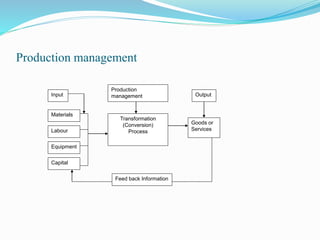
This document provides an introduction to production management, defining it as the organized activity of making goods and services while emphasizing quality, quantity, cost, and timely delivery. It outlines the production system, including essential elements such as design, purchasing, and quality control, and discusses the historical context of production management from traditional craftsmanship to modern practices. The document identifies key objectives and intermediate goals necessary for effective production management, ultimately aimed at meeting customer needs and enhancing profitability.