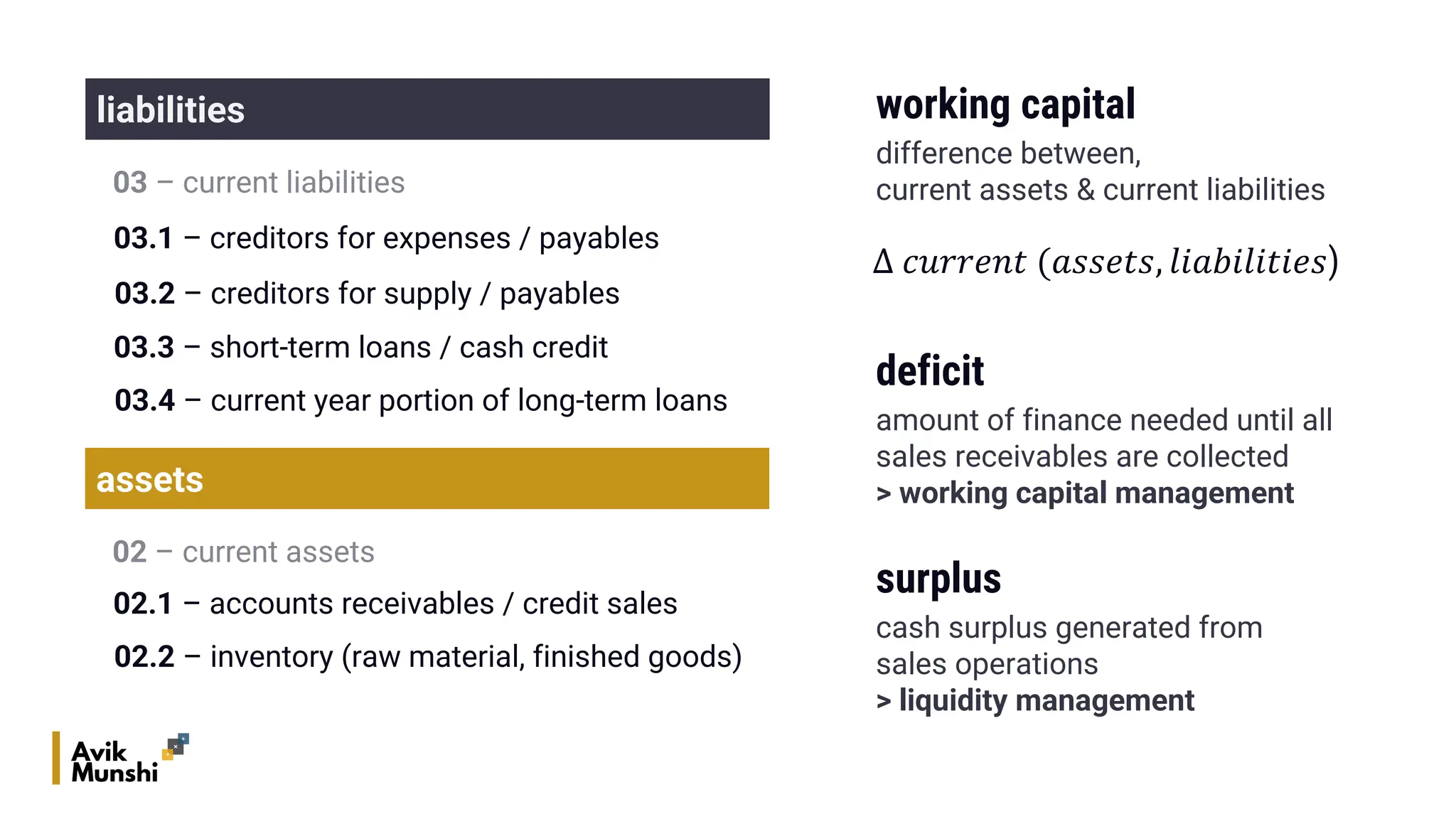
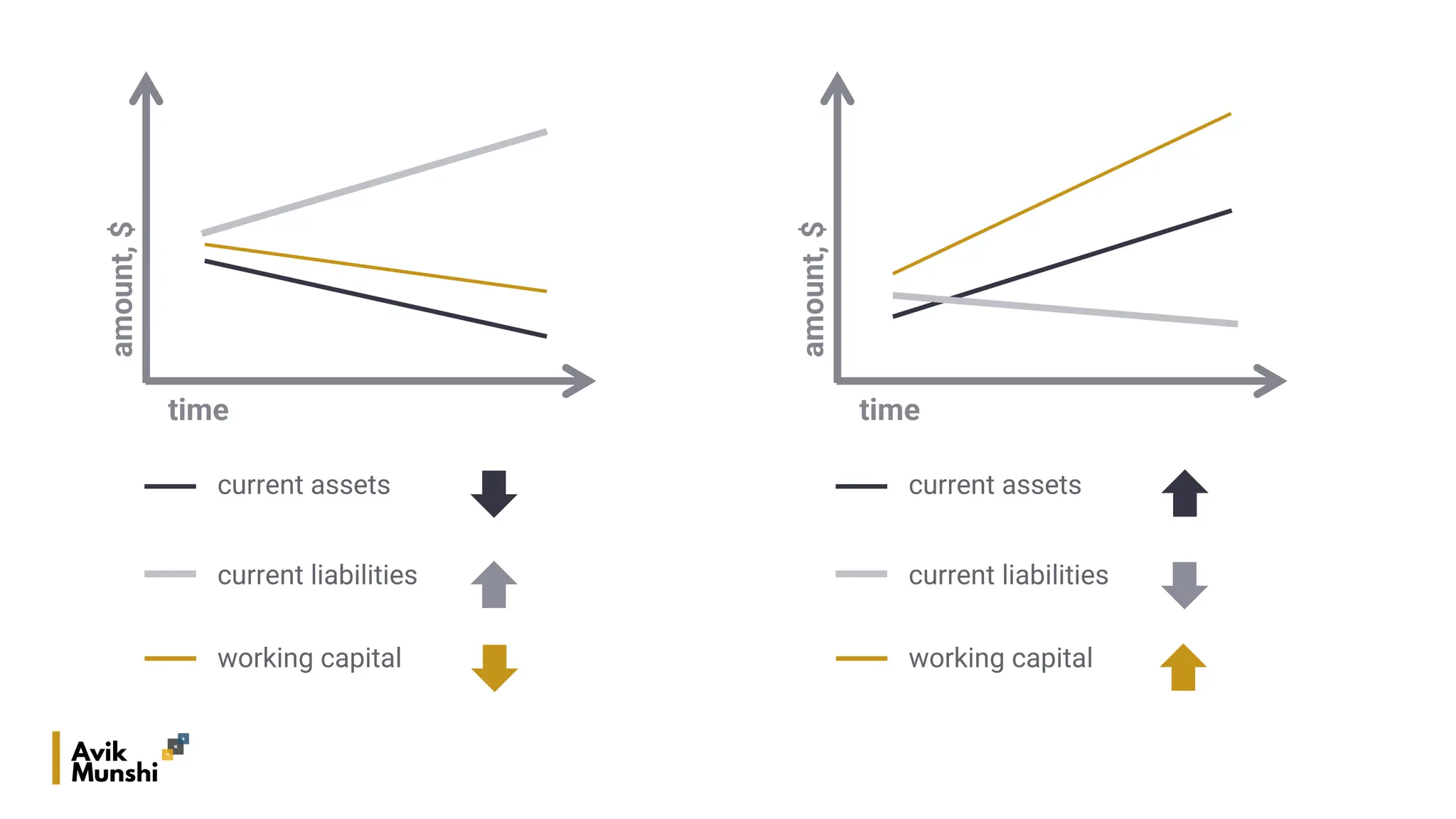
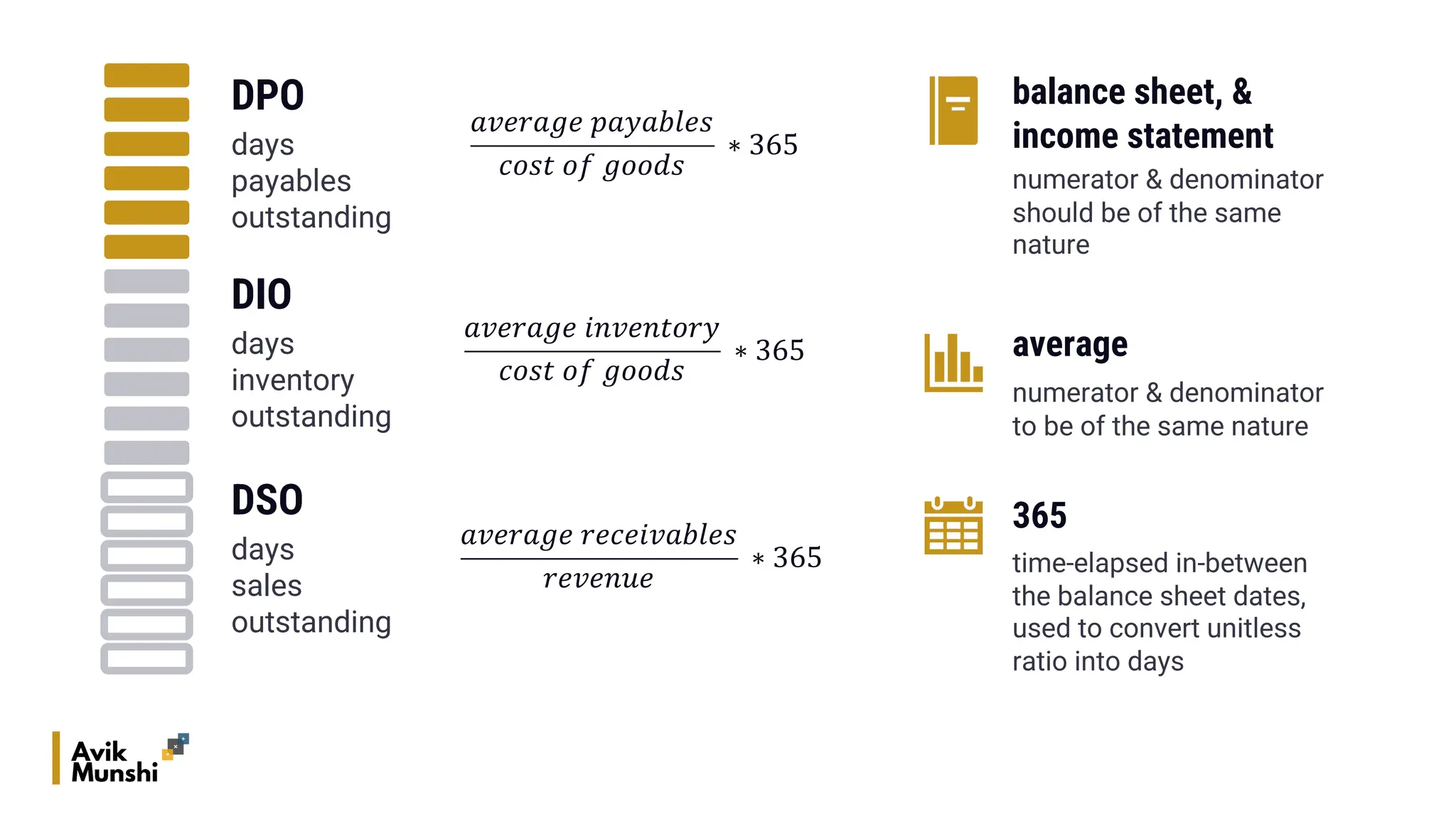
