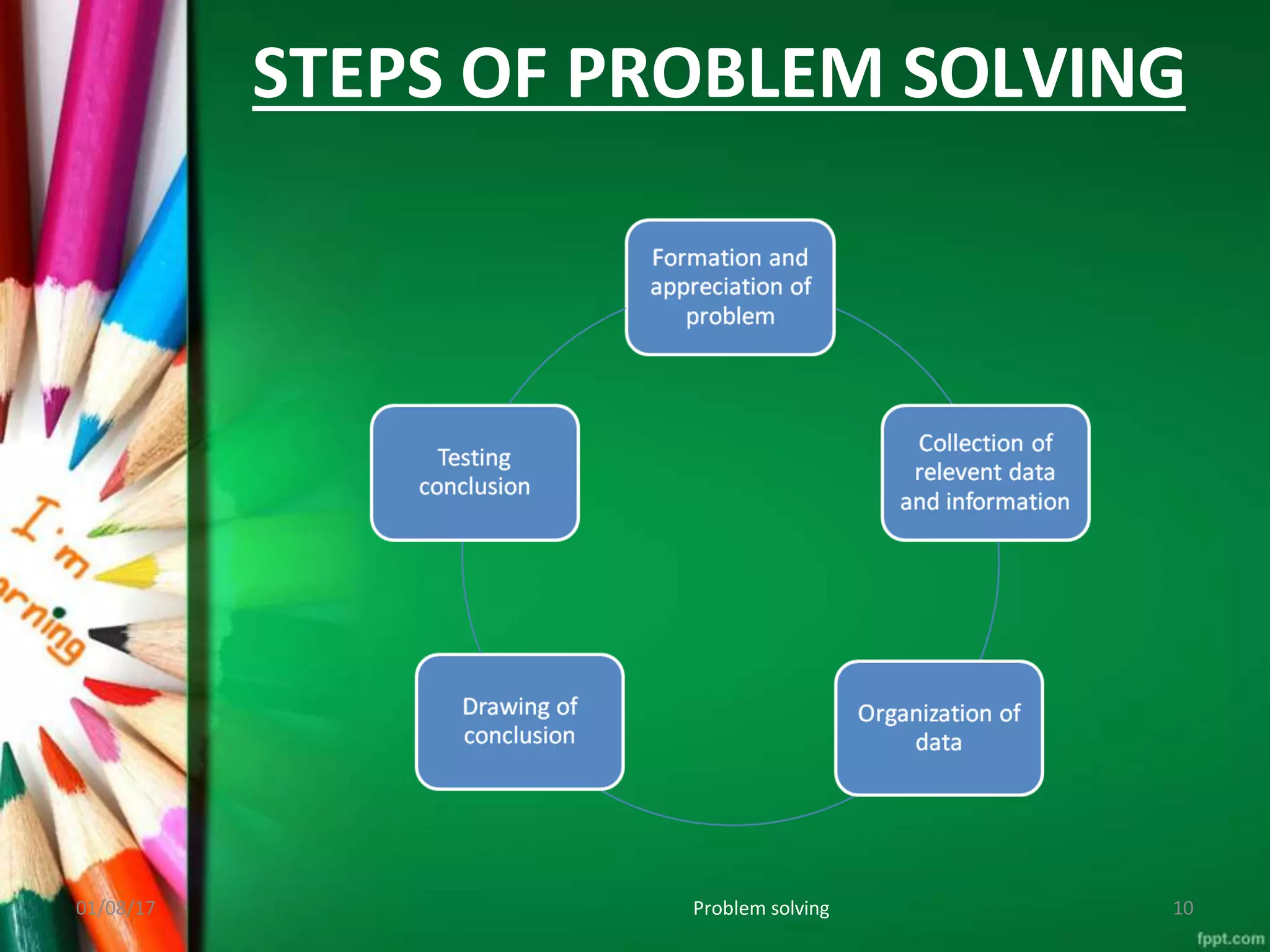
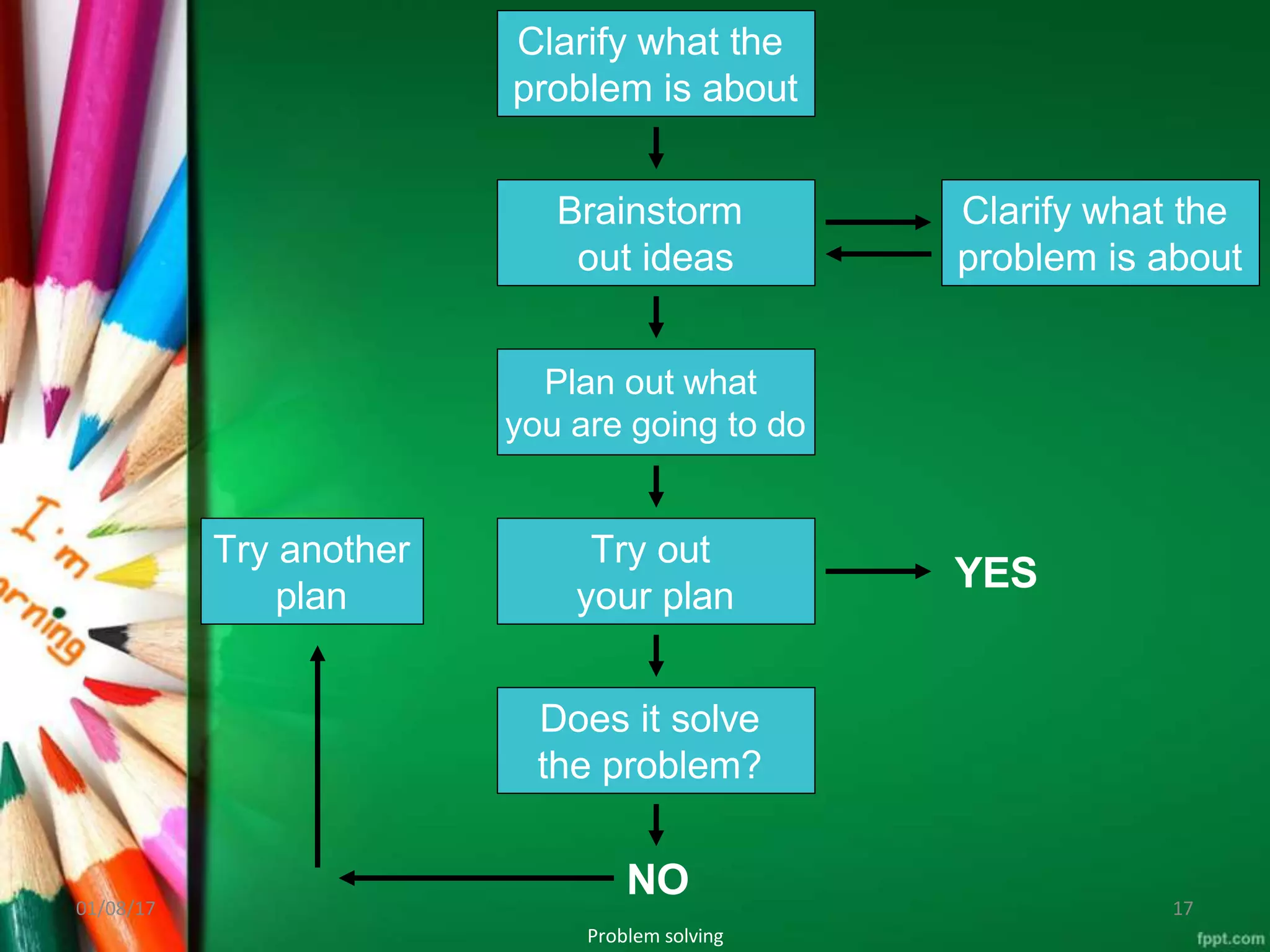
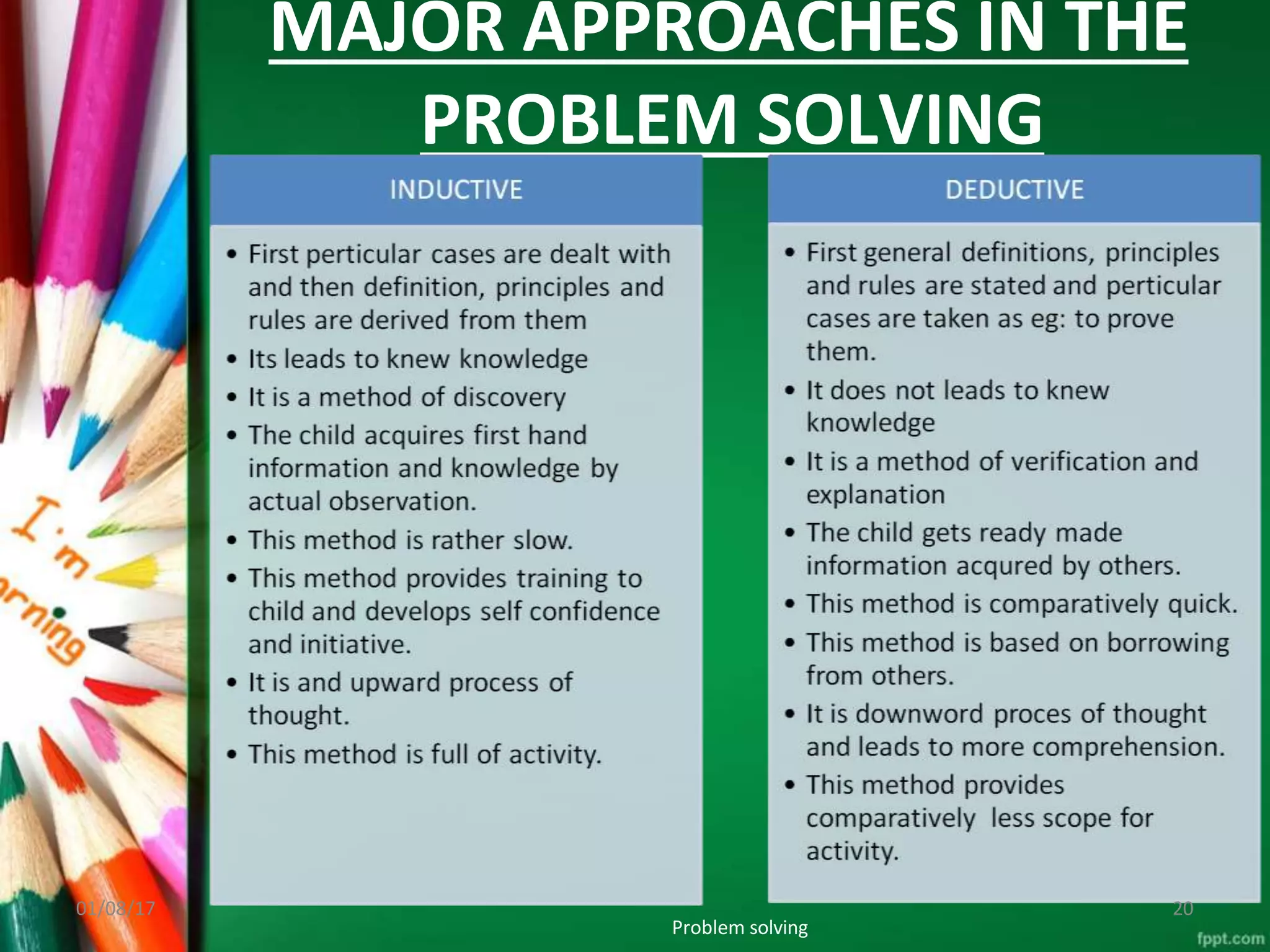
This document discusses problem solving as an instructional method where teachers and students work together to find solutions to educational problems. It defines problem solving as a systematic process of defining problems, gathering information, organizing data, drawing conclusions, and testing solutions. The key steps of problem solving are clarifying the problem, brainstorming ideas, planning a solution, trying the plan, and evaluating if it solves the problem. Problem solving is useful in nursing education as it helps students develop critical thinking and the ability to analyze problems and find appropriate solutions in clinical settings.