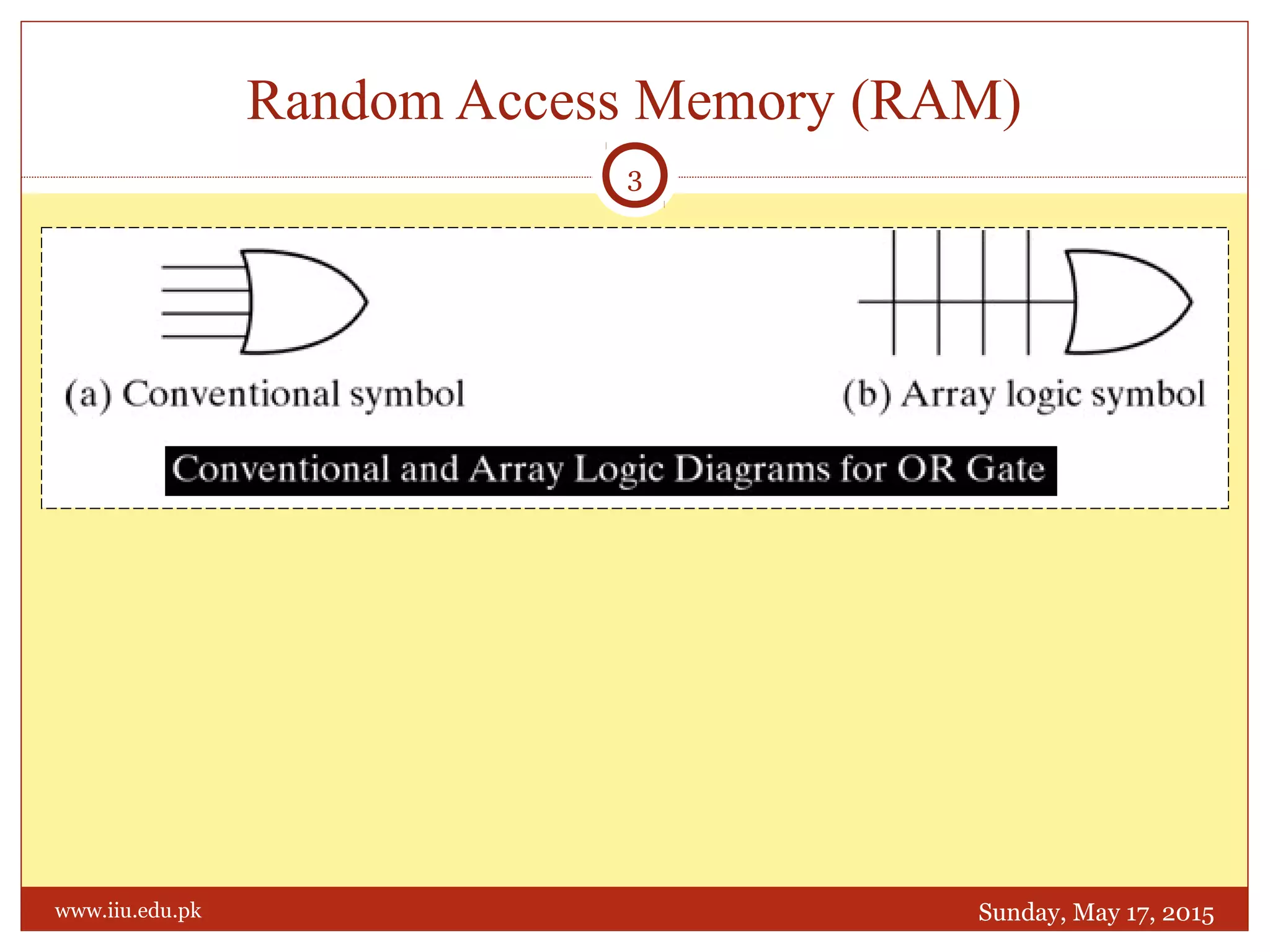
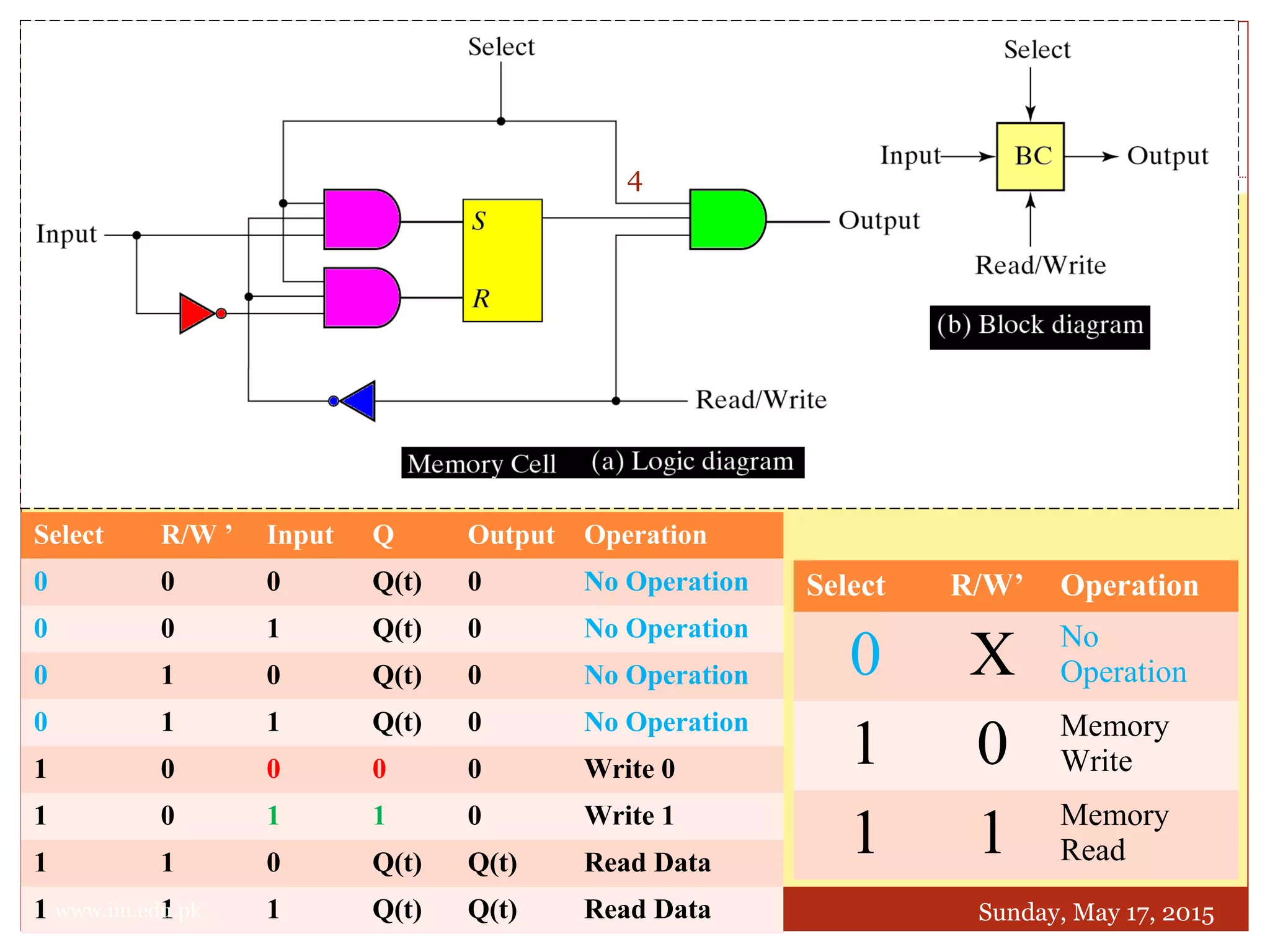
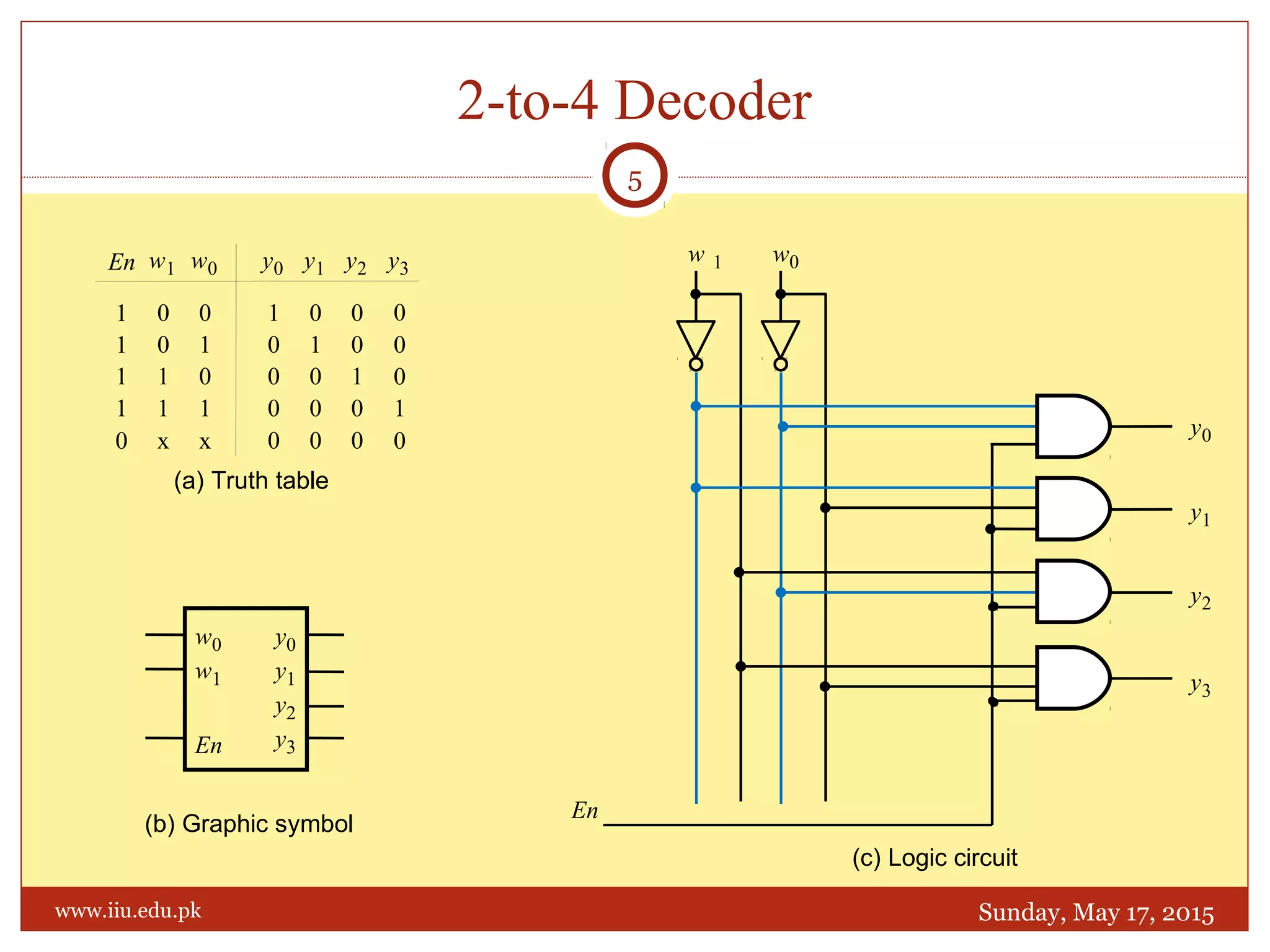
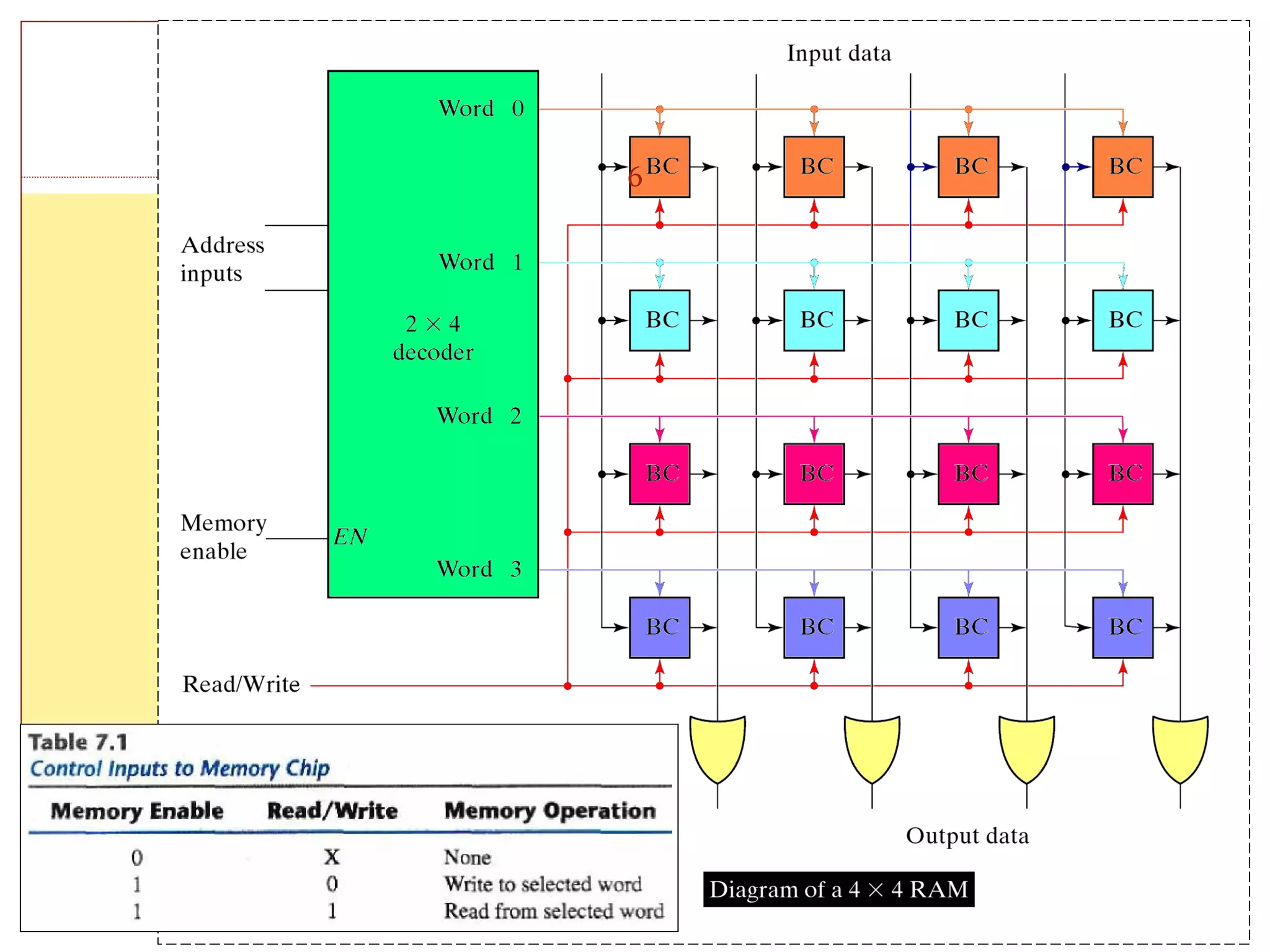
