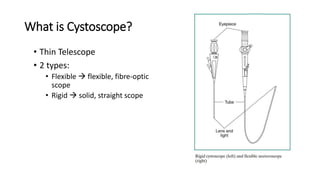
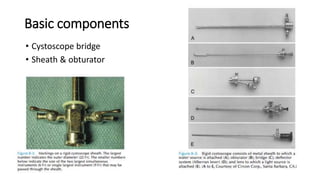
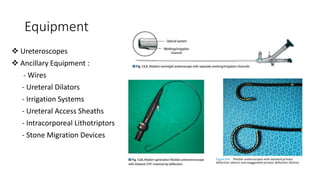
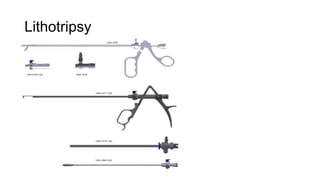
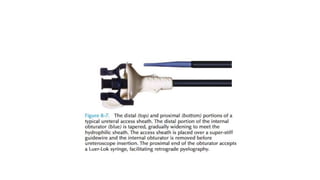
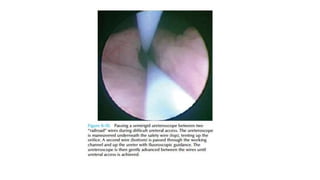
Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy are endoscopic procedures used to visualize the bladder and upper urinary tract. Cystoscopy can be performed rigidly or flexibly, with rigid cystoscopes providing better optics and larger working channels while flexible cystoscopes are more comfortable for patients. Important components of cystoscopes include the telescope lens, bridge, and sheath. Rigid and flexible ureteroscopes are used to inspect the ureters and kidneys. Proper patient preparation, use of irrigation, and careful technique help ensure safe and effective visualization and potential treatment of conditions like stones.