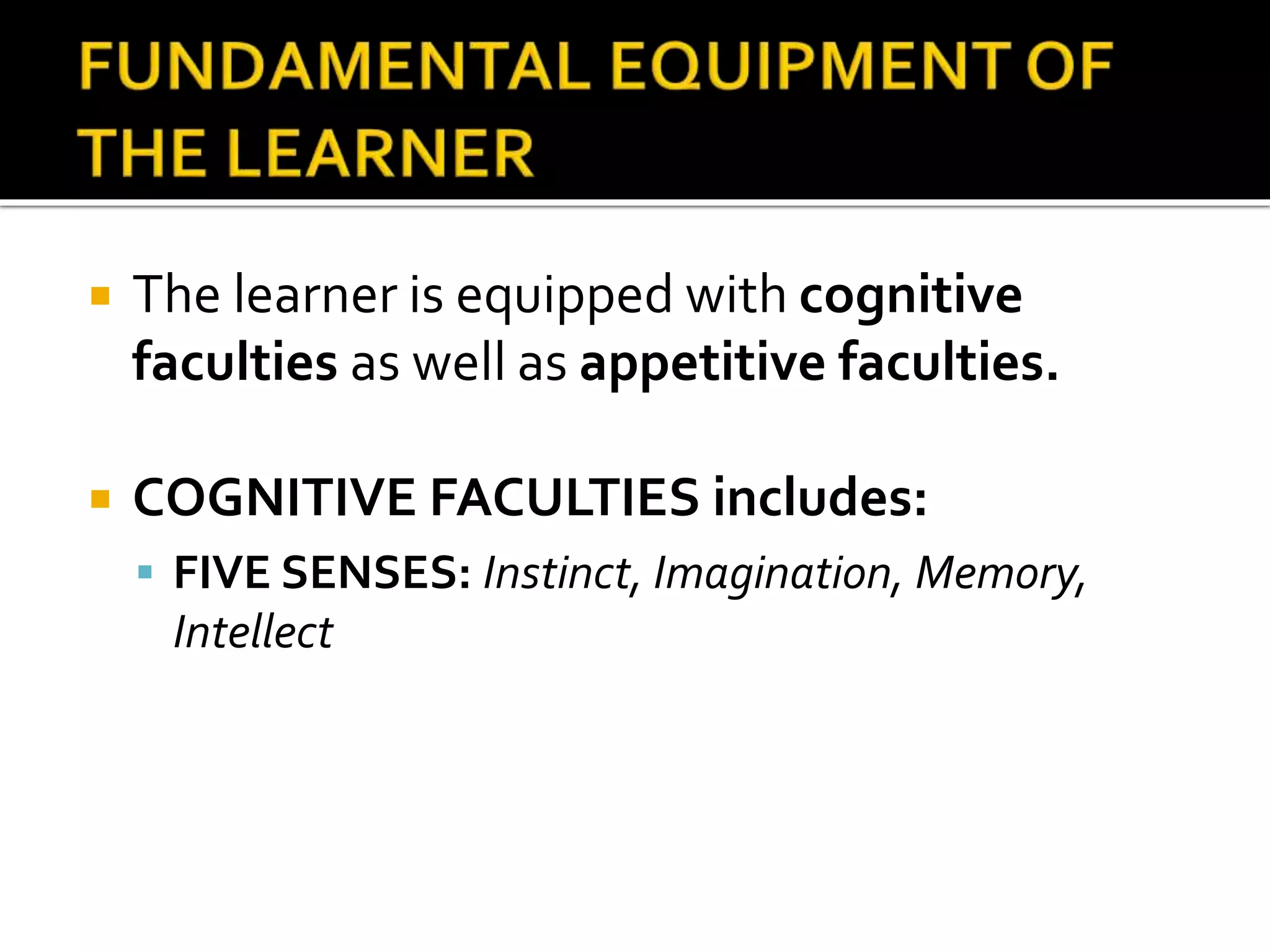
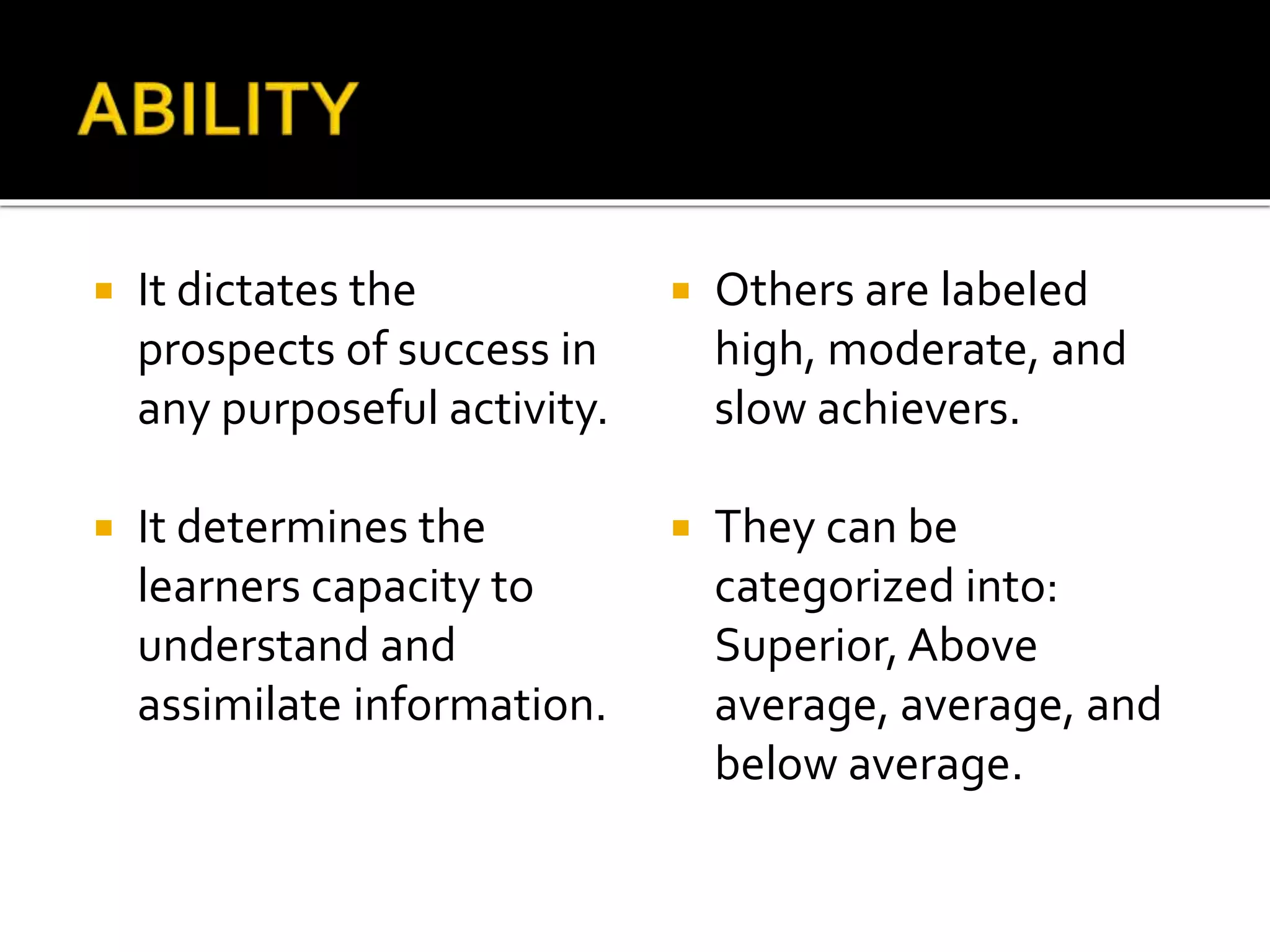
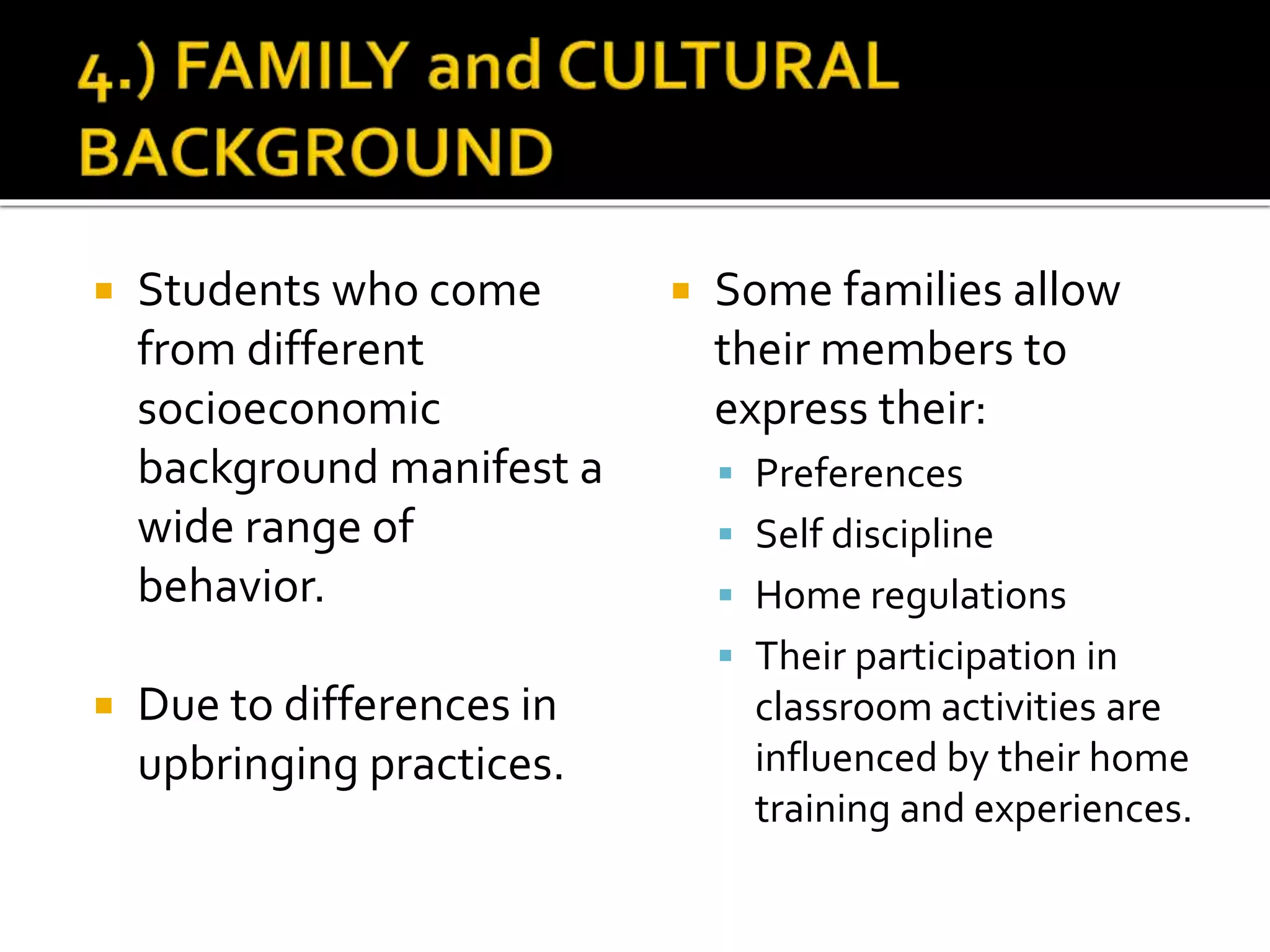
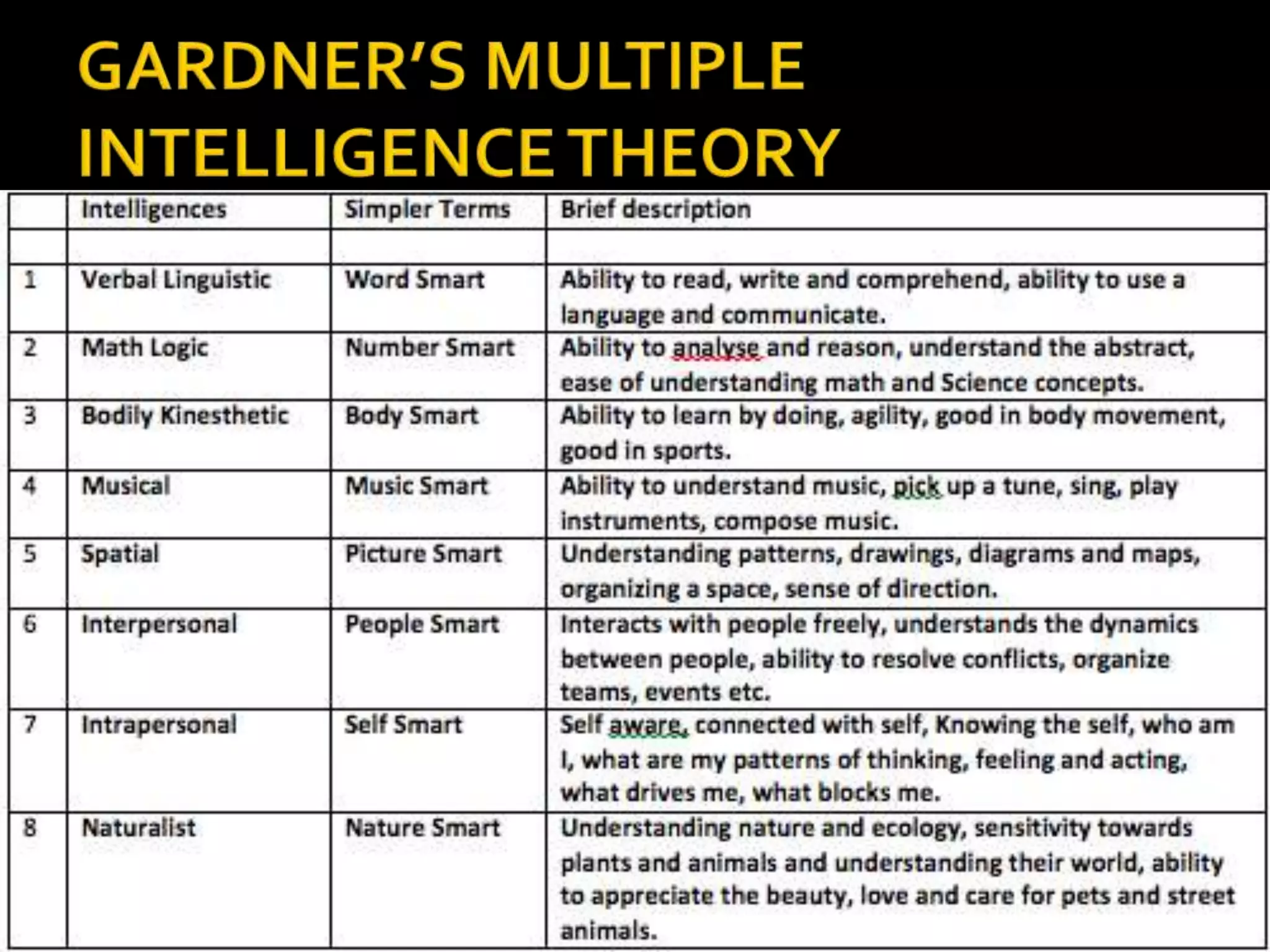
