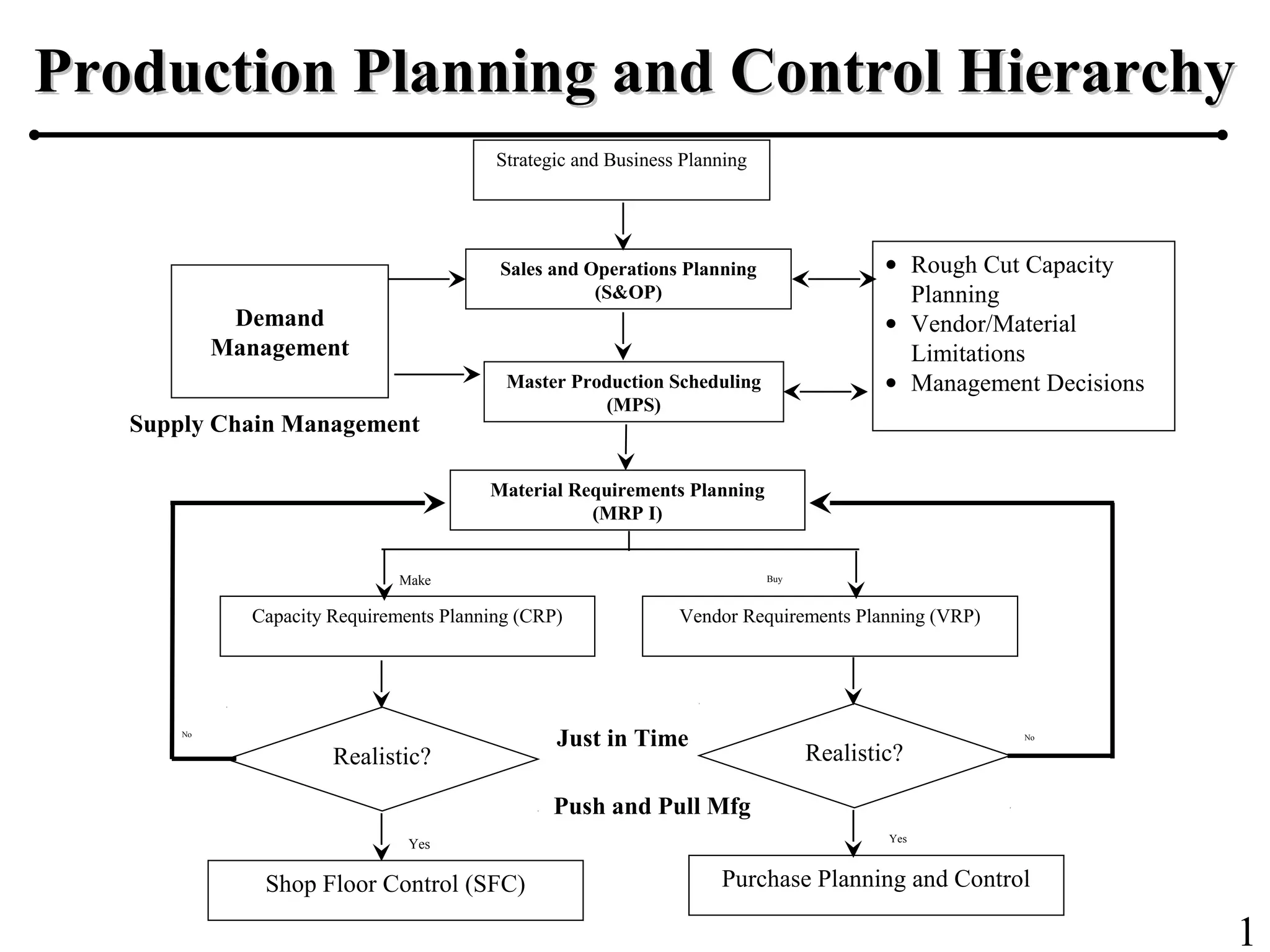
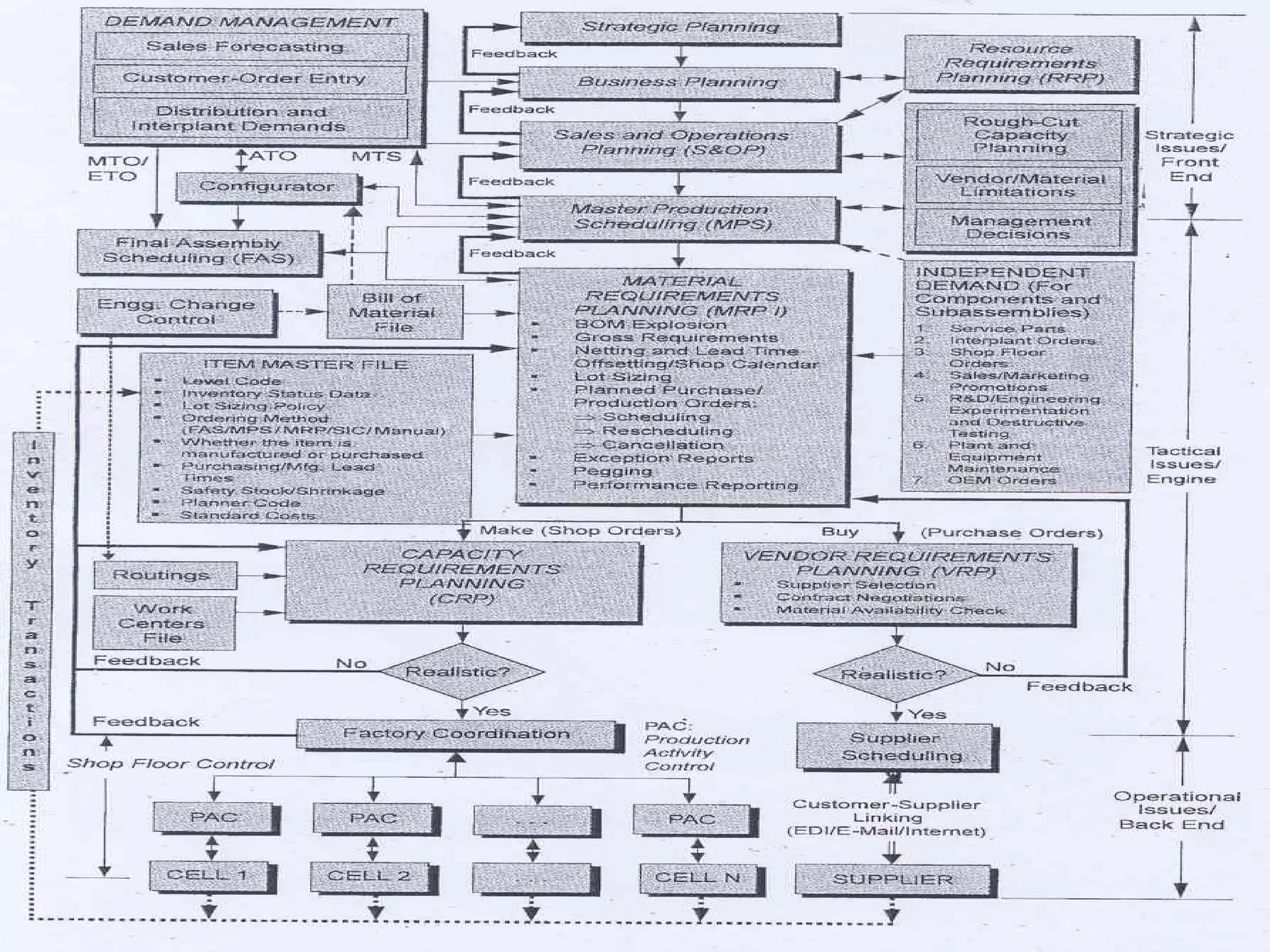
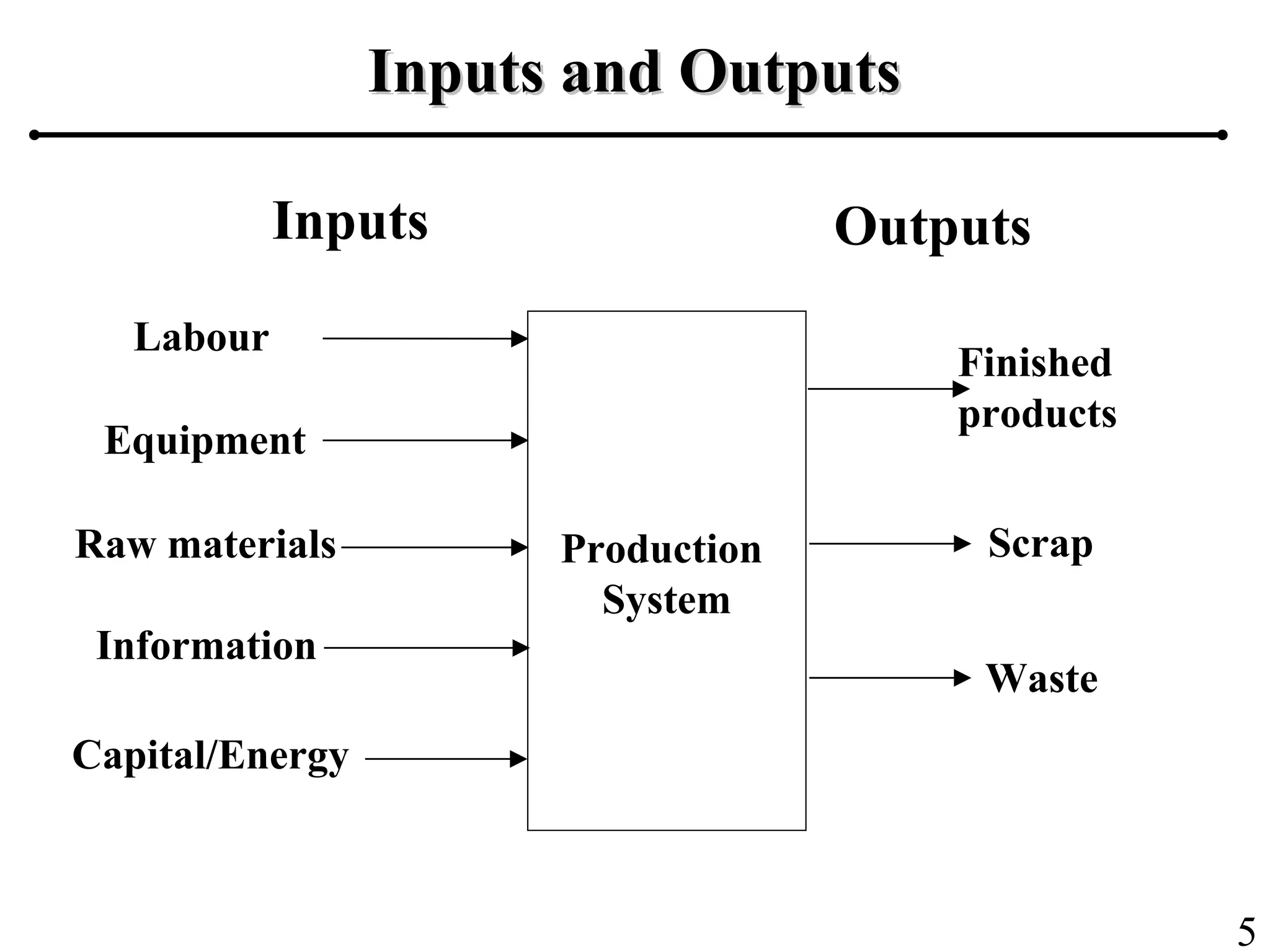
