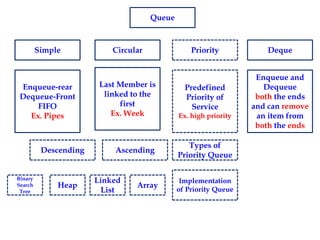
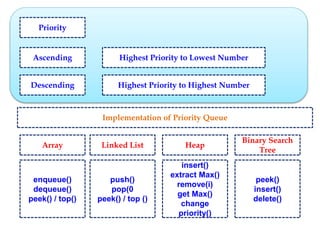
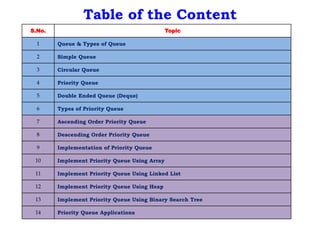
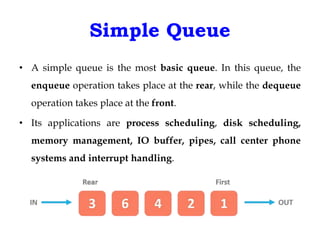
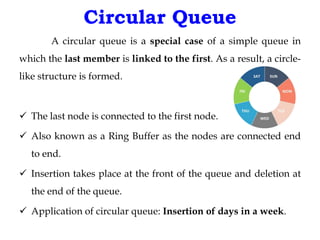
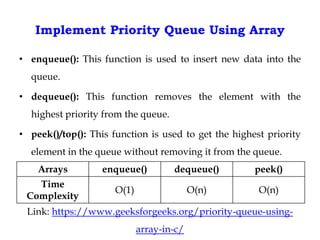
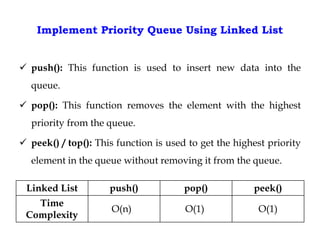
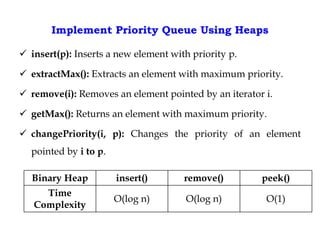
This document discusses priority queues and their implementation. It begins by defining different types of queues like simple, circular, priority, and double-ended queues. It then focuses on priority queues, explaining ascending and descending order priority queues. Various data structures for implementing priority queues are covered, including arrays, linked lists, heaps, and binary search trees. Common operations on priority queues like enqueue, dequeue, and peek are also defined. Finally, applications of priority queues in areas like CPU scheduling, graph algorithms, and data compression are mentioned.