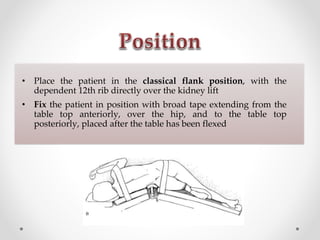
1. Open ureterolithotomy is indicated for stones with a low likelihood of success with less invasive techniques or in areas without access to ureteroscopy or lithotripsy.
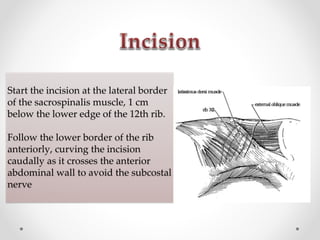
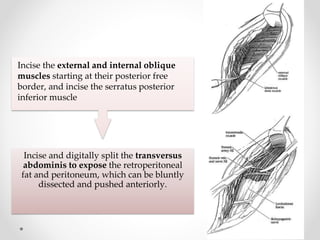
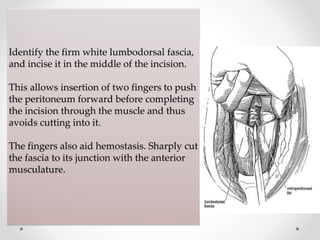
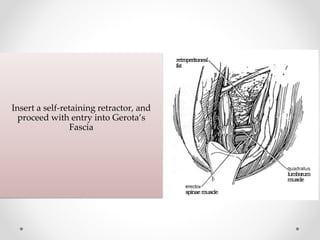
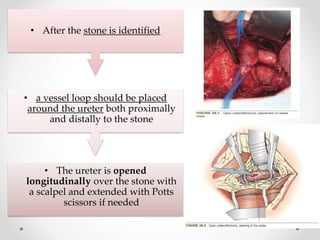
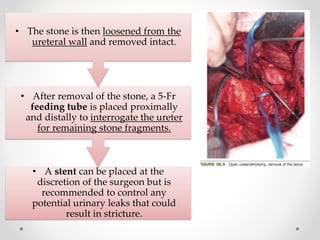
2. The procedure involves making an extraperitoneal or transperitoneal incision to access the ureter, dissecting and opening the ureter longitudinally over the stone, removing the stone, and closing the ureterotomy with sutures.
3. Postoperatively, patients are monitored for vital signs and urine output, given antibiotics and analgesics, and the drain is removed if output is low after 24 hours.