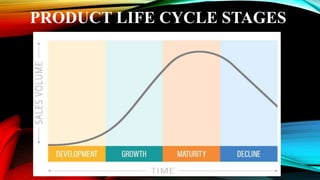
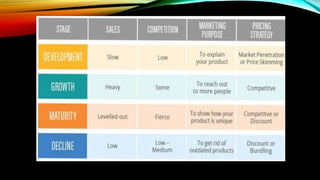
The document discusses the product life cycle, which consists of four stages: development, growth, maturity, and decline. It describes each stage, noting that sales are typically slow in development but grow in growth, level off in maturity, and decline in the decline stage. Managing a product through its life cycle by observing these stages can help businesses determine pricing, anticipate profitability, and compete effectively at each phase.