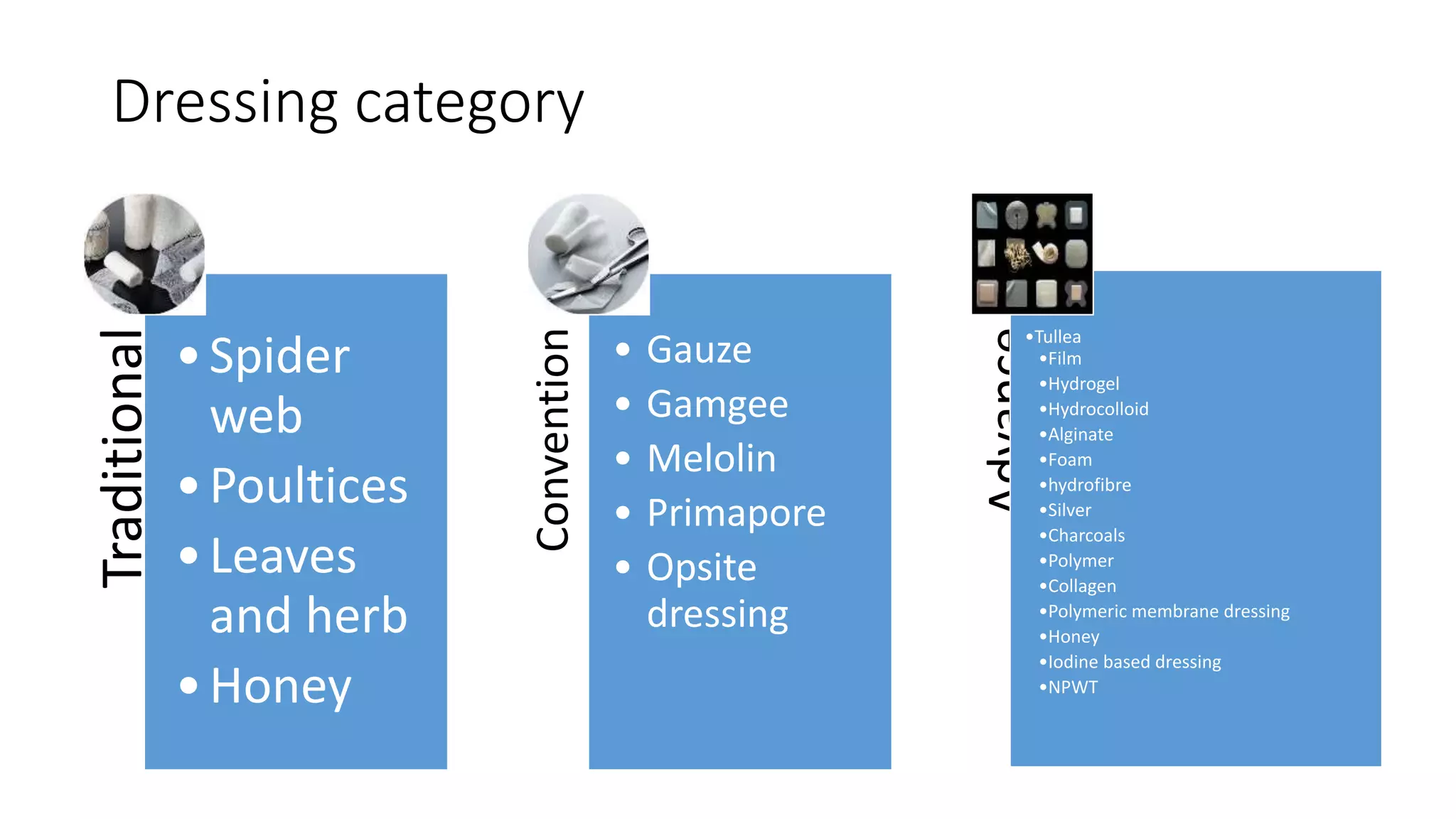