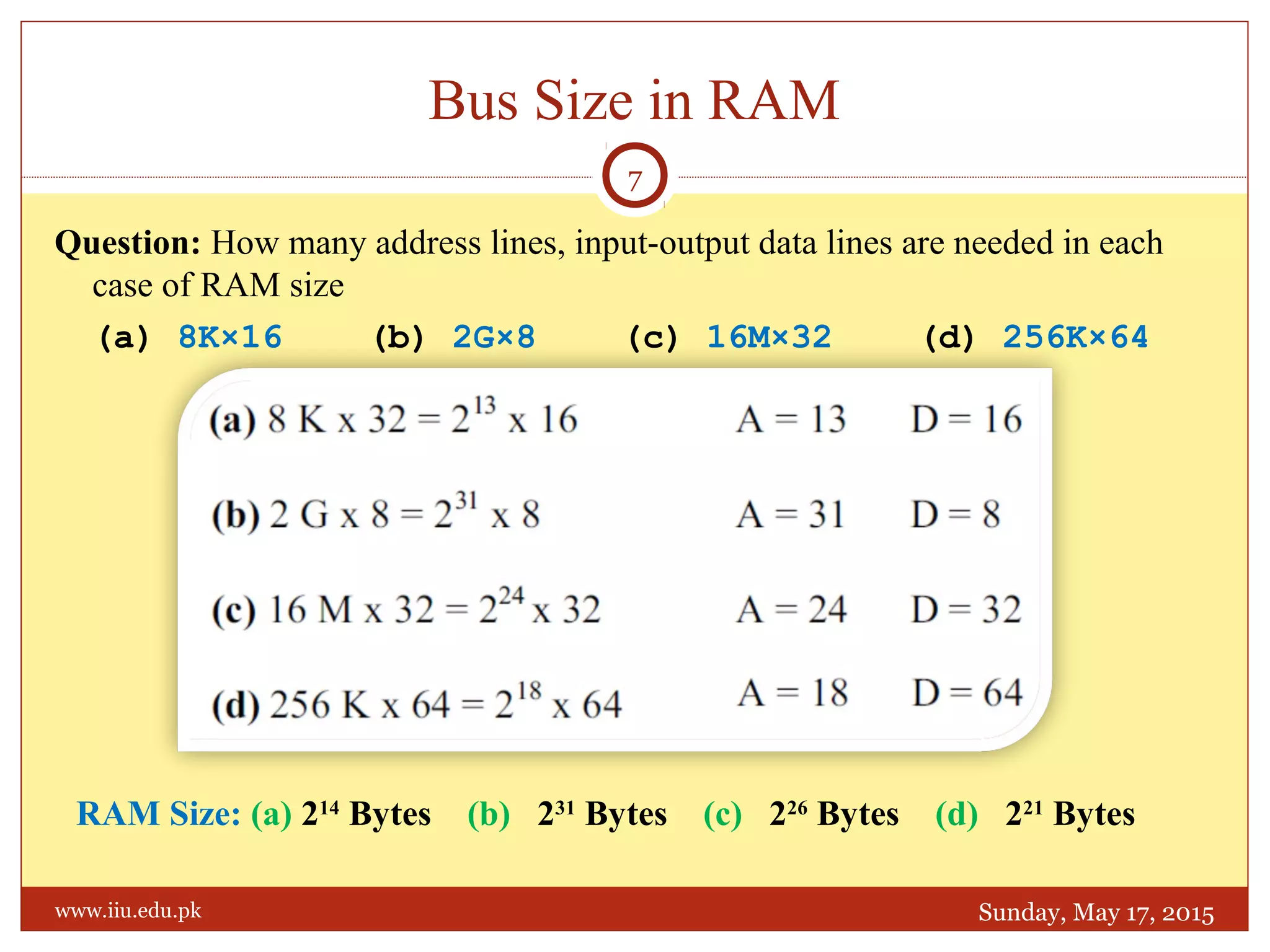
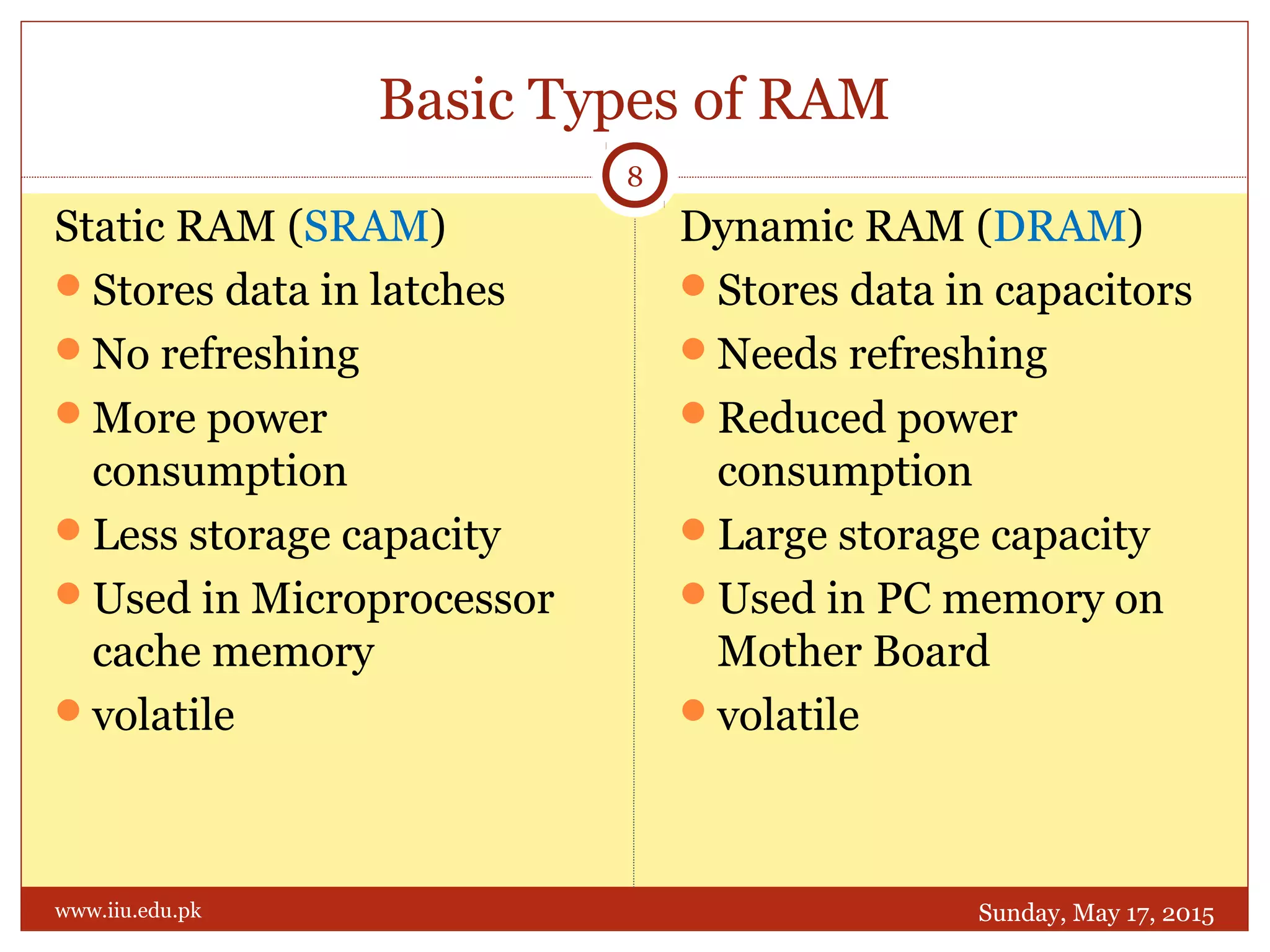
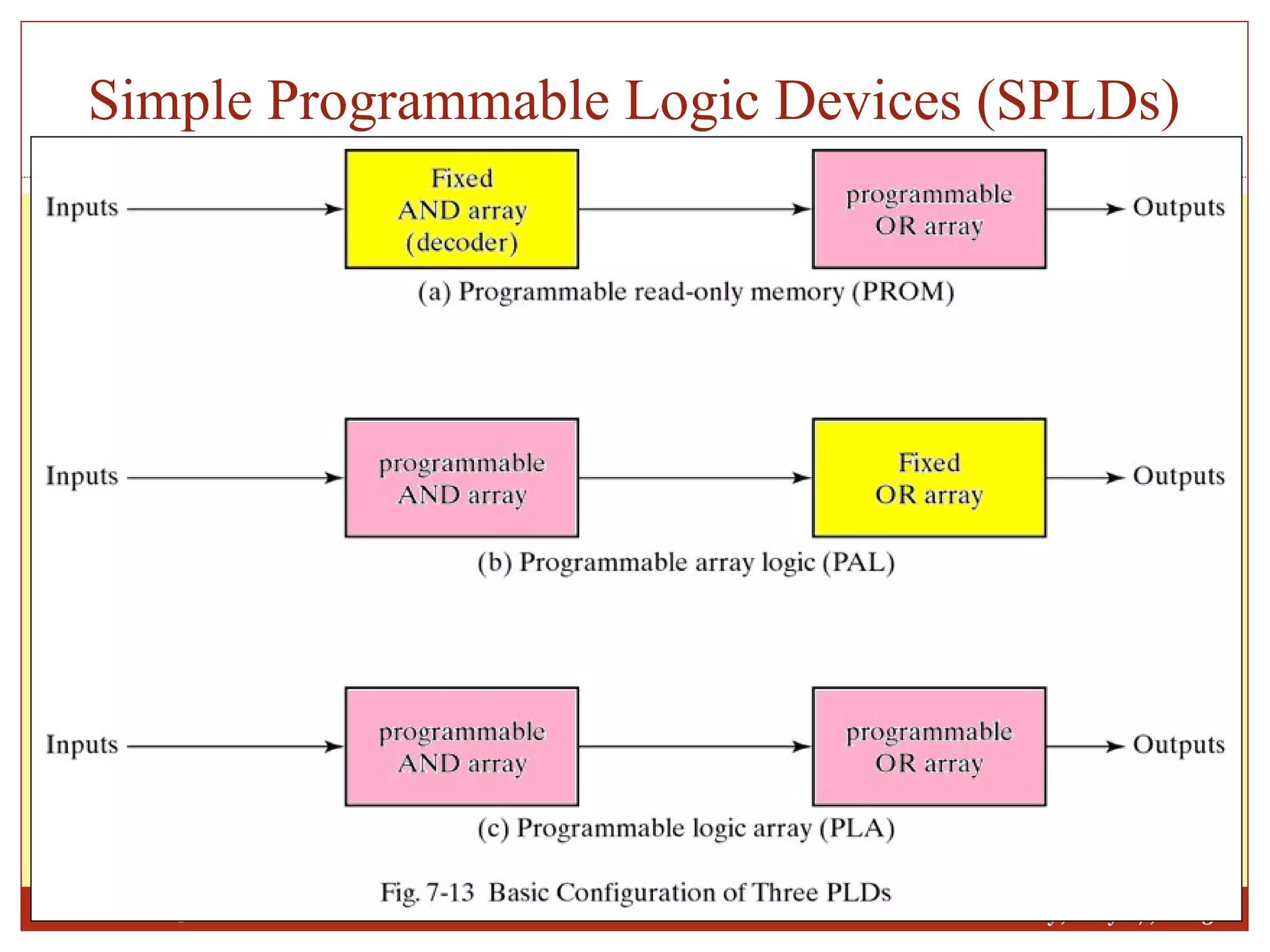
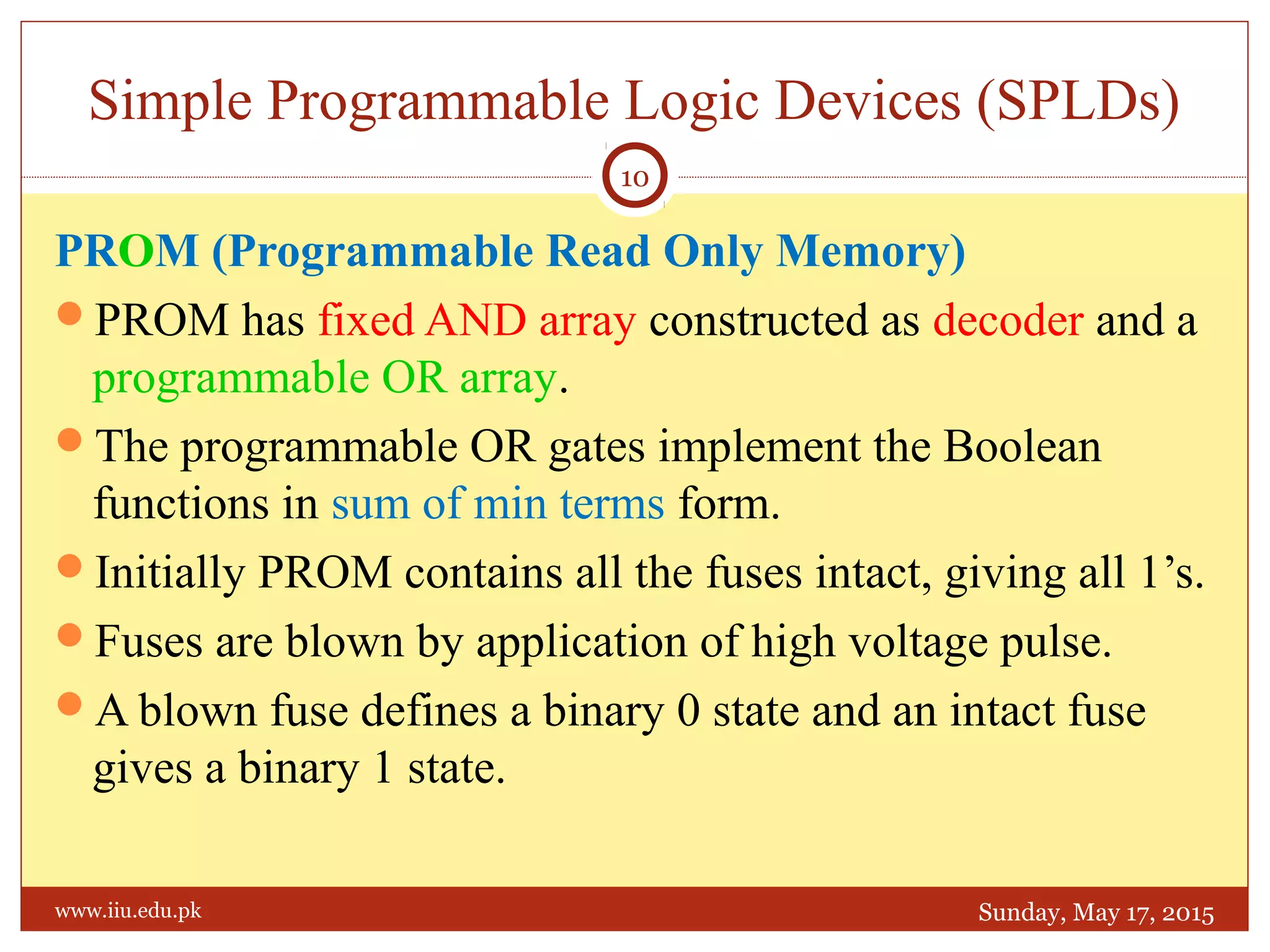
