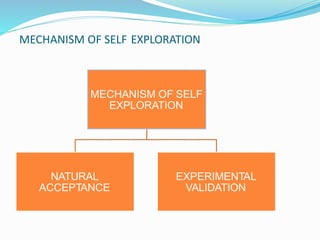
The document discusses ethics, human values, and value education. It defines ethics as moral philosophy that examines concepts of right and wrong conduct. It notes that ethics is divided into four categories: normative ethics, applied ethics, descriptive ethics, and meta ethics. It also discusses the need for value education in society given issues like value erosion. It outlines some key human values like love, peace, truth, and right conduct. Finally, it discusses concepts like self-exploration, introspection, and the process and mechanisms of self-exploration.












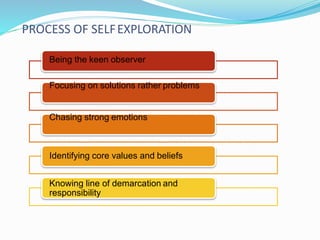
![Self exploration
self-exploration involves “taking a look at your own
thoughts, feelings, behaviors and motivations and asking
why. It's looking for the roots of who we are — answers to
all the questions we have about [ourselves]
It is process to find out what is valuable to me by investigating
with in myself. Since it is me who feel happy, successful,
unhappy or unsuccessful. Therefore what is right for me is to
be judged by myself only. This whole process is called self
exploration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/professionalethicsandhumanvalues-init1-210319142159/85/Professional-ethics-and-human-values-init-1-13-320.jpg)