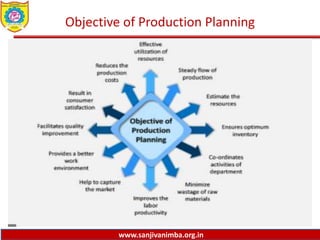
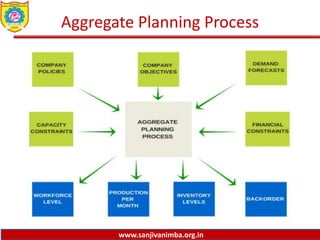
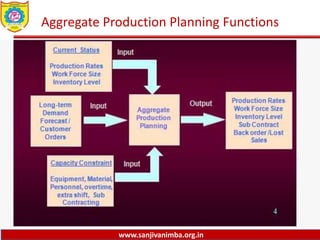
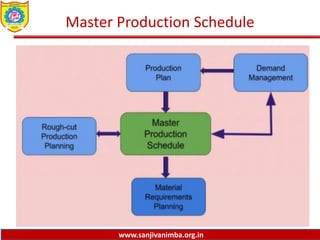
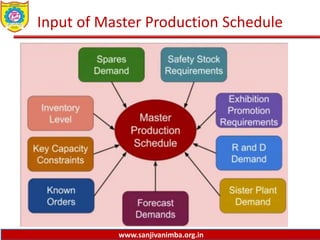
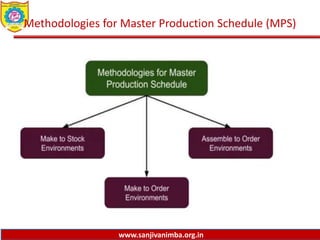
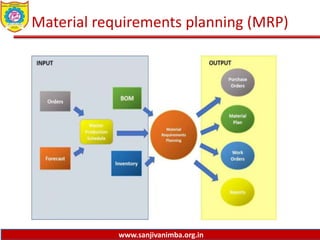
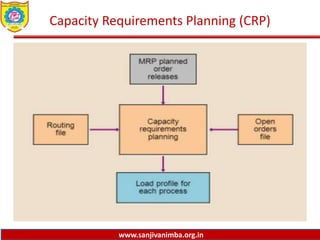
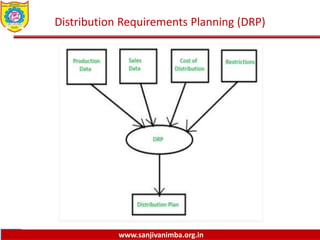
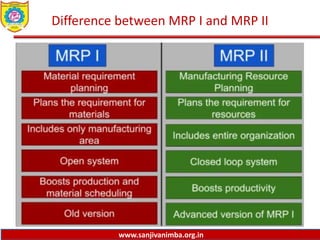
The document discusses various production planning techniques used in operations management, including production planning, aggregate production planning, master production scheduling, material requirements planning (MRP), capacity requirements planning (CRP), and distribution requirements planning (DRP). It provides details on the objectives, processes, inputs, and methodologies involved in each of these techniques. The key goal of these techniques is to optimize production levels and resource utilization to meet fluctuating demand over time in the most efficient and cost-effective manner.