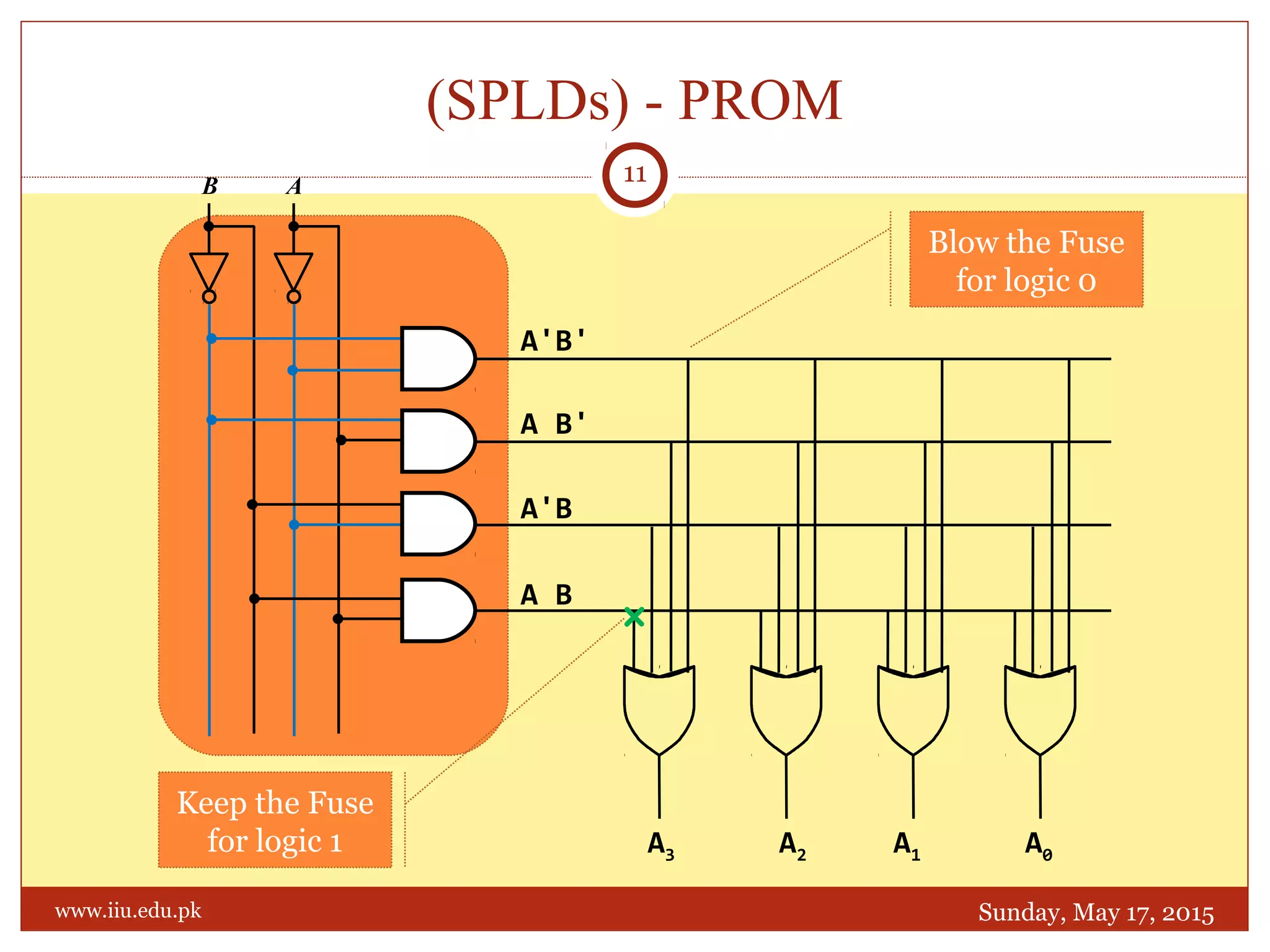
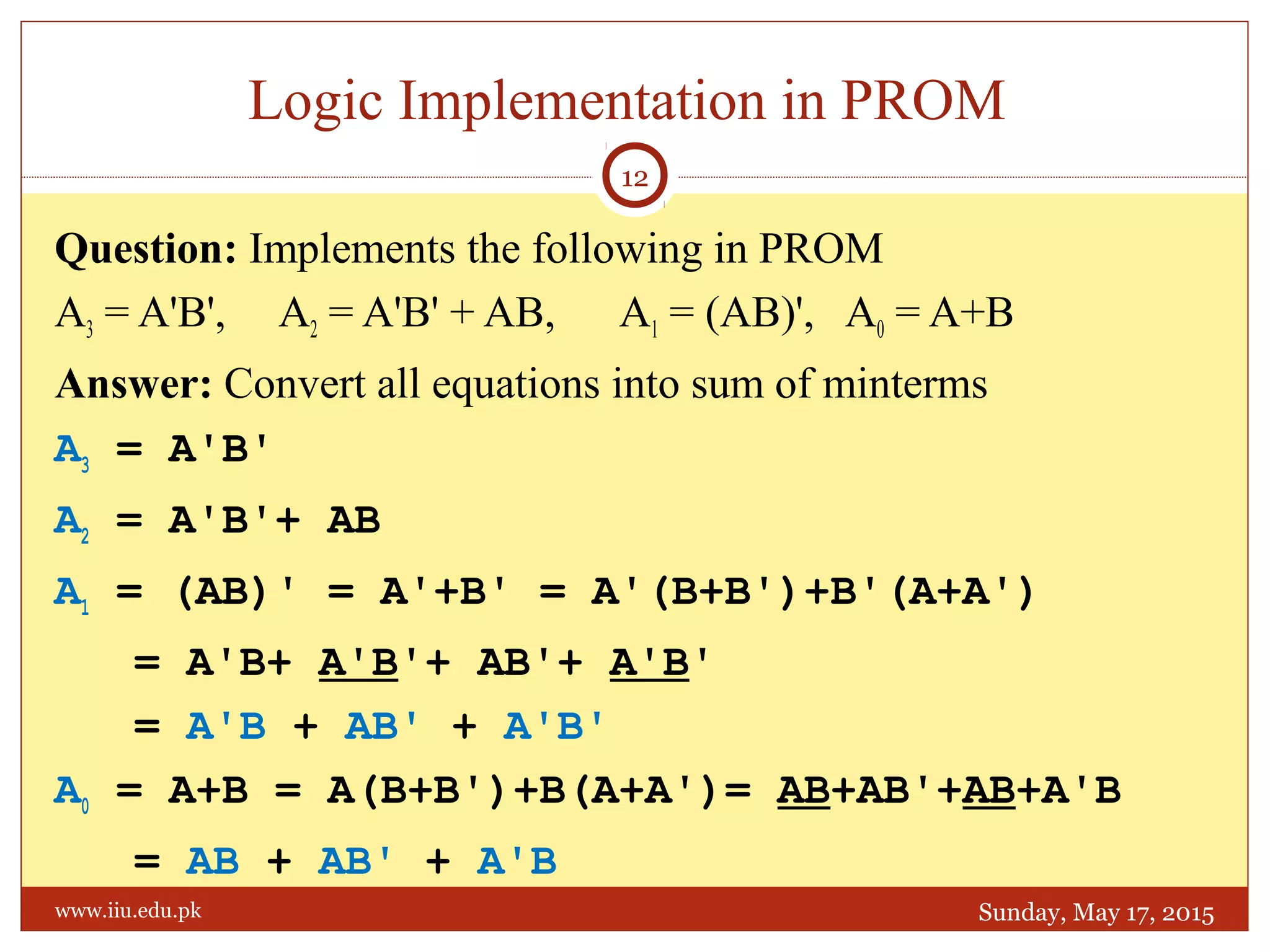
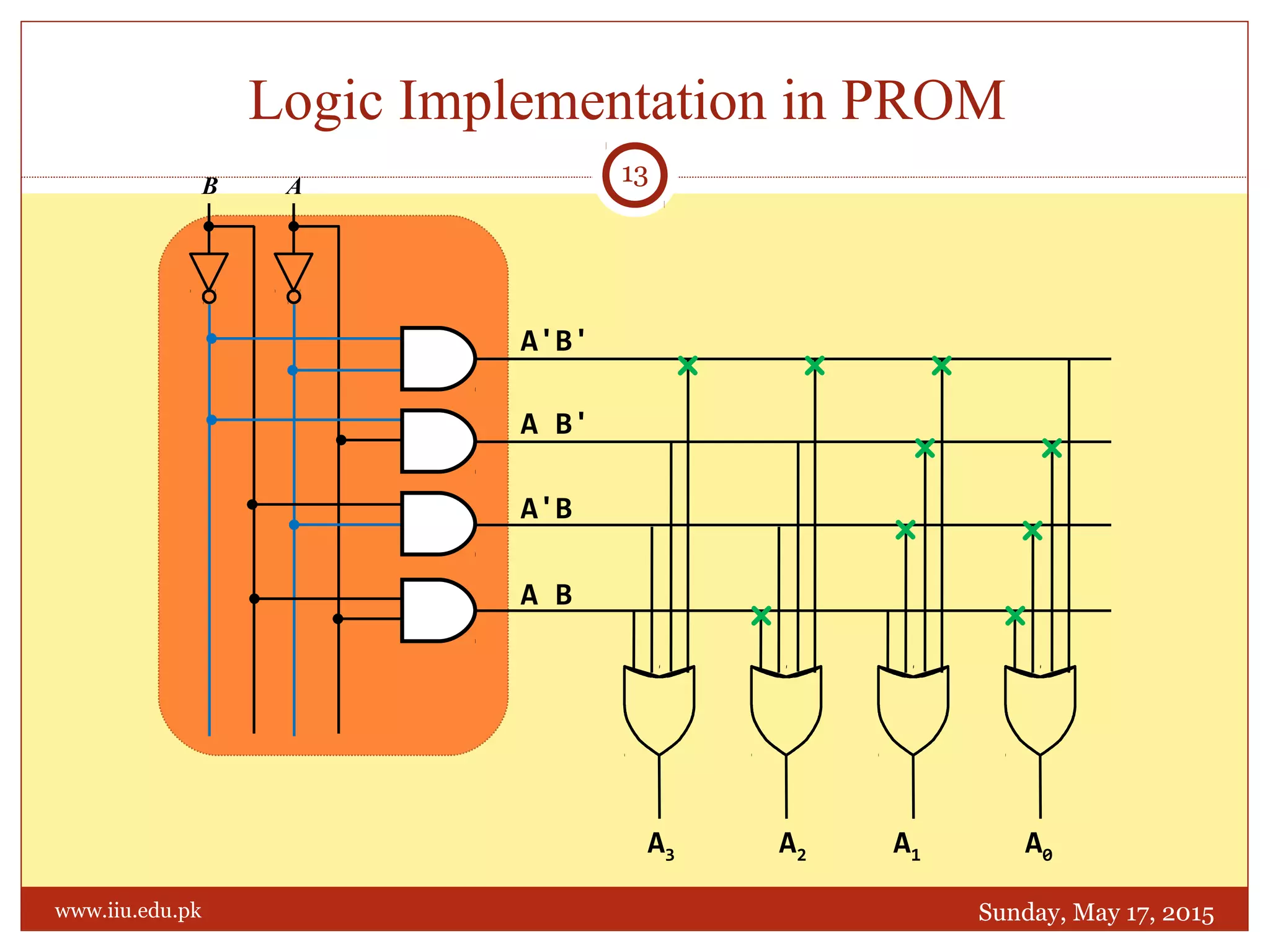
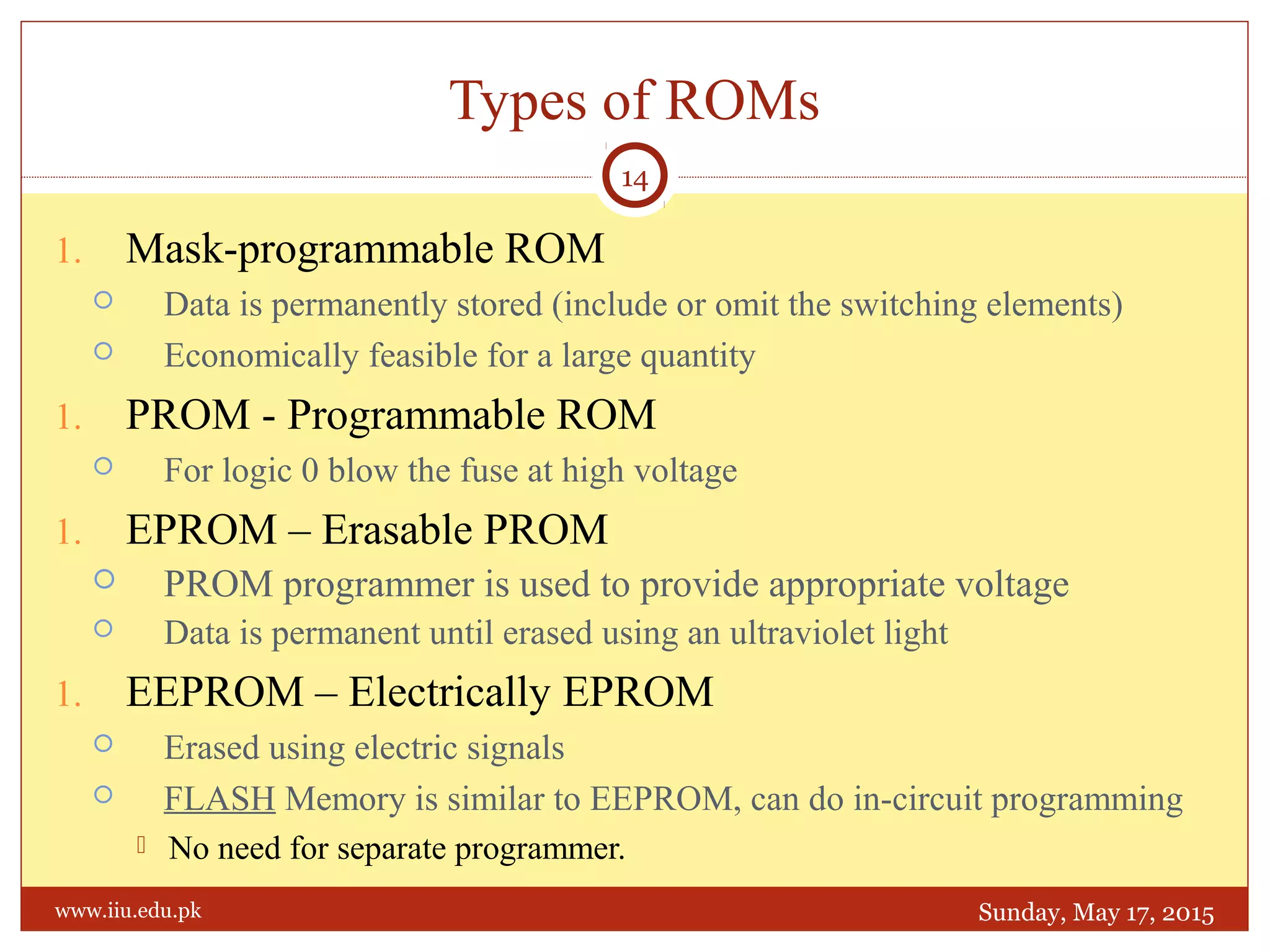
