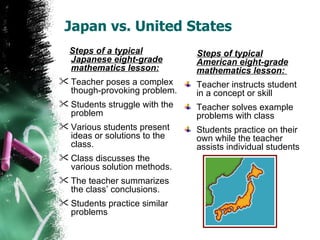
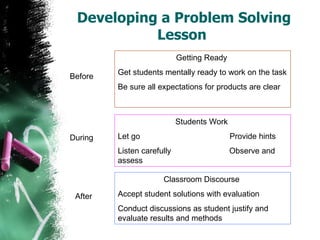
The document discusses teaching mathematics through problem solving using a three P's framework of purpose, process, and payoff. It emphasizes that important math concepts are best taught by engaging students in thinking about and developing problems of a reflective nature. The teacher's role is to pose thought-provoking problems and facilitate discussion of various solution methods rather than simply demonstrating examples. Effective problem solving lessons involve preparing students mentally, letting them work through problems with guidance, and conducting class discussions to justify and evaluate results.