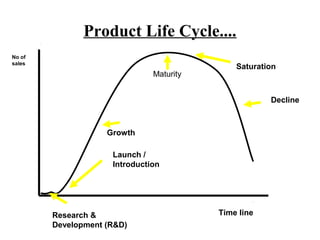
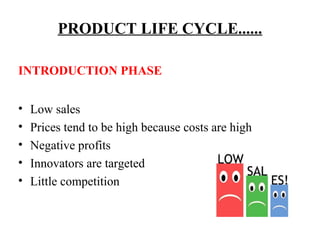
Every product has a limited life cycle that passes through different stages - introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. At each stage, sales, profits, and the appropriate marketing strategy differ. In introduction, sales are low but prices are high as costs are also high. In growth, sales rapidly rise as more customers are attracted. Maturity sees a slowing of growth until sales eventually decline. During decline, companies withdraw products or focus on reducing costs and prices to extract remaining value. The optimal marketing strategy changes for each phase, focusing on promotion in early stages and modification or reduction in later stages.