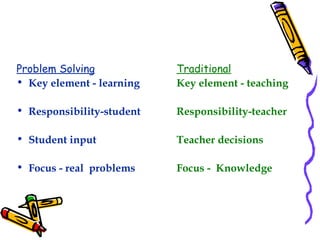
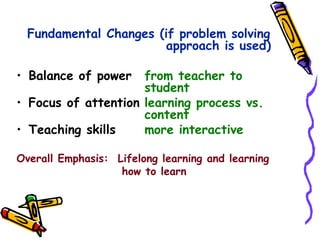
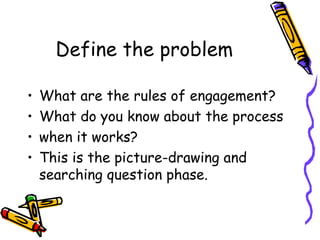
The document discusses the importance of problem-based learning as an instructional method that encourages students to develop problem-solving skills through collaboration and inquiry. It highlights the shift in focus from teacher-led instruction to student-centered learning, promoting independent thinking and social skills. The text outlines the problem-solving process and its significance in creating meaningful and relevant learning experiences for students.