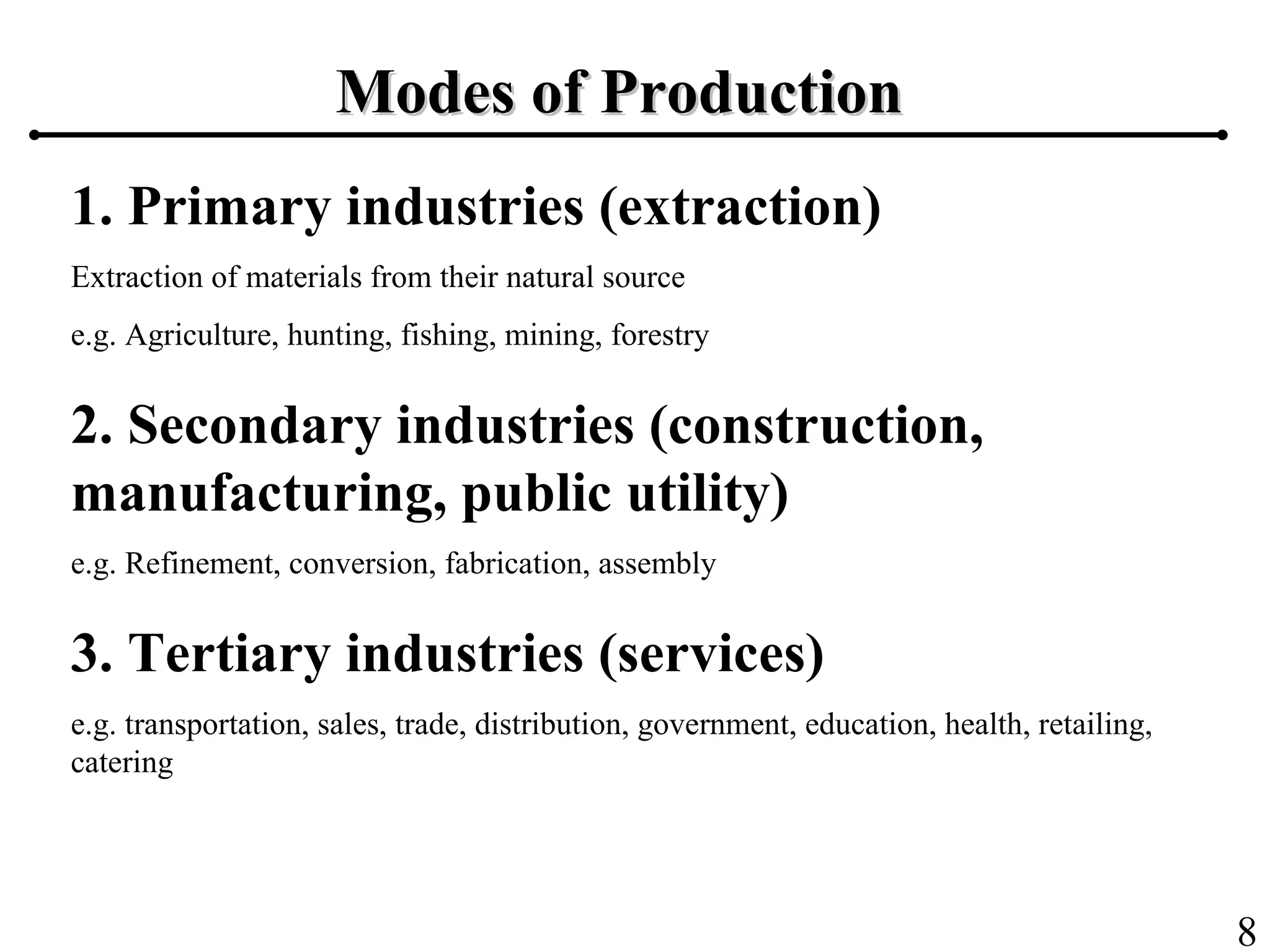
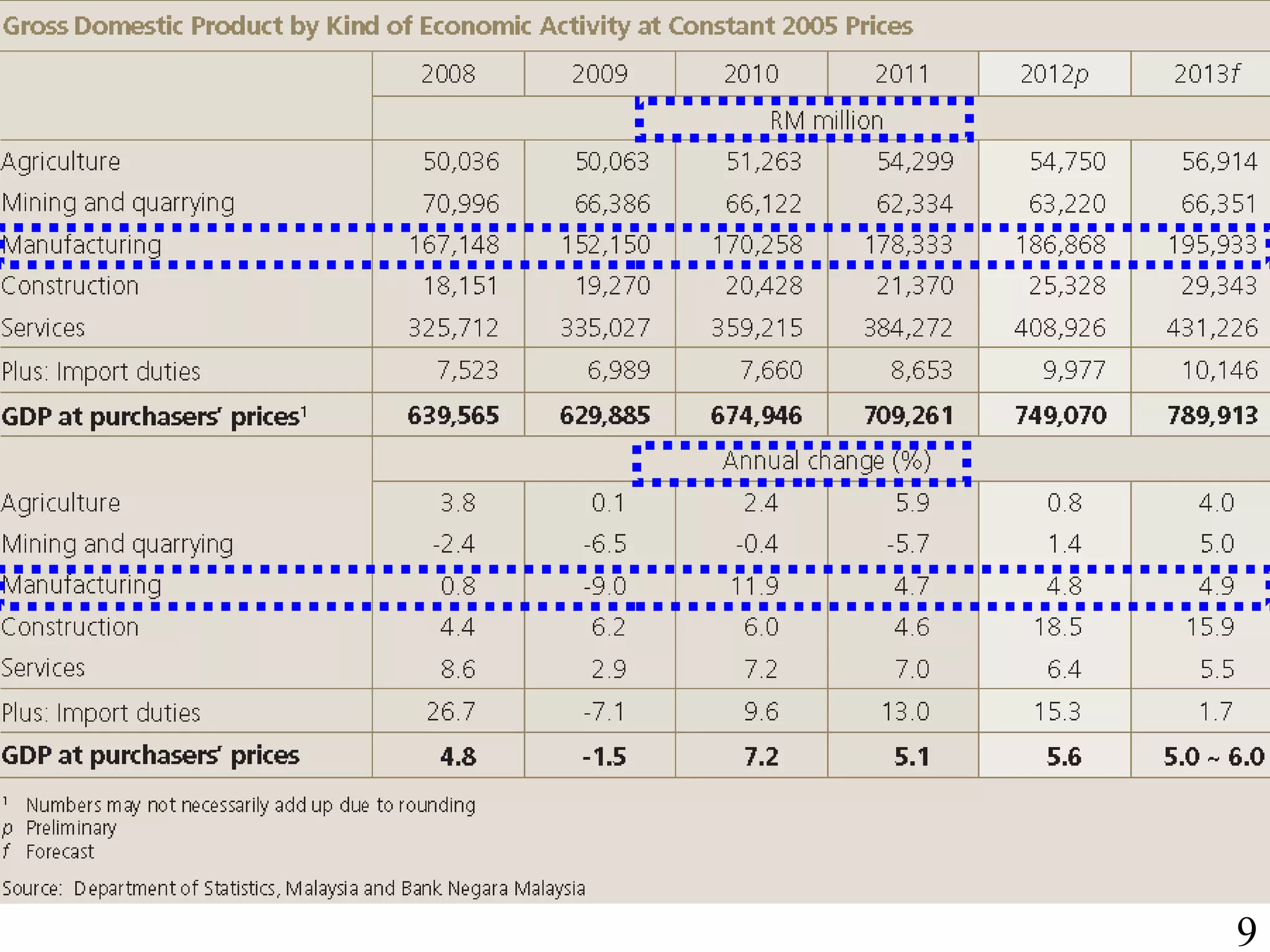
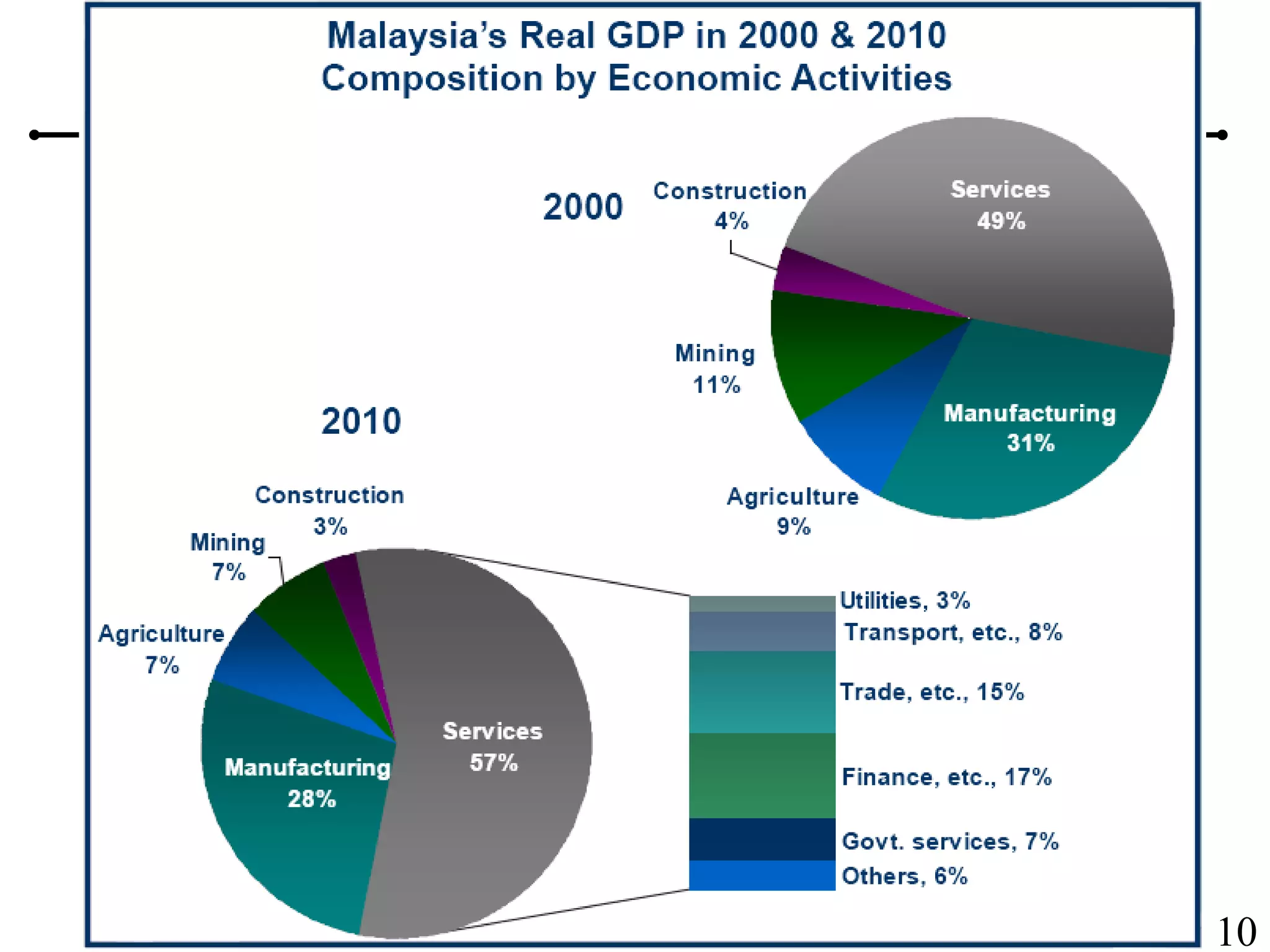
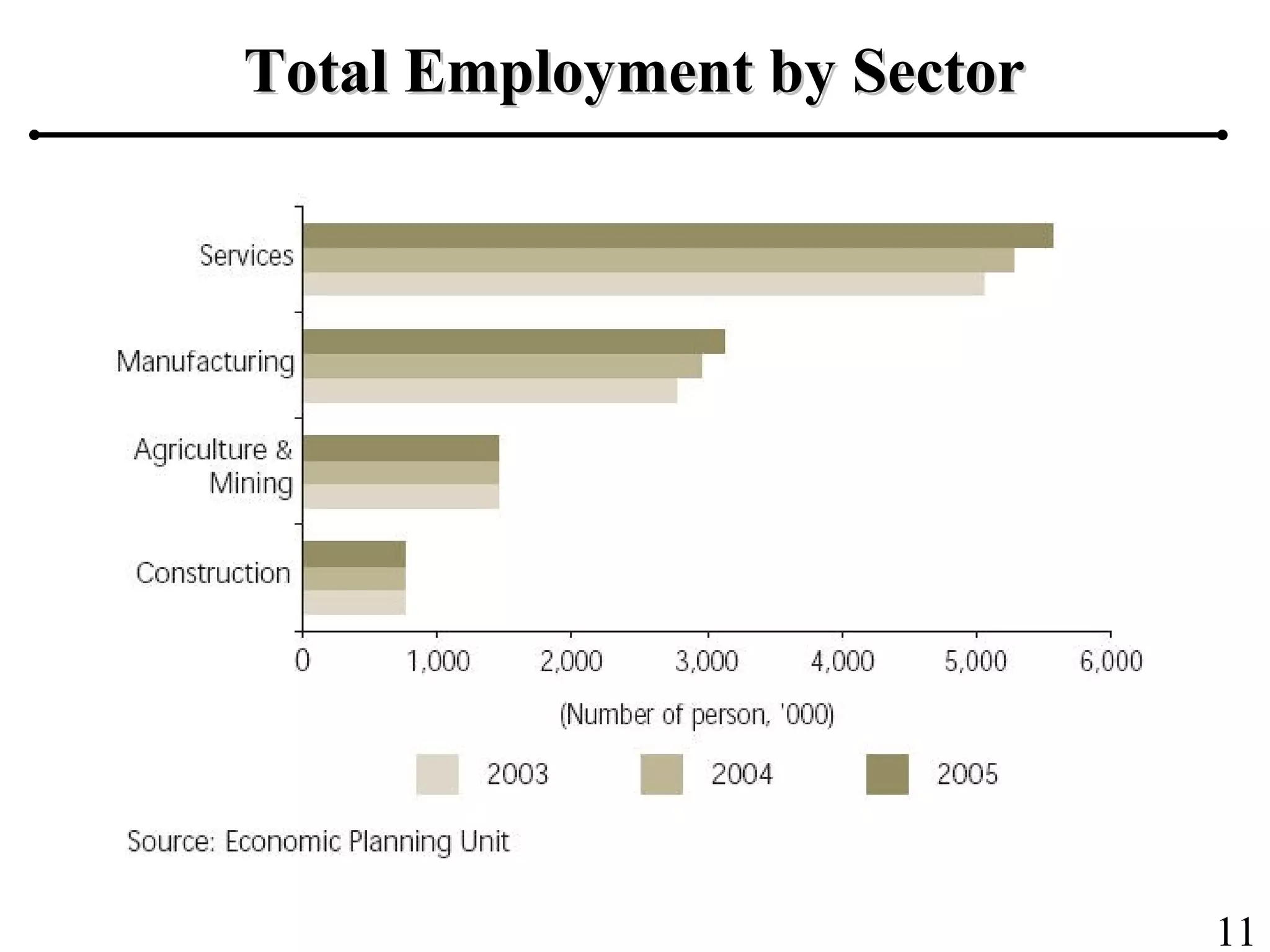