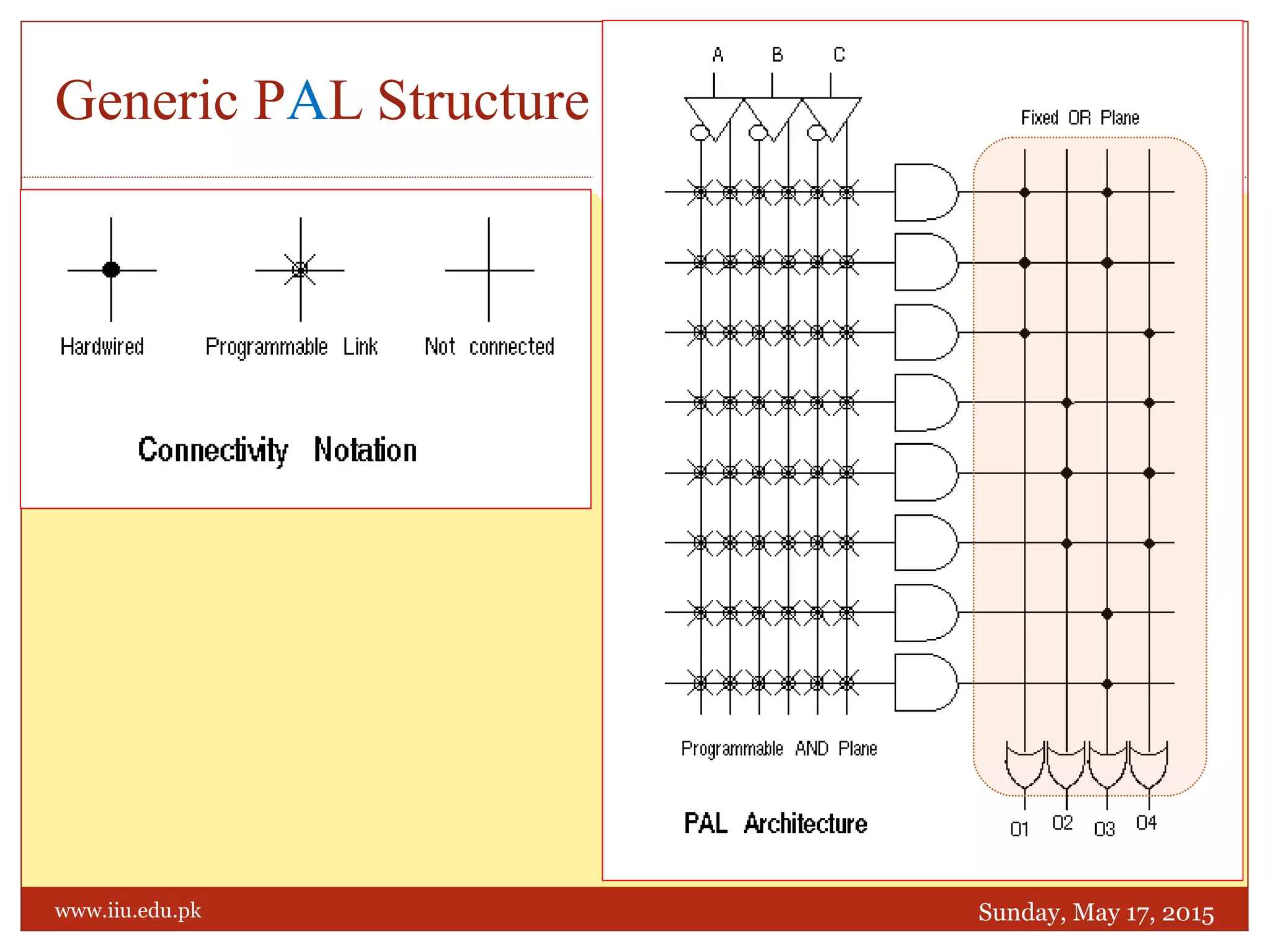
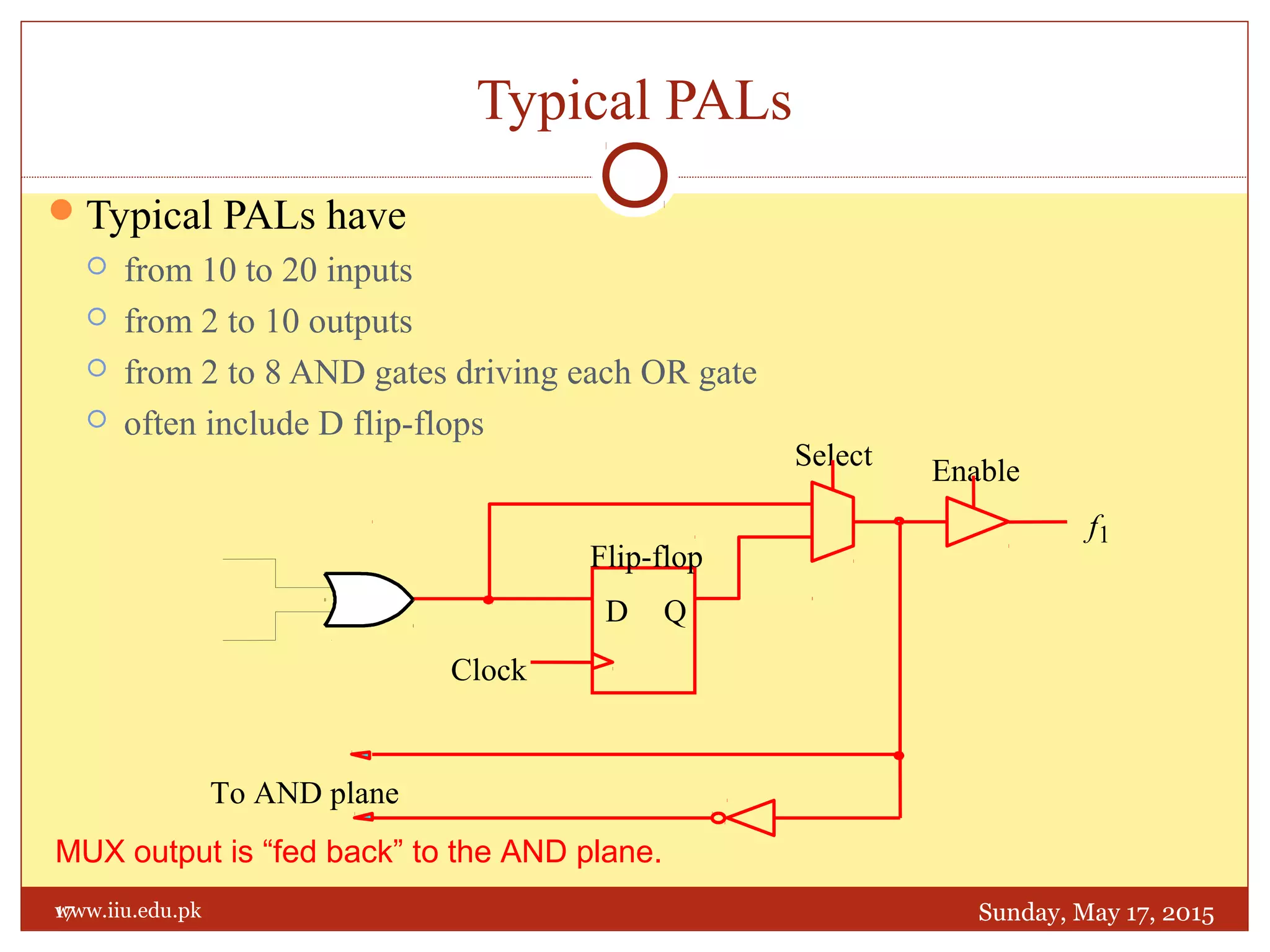
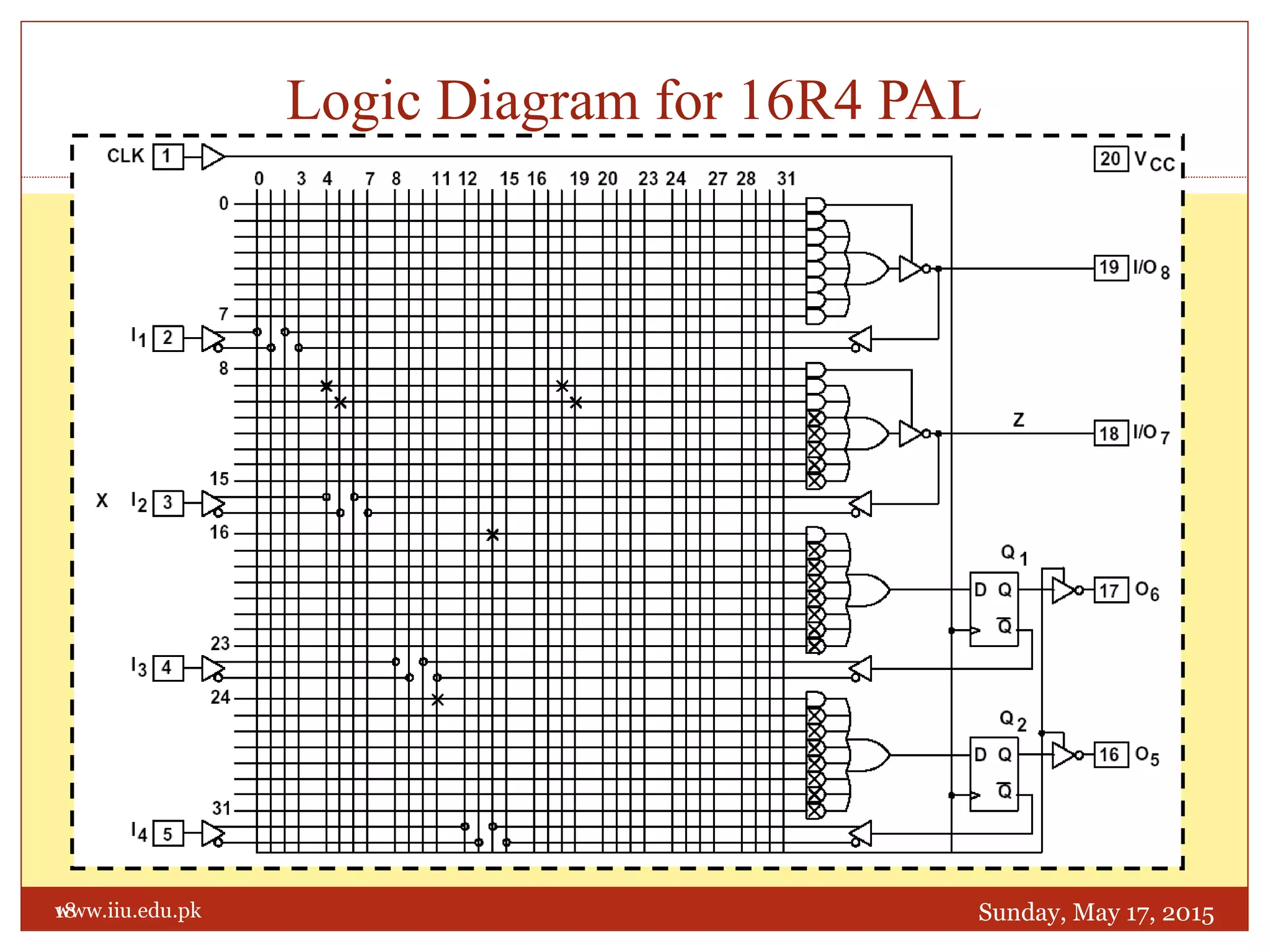
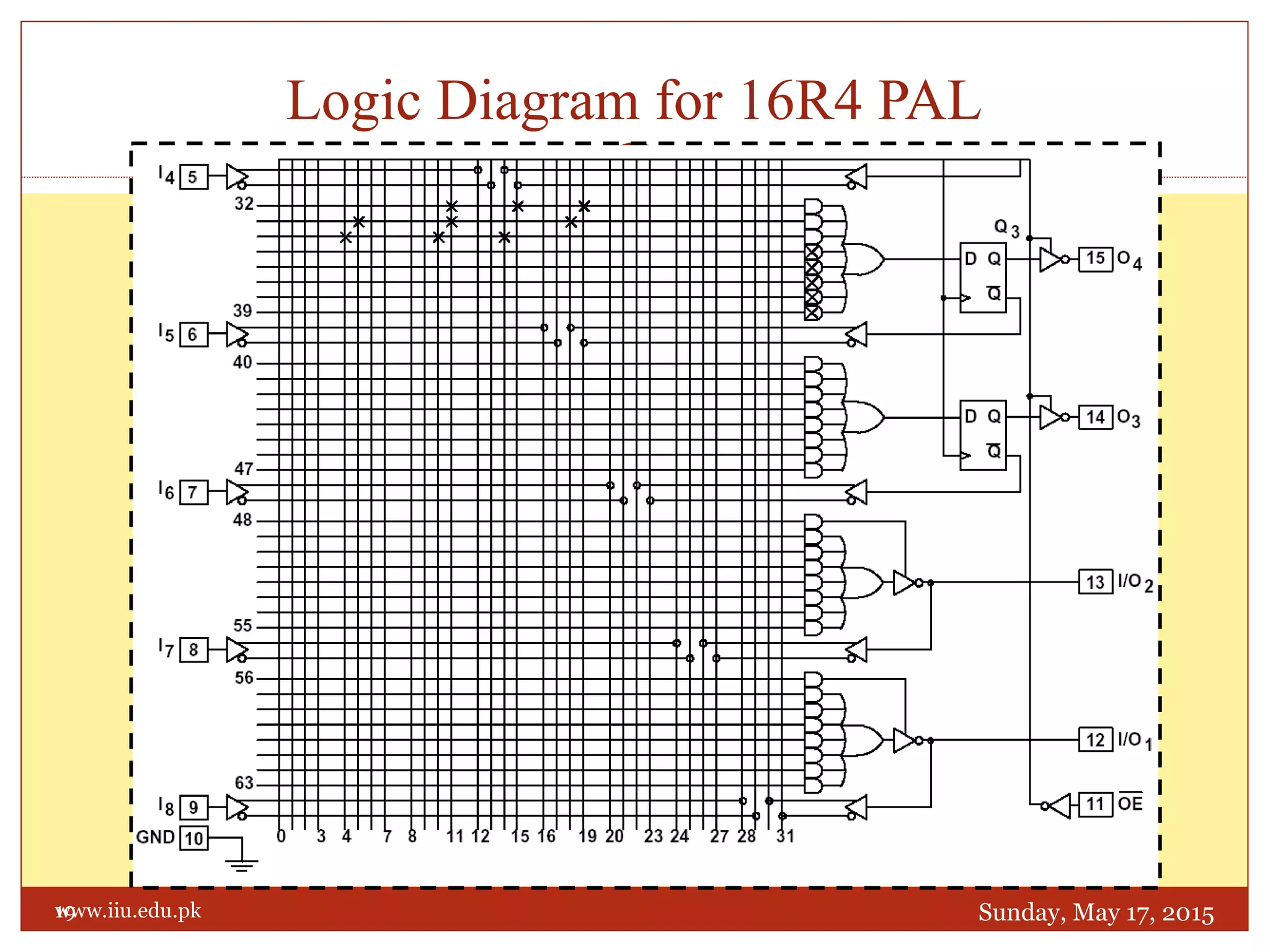
