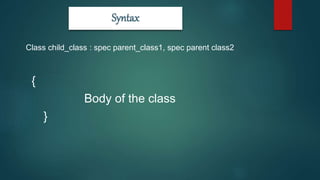
Multiple inheritance allows a derived class to inherit from multiple base classes. The derived class combines the members of all base classes. There are three types of inheritance access specifiers: private, public, and protected. Private inheritance makes base class members private in the derived class. Public inheritance, which is most commonly used, makes protected members protected and public members public in the derived class. Protected inheritance makes base class public and protected members protected in the derived class. An example shows a class C derived from classes A and B publicly, allowing C to access members of both base classes.