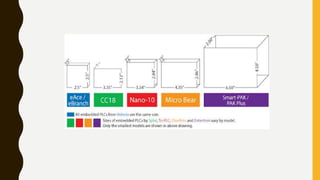
The document discusses different sizes of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and their applications. PLCs are categorized based on functionality, inputs/outputs, cost, and size, ranging from nano to micro to medium to large. Key factors in selecting a PLC include matching its size to the application. There are three main types of PLC applications: single-ended, multitask, and control management. Memory requirements depend on the number of inputs/outputs, program size, data needs, and future expansion requirements. PLCs are used across various industries including petrochemical, steel, power generation, chemical, and more.