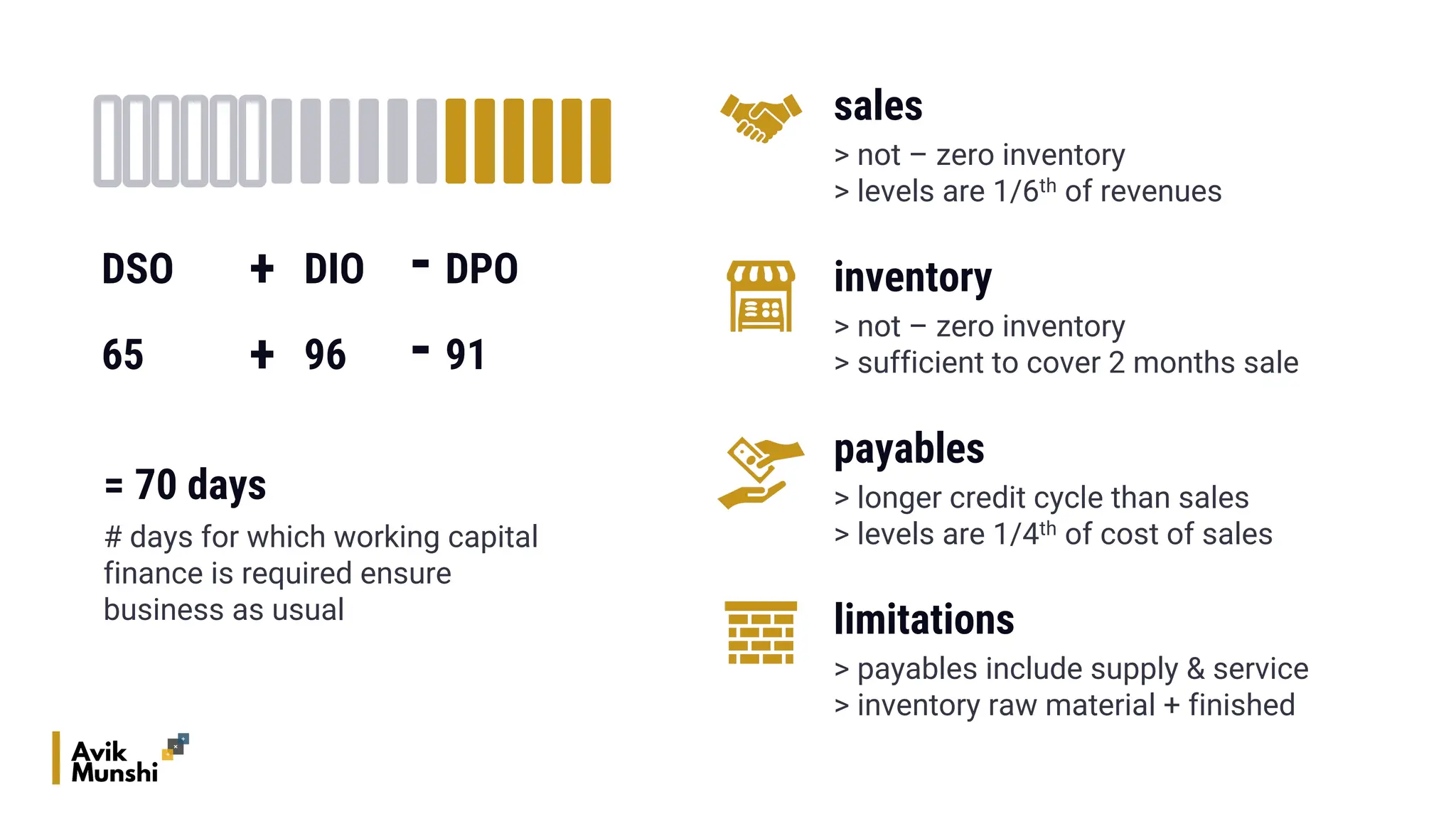
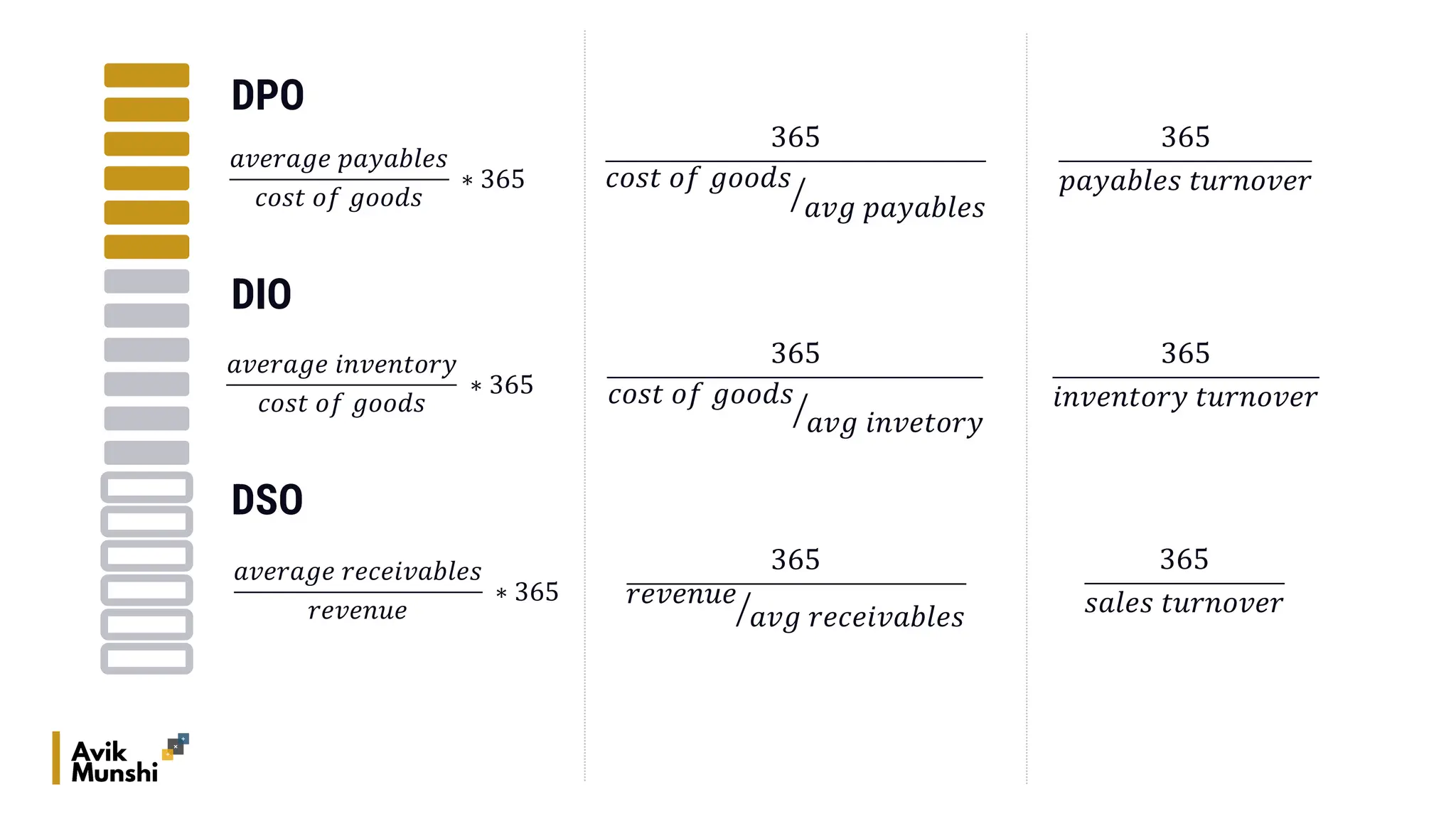
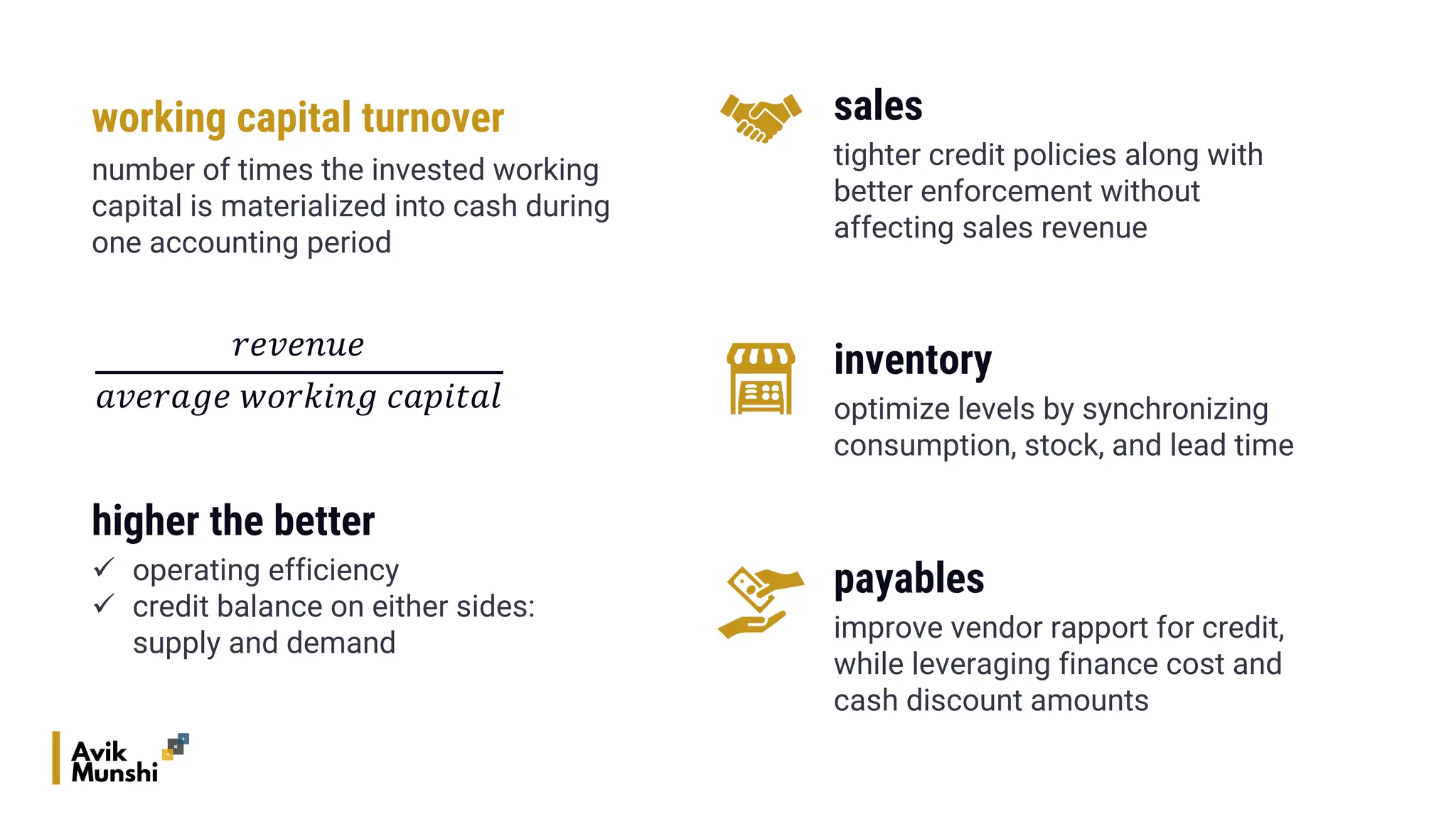
The document provides an overview of procurement finance, focusing on working capital management, current assets and liabilities, and the cash conversion cycle. It includes key financial metrics such as days payables outstanding (DPO), days inventory outstanding (DIO), and days sales outstanding (DSO) to assess business efficiency. Additionally, it addresses the importance of strategic cash management and the balance between inventory levels and payables to optimize cash flow.