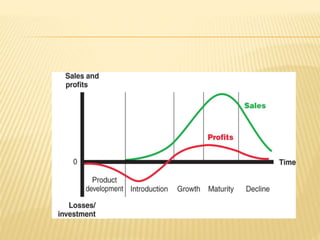
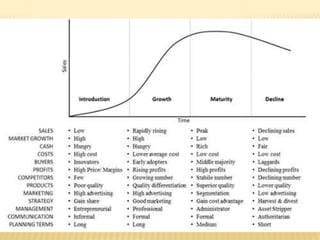
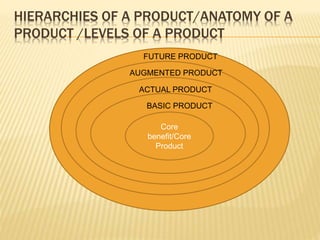
The document discusses product and pricing management, emphasizing the concept of the product life cycle which includes four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage is characterized by changes in sales volume, profits, promotional efforts, and competition, requiring unique marketing strategies. Additionally, it outlines the different levels of a product, from core benefit to potential product, highlighting the evolving expectations and attributes consumers seek.