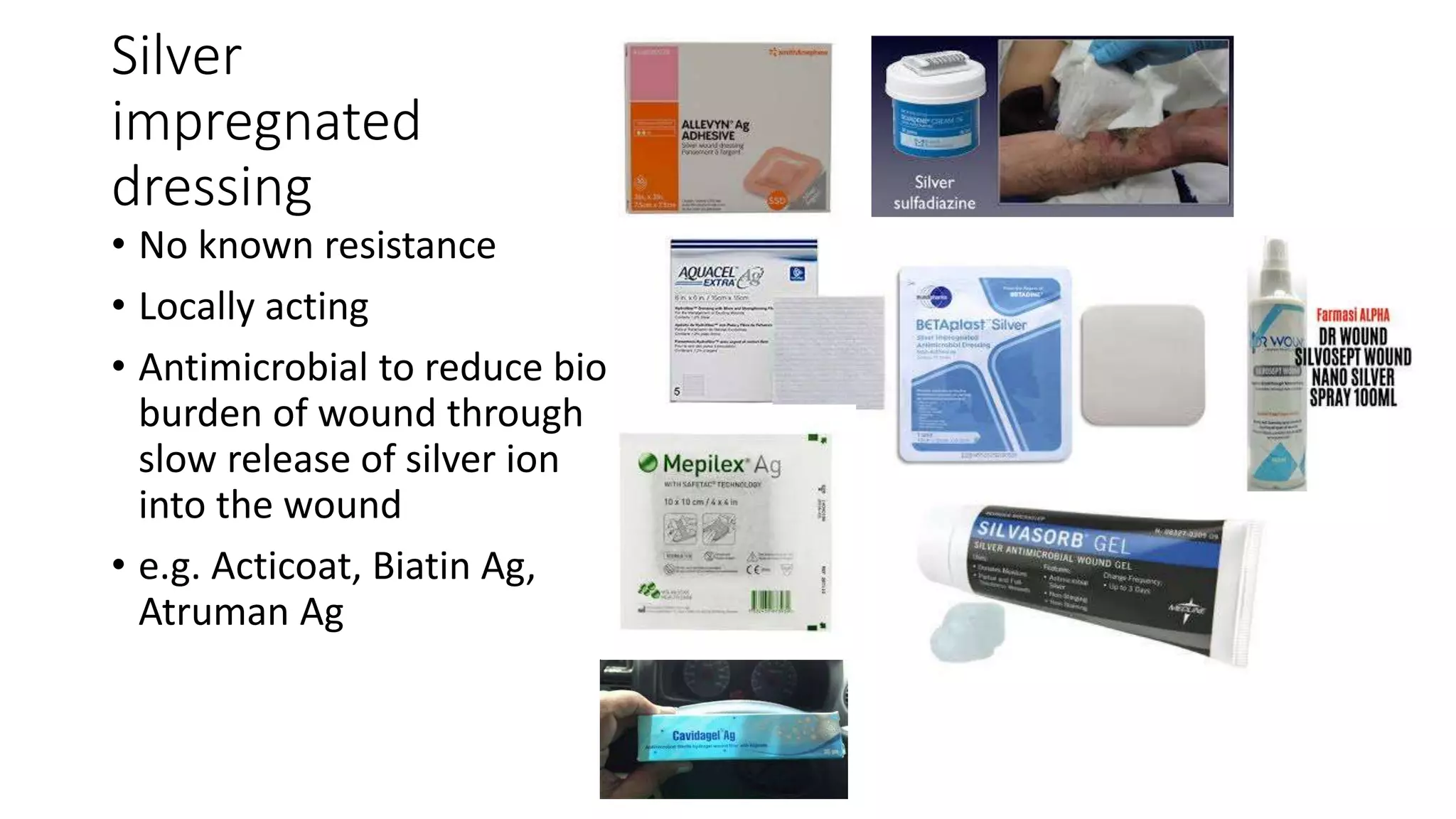
