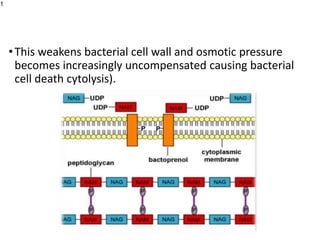
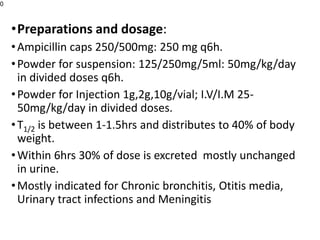
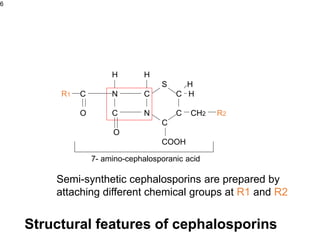
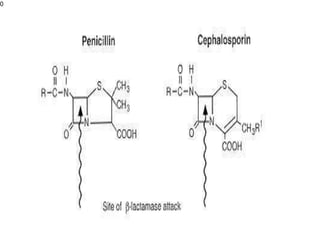
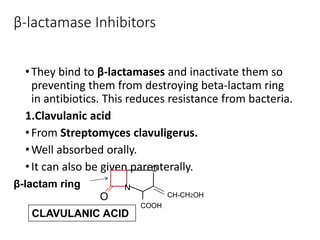
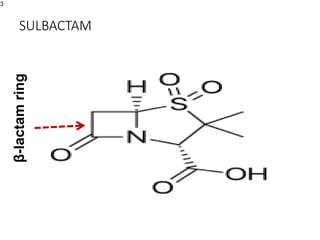
This document provides an overview of antibiotics, including their sources, classifications, mechanisms of action, and principles of antimicrobial therapy and selection. It focuses on penicillins as a class of antibiotics that act by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Penicillins were discovered from the mold Penicillium and their basic structure consists of a beta-lactam ring. They work by inhibiting the bacterial enzyme DD-transpeptidase and preventing cell wall synthesis, ultimately causing bacterial cell lysis. Factors such as acid stability, spectrum of activity, and resistance are considered in developing different penicillin derivatives.






![A. Identification of the infecting organism
•Characterizing the organism is central to selection of the
proper drug. The following methods can be used;
• Gram Staining: a rapid assessment. Useful in identifying the
presence and morphologic features of organism.
• Other laboratory techniques: Definitive identification of the
infecting organism. Such as detection of microbial antigens,
DNA, or RNA, or an inflammatory or host immune response to
the microorganism.
•In body fluids that are normally sterile (blood, serum,
cerebrospinal fluid [CSF], pleural fluid, synovial fluid,
peritoneal fluid, and urine).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-221024181317-c09a0aaf/85/1-ANTIBIOTICS-ppt-7-320.jpg)