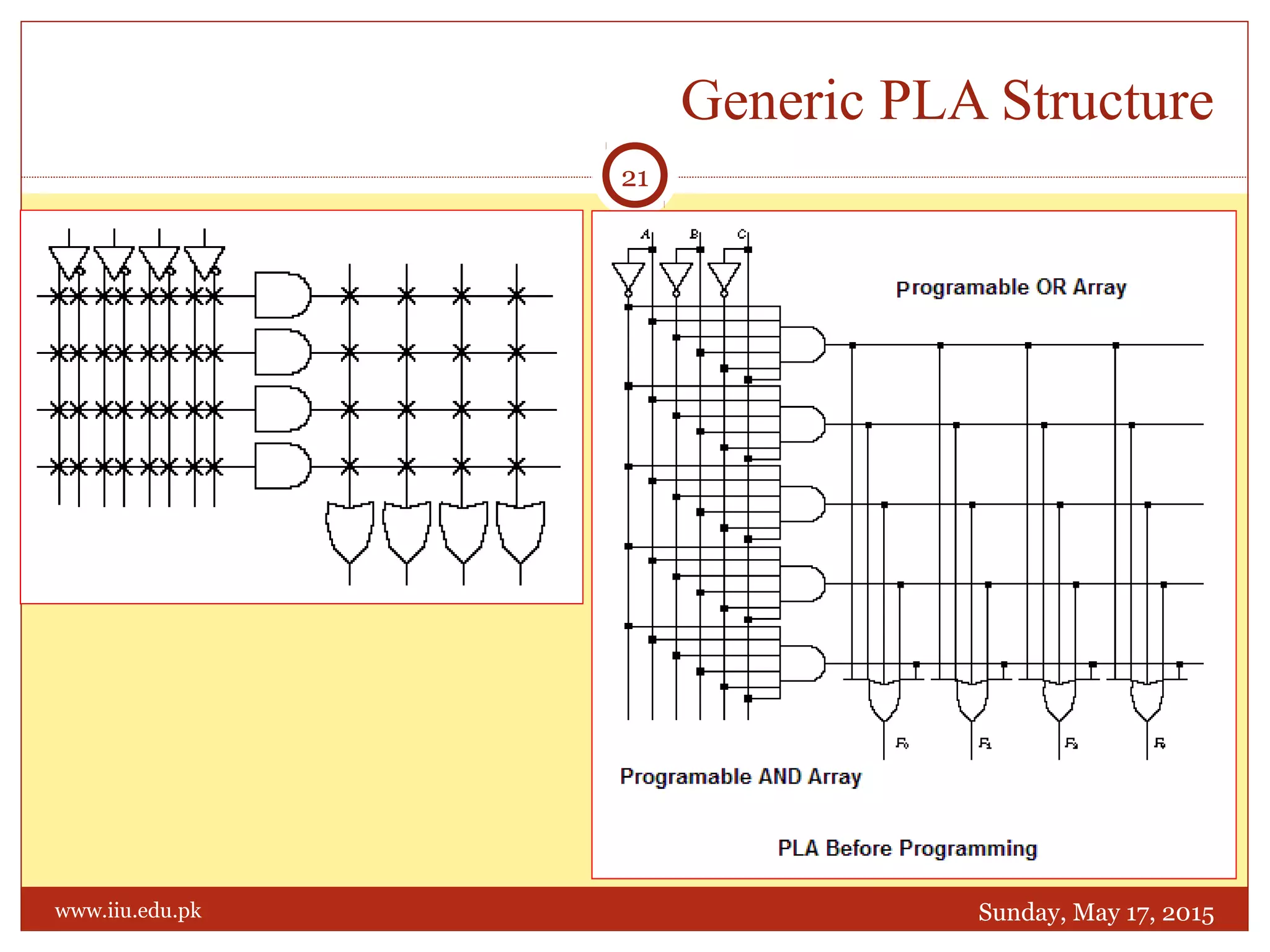
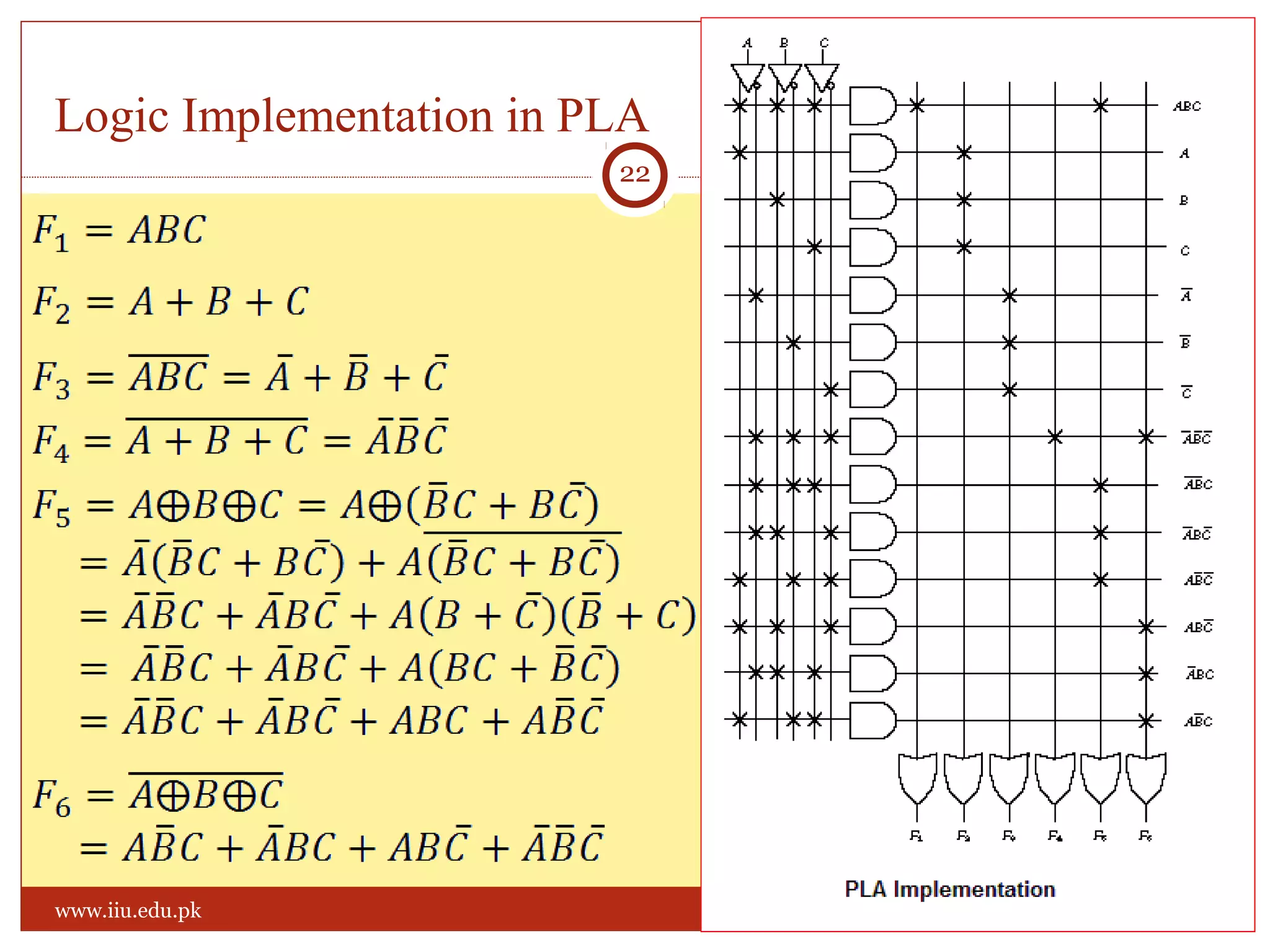
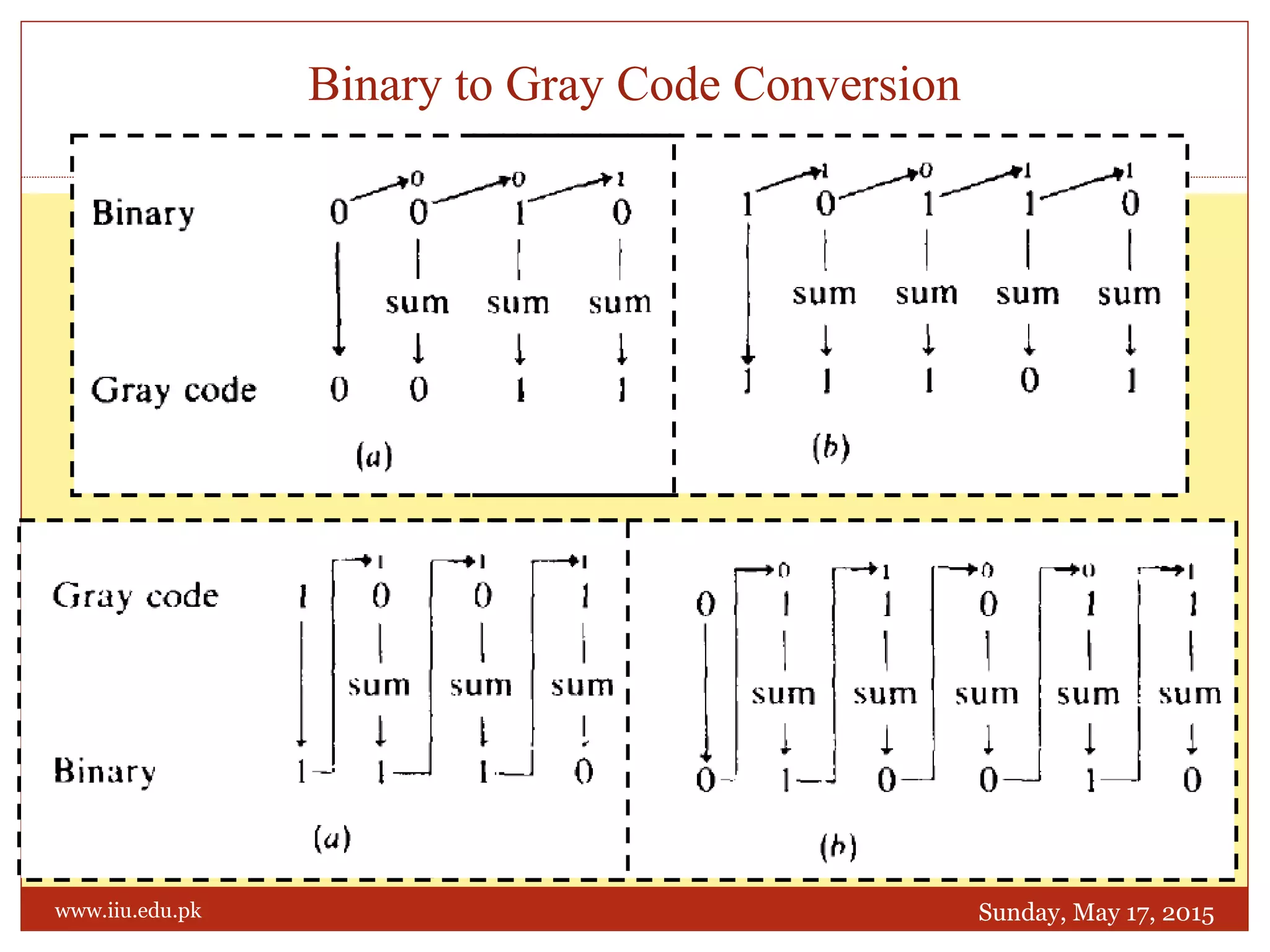
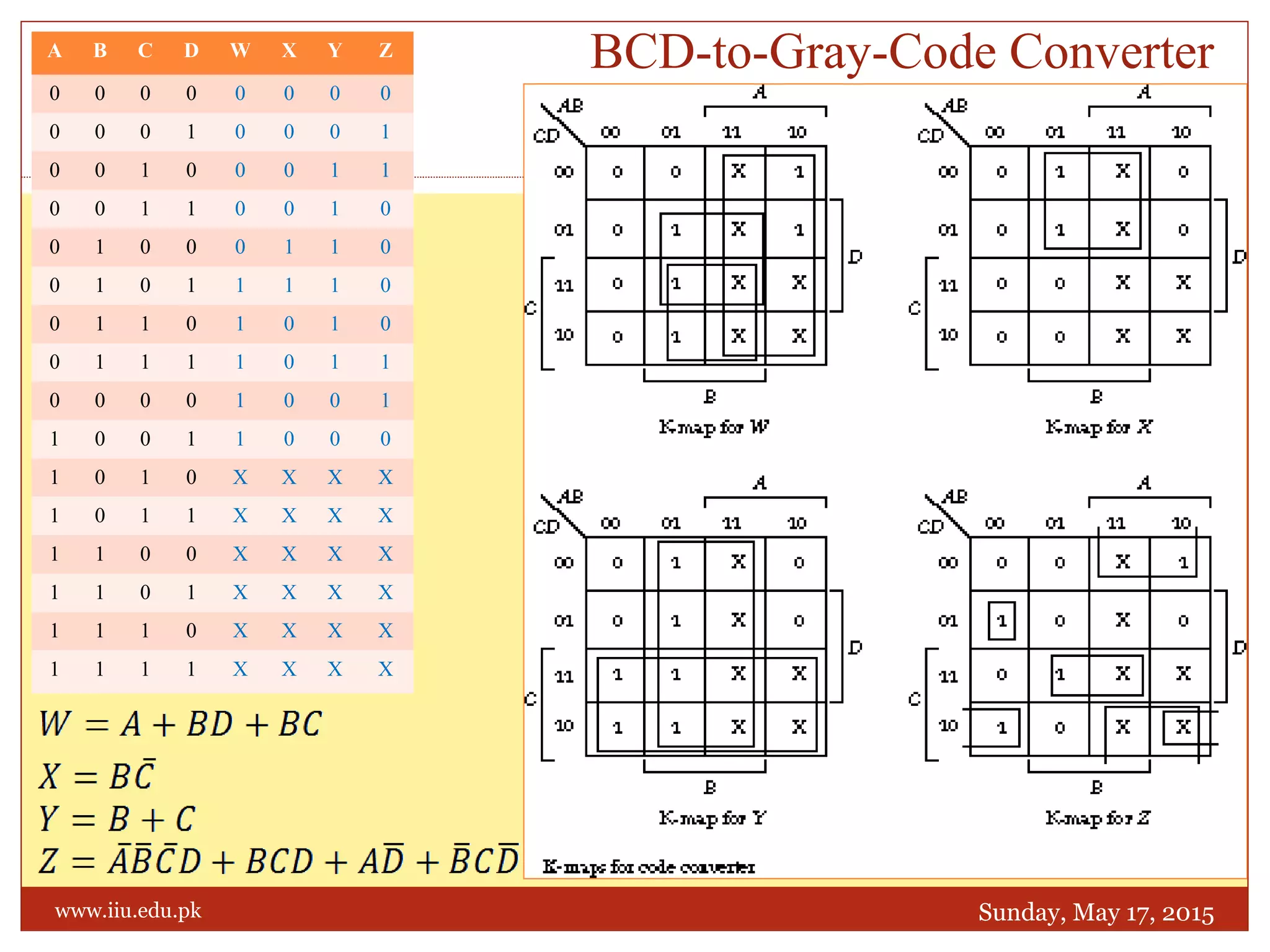
