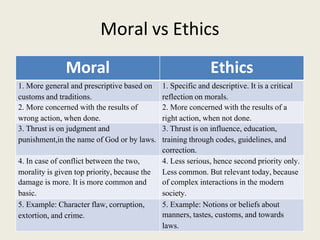
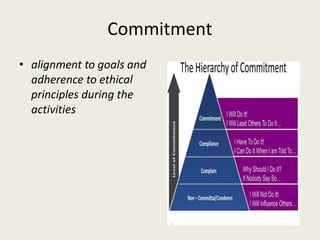
The document discusses various aspects of human values such as morals, ethics, integrity, work ethic, and civic virtues, emphasizing their importance in personal and professional development. It defines key concepts like values, discernment, and perseverance while exploring the relationship between ethics, character, and successful workplace behavior. Additionally, it advocates for service learning and community engagement as means to develop civic virtues and enhance the quality of life.