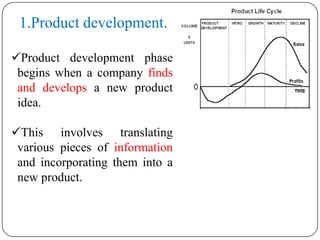
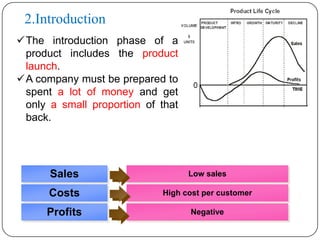
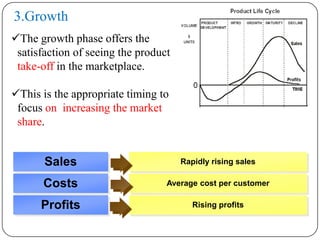
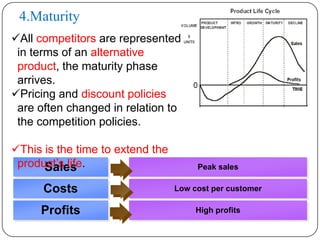
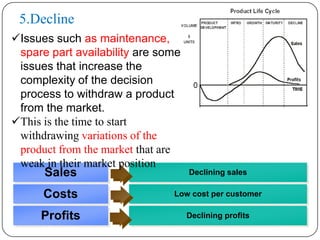
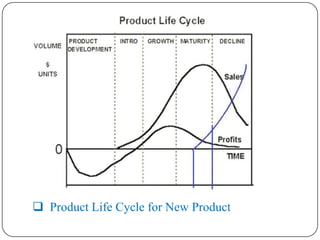
The document discusses the product life cycle, which refers to the various phases a product goes through from development to withdrawal from the market. It identifies five main phases: 1) product development, 2) introduction, 3) growth, 4) maturity, and 5) decline. Each phase is characterized by different levels of sales, costs, and profits. The product life cycle model shows how a product evolves over time as it is commercialized, gains widespread adoption, and eventually is replaced in the market.