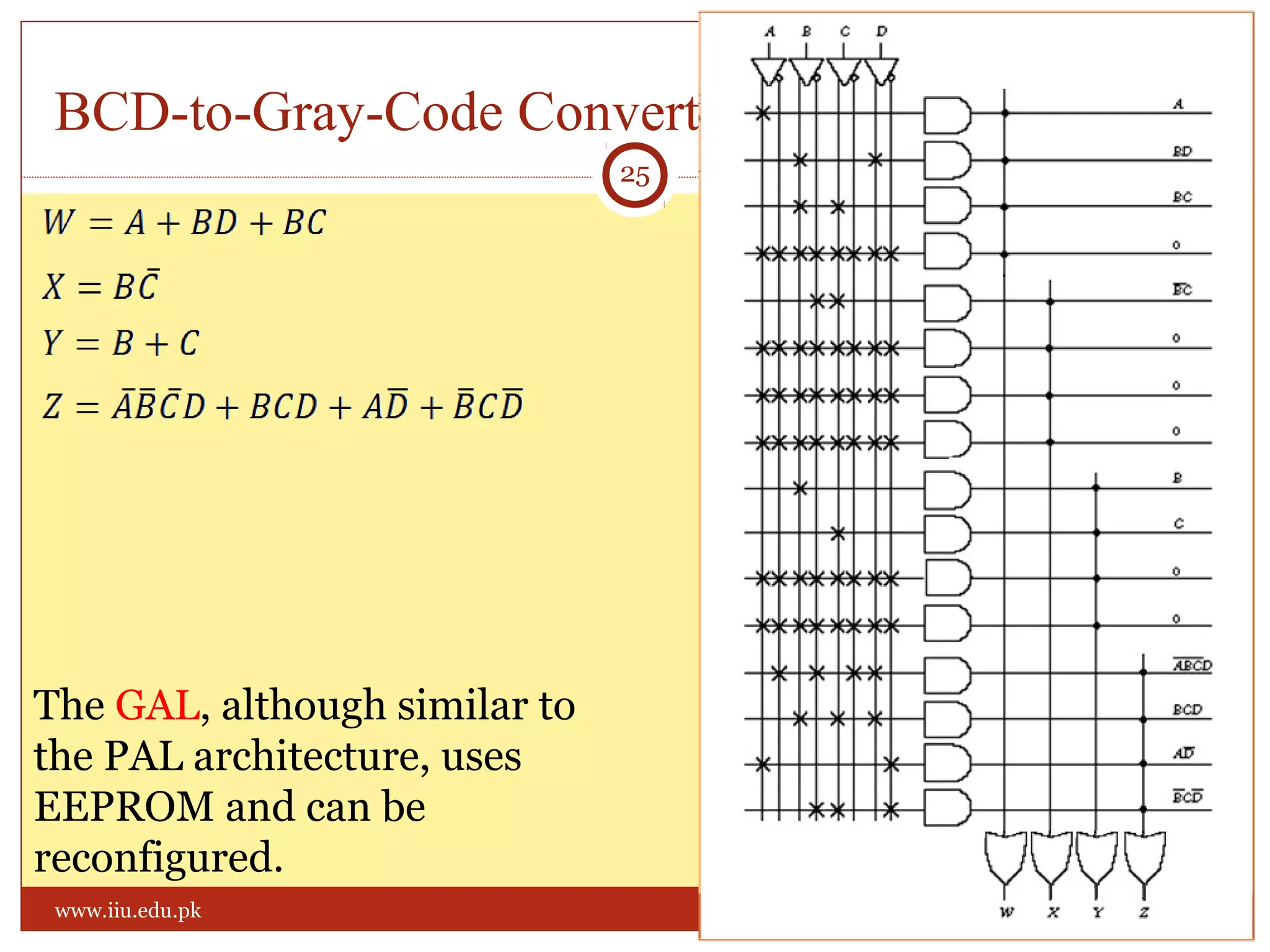
This document discusses memory and programmable logic devices. It begins by defining random access memory (RAM) and simple programmable logic devices (SPLDs) such as programmable read only memory (PROM), programmable array logic (PAL), and programmable logic array (PLA). It then provides more details on RAM, PROMs, PALs, and PLAs including their structures, programming methods, and applications. Examples of converting logic functions and binary to gray code are also presented.