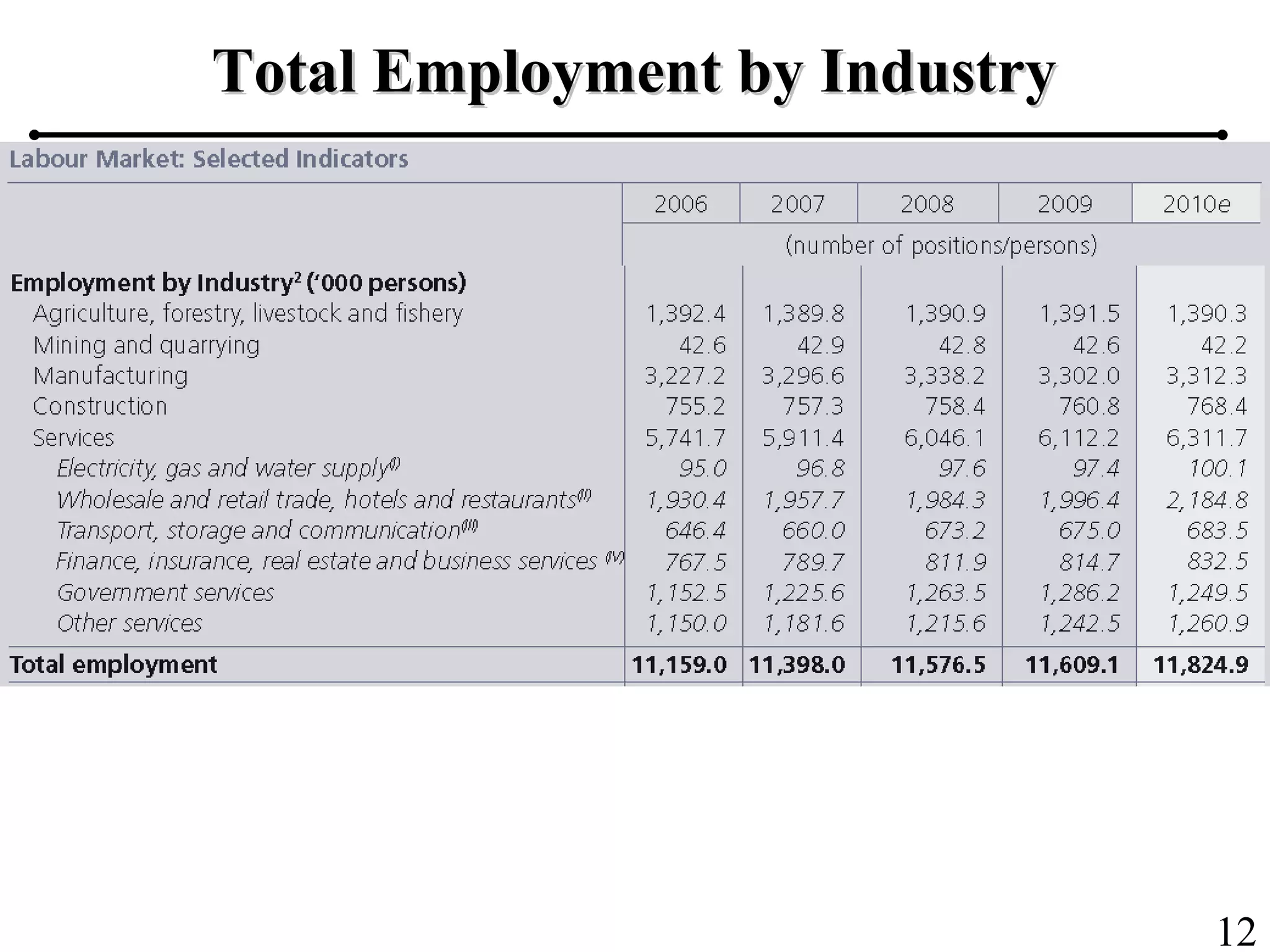
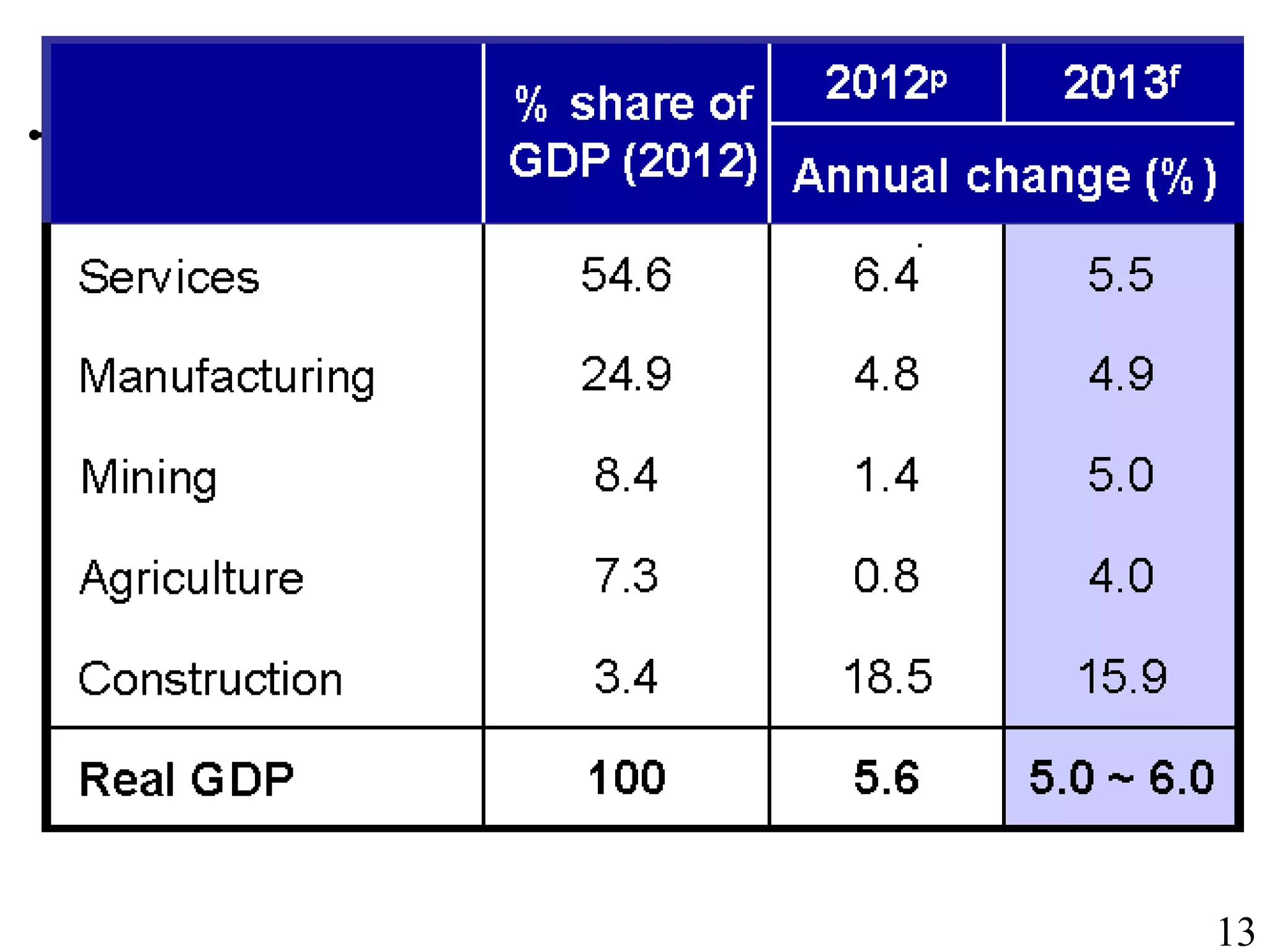
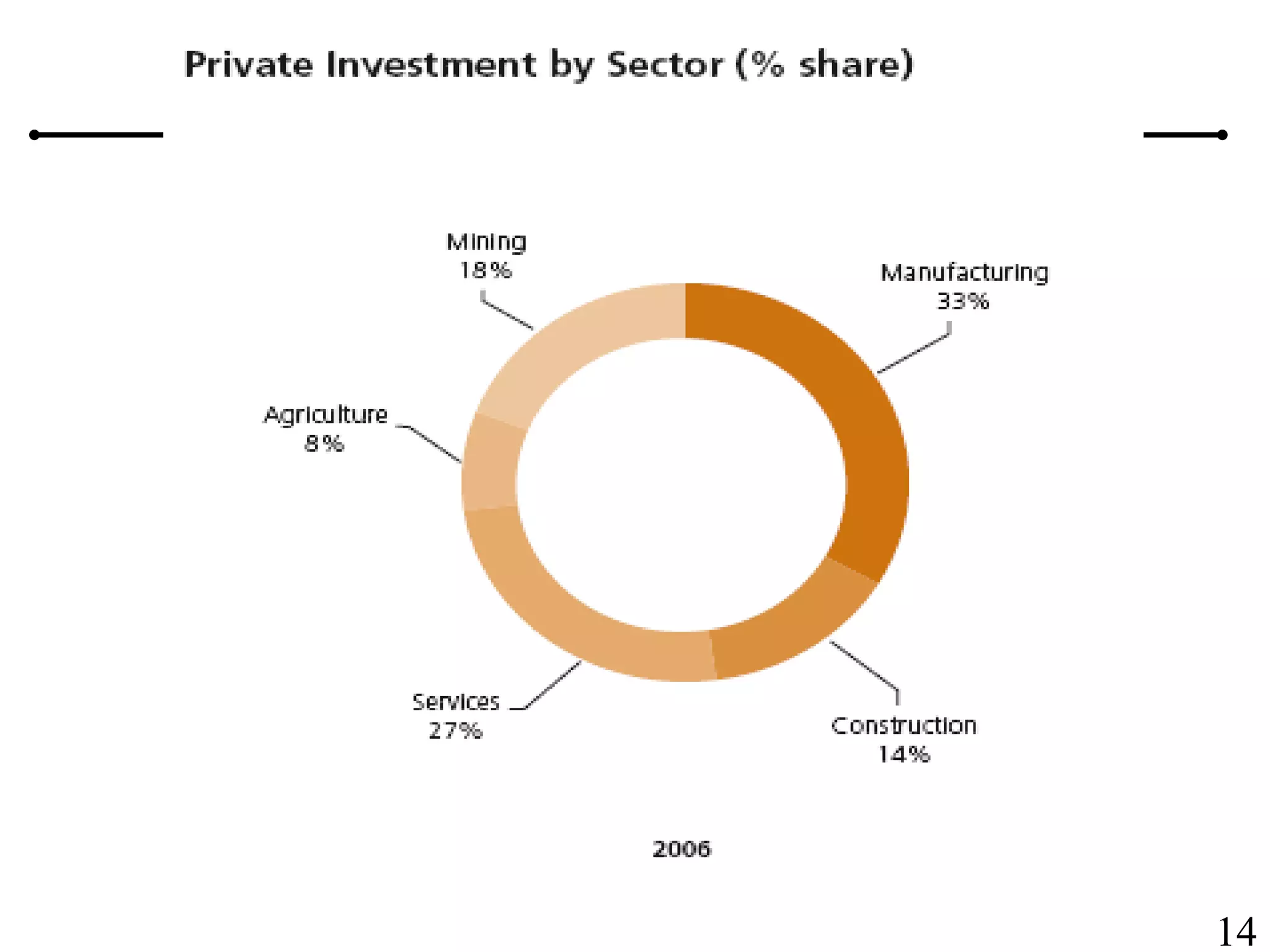
