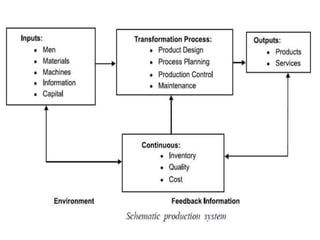
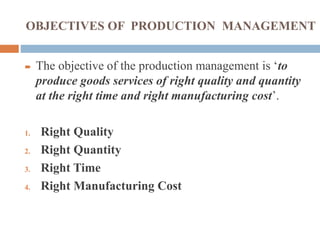
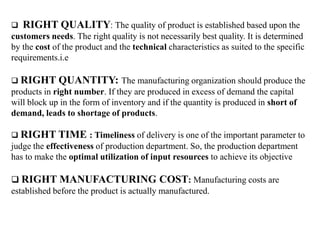
The document discusses production management, which involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling production activities to transform raw materials into finished goods or services. The key objectives of production management are to produce goods and services of the right quality and quantity, at the right time, and at the right manufacturing cost. Production management activities include specifying and procuring input resources, product design and development, and supervising the transformation process. The goals are to accomplish business objectives, build reputation and goodwill, introduce new products, support other business functions, utilize resources optimally, and minimize costs while boosting the economy and standards of living.