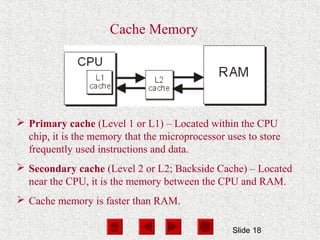
The document discusses computer components including the CPU, memory, and hard disks. It provides details on:
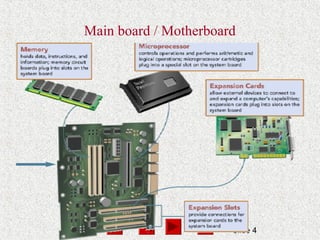
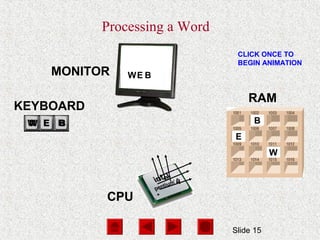
- The CPU processes data and consists of a control unit and arithmetic logic unit. The control unit manages the fetch, decode, execute, and store processing cycle.
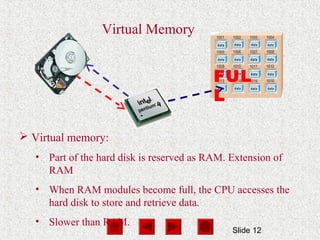
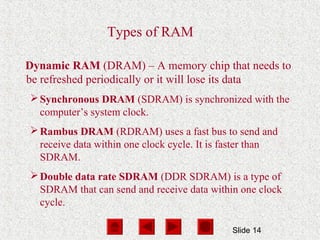
- Memory, including RAM and ROM, temporarily stores programs and data for quick CPU access. RAM is volatile while ROM is read-only.
- Storage devices like hard disks provide non-volatile storage and come in varieties like removable disks and internet drives. Hard disks use platters, read/write heads, and partitions to store and retrieve files from its file allocation table.