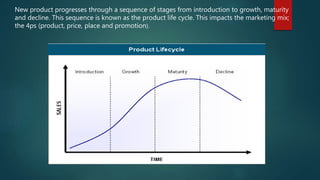
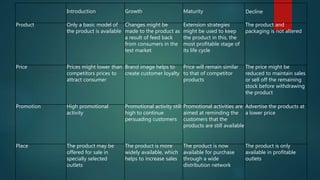
The document summarizes the product life cycle stages of introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. It describes how the marketing mix of product, price, promotion, and place changes throughout each stage. During introduction, the product has limited availability and higher prices. Growth involves more widespread distribution and promotional activities to increase sales. Maturity is the most profitable stage where distribution is broad and promotions remind customers. In decline, prices are reduced to clear remaining stock before withdrawing the product. Extending the life cycle involves selling mature domestic products to new international markets to continue sales without additional research costs.