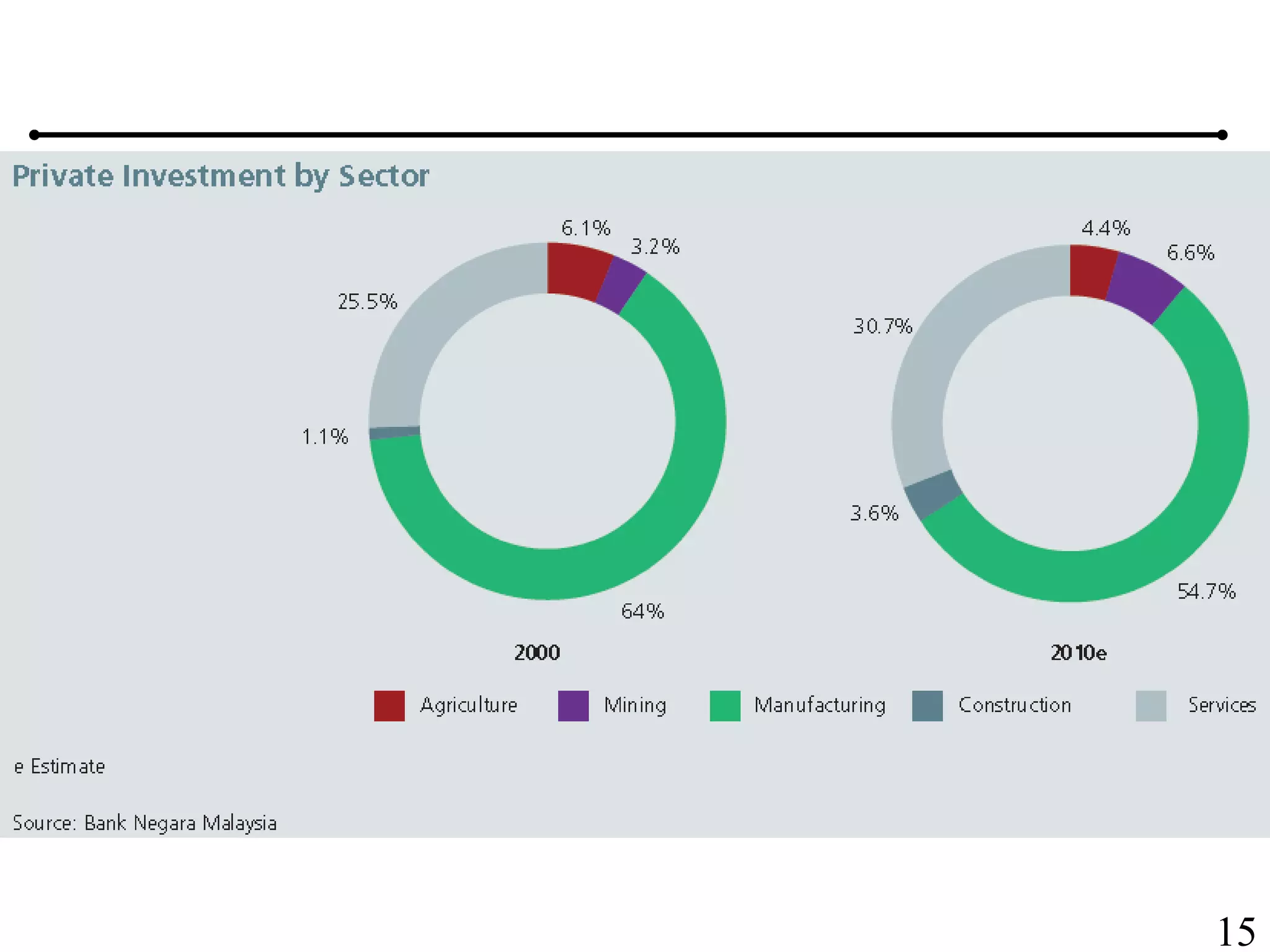
The document outlines the production planning and control hierarchy which includes strategic and business planning, demand management, sales and operations planning, master production scheduling, material requirements planning, capacity requirements planning, and shop floor control. It then defines production/manufacturing as the process of converting raw materials into finished products. Planning involves looking ahead and setting actions to achieve objectives, while control compares actual performance to plans. Production planning and control aims to effectively utilize resources to satisfy customer demand and create profits.