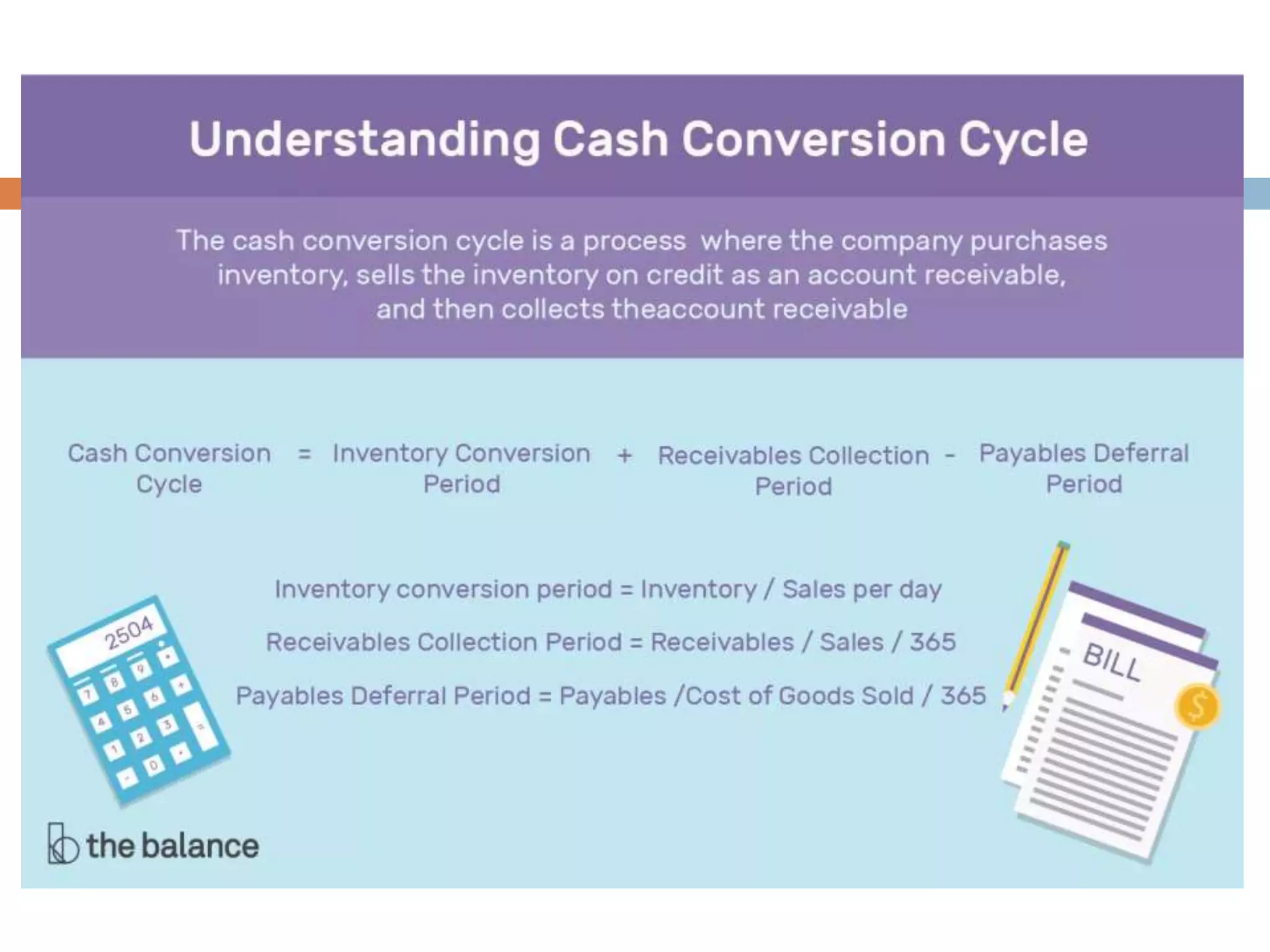
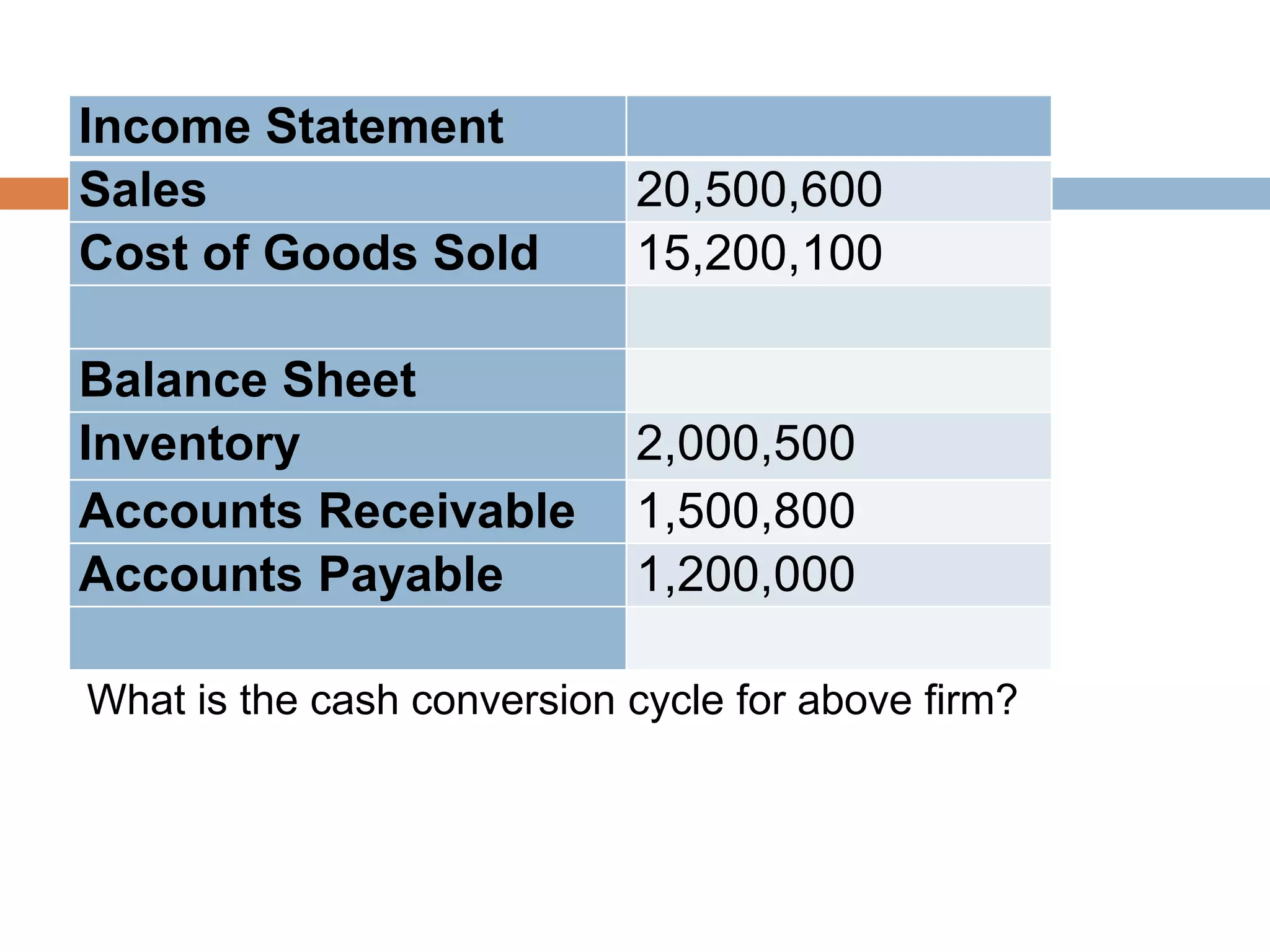
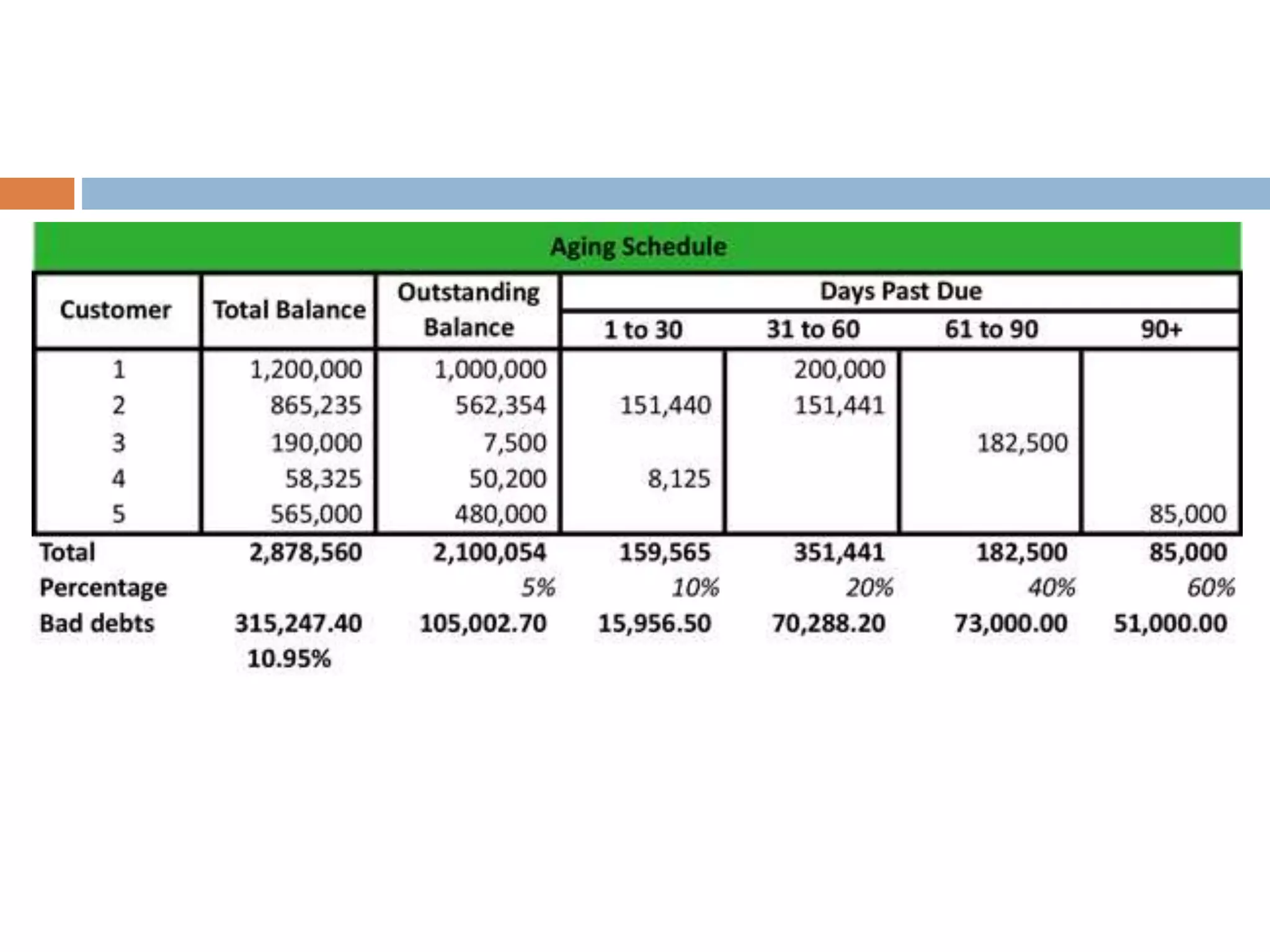
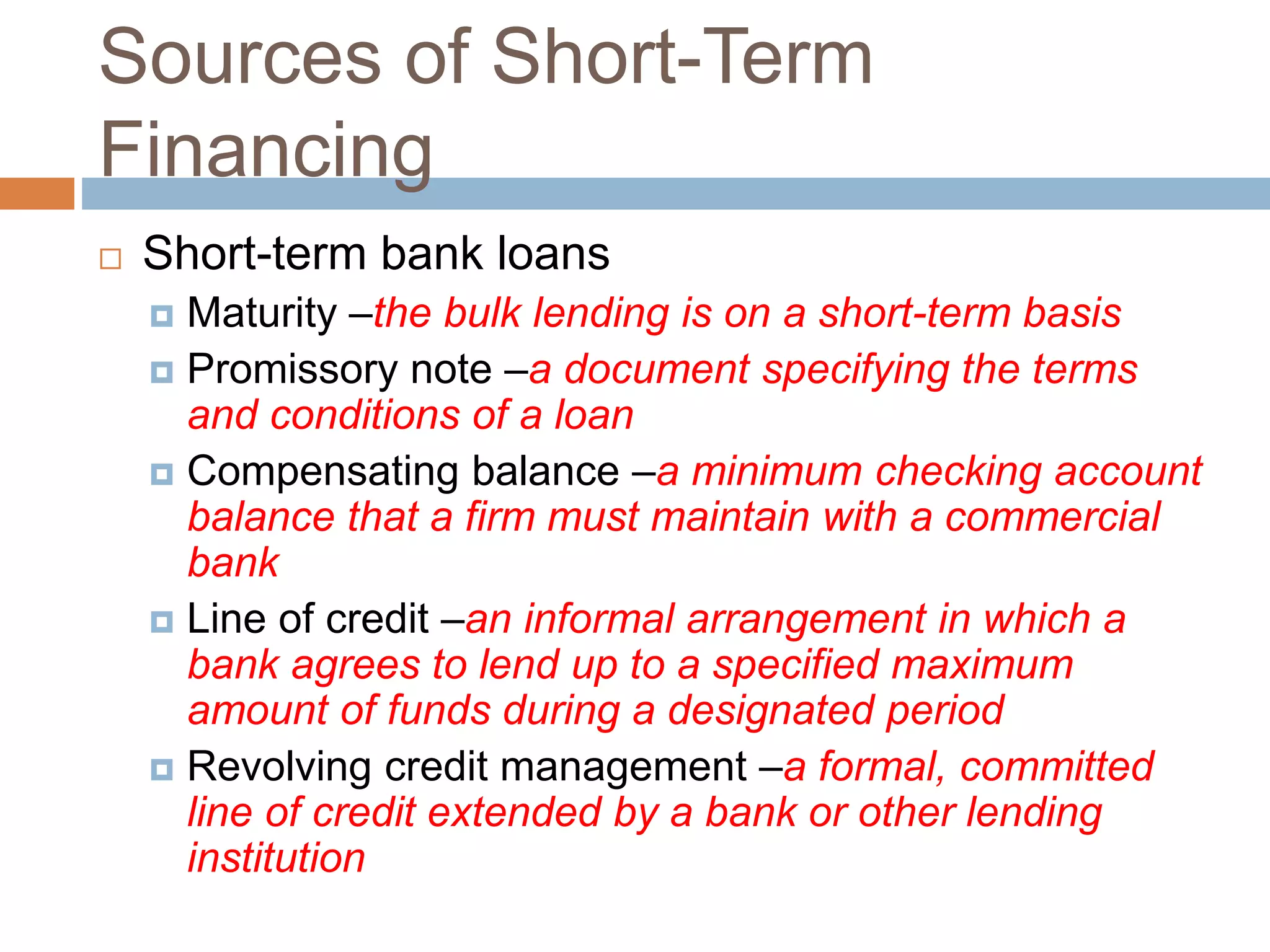
This document summarizes key concepts about working capital management. It discusses working capital terminology like net working capital and cash conversion cycle. The cash conversion cycle measures the average number of days from paying for inventory to collecting from sales. It then discusses factors like inventory, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and cash budgets that influence working capital management policies. Finally, it covers short-term financing sources for working capital like bank loans, commercial paper, and accounts payable.