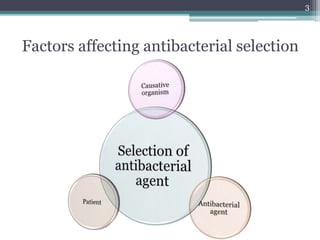
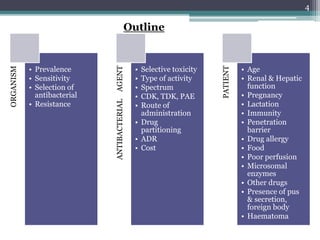
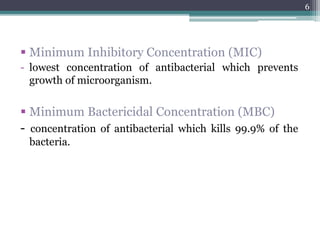
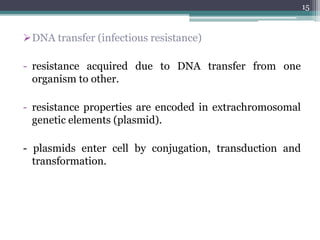
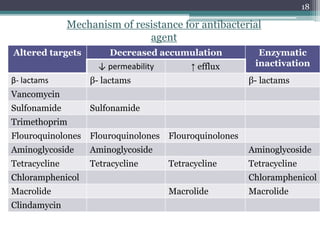
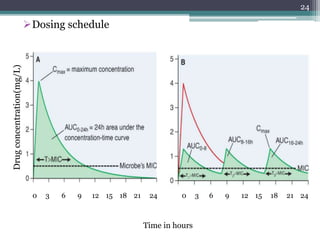
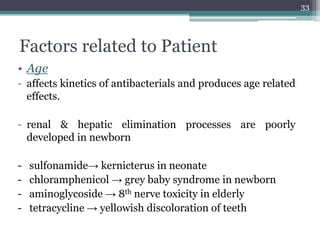
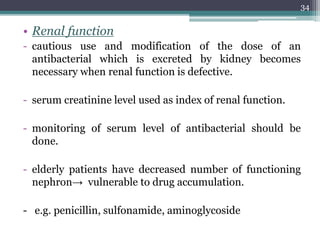
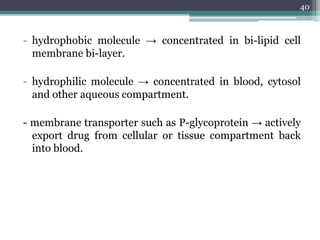
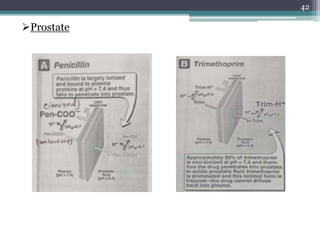
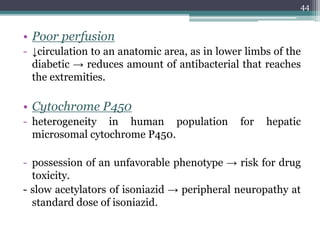
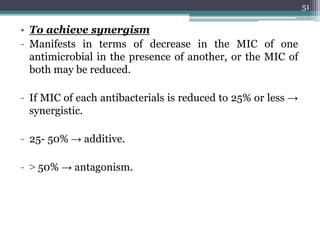
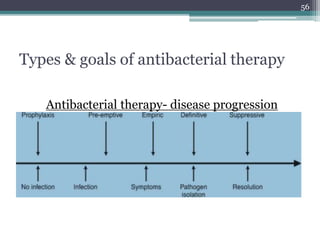
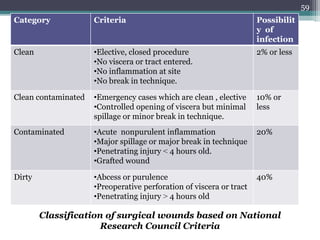
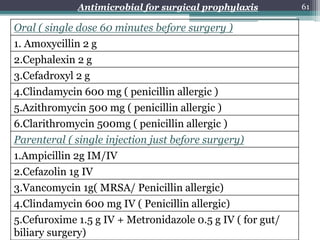
This document discusses the general principles and factors to consider when selecting an antibacterial agent. The three main factors are the organism, the antibacterial agent, and the patient. Selection involves considering the prevalence and sensitivity of the organism. It is also important to understand the antibacterial's spectrum of activity, pharmacokinetic properties like concentration-dependent or time-dependent killing, and potential for resistance development. Patient factors involve their health status, organ function, drug interactions, and barriers to drug penetration. Culture and sensitivity testing can help identify the organism and most effective antibacterial, while empirical therapy may be initially used if results will be delayed.