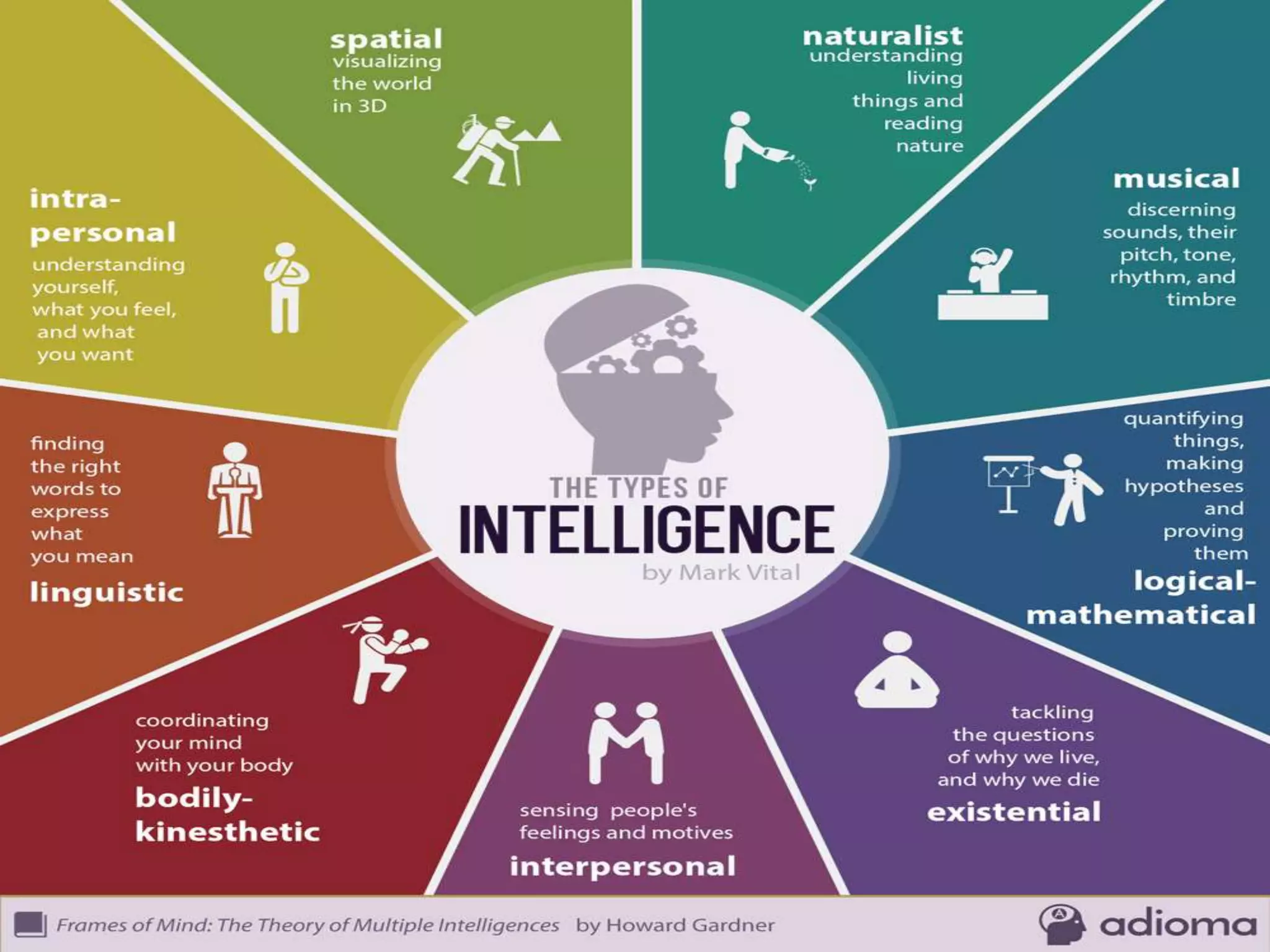
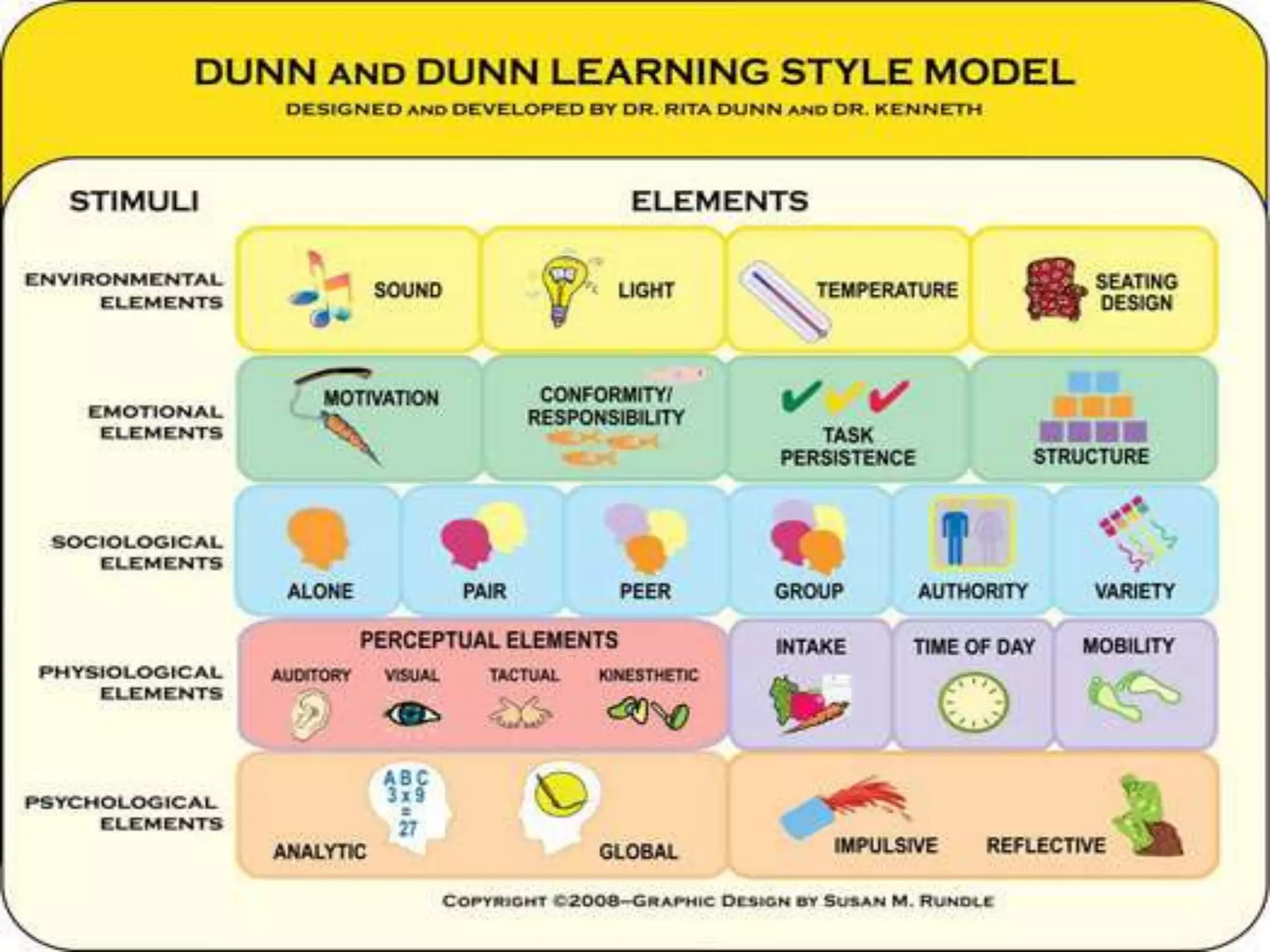
This document discusses the key elements of teaching and learning from a philosophical perspective. It describes the learner as having both a body and a soul, and that teachers must nourish both the physical and spiritual needs of students. It outlines several of the learner's cognitive and appetitive faculties, including the five senses, imagination, memory, intellect, feelings, emotion, and will. It also discusses factors that contribute to differences among learners such as ability, aptitude, interests, family background, attitudes, and values. The document emphasizes the importance of developing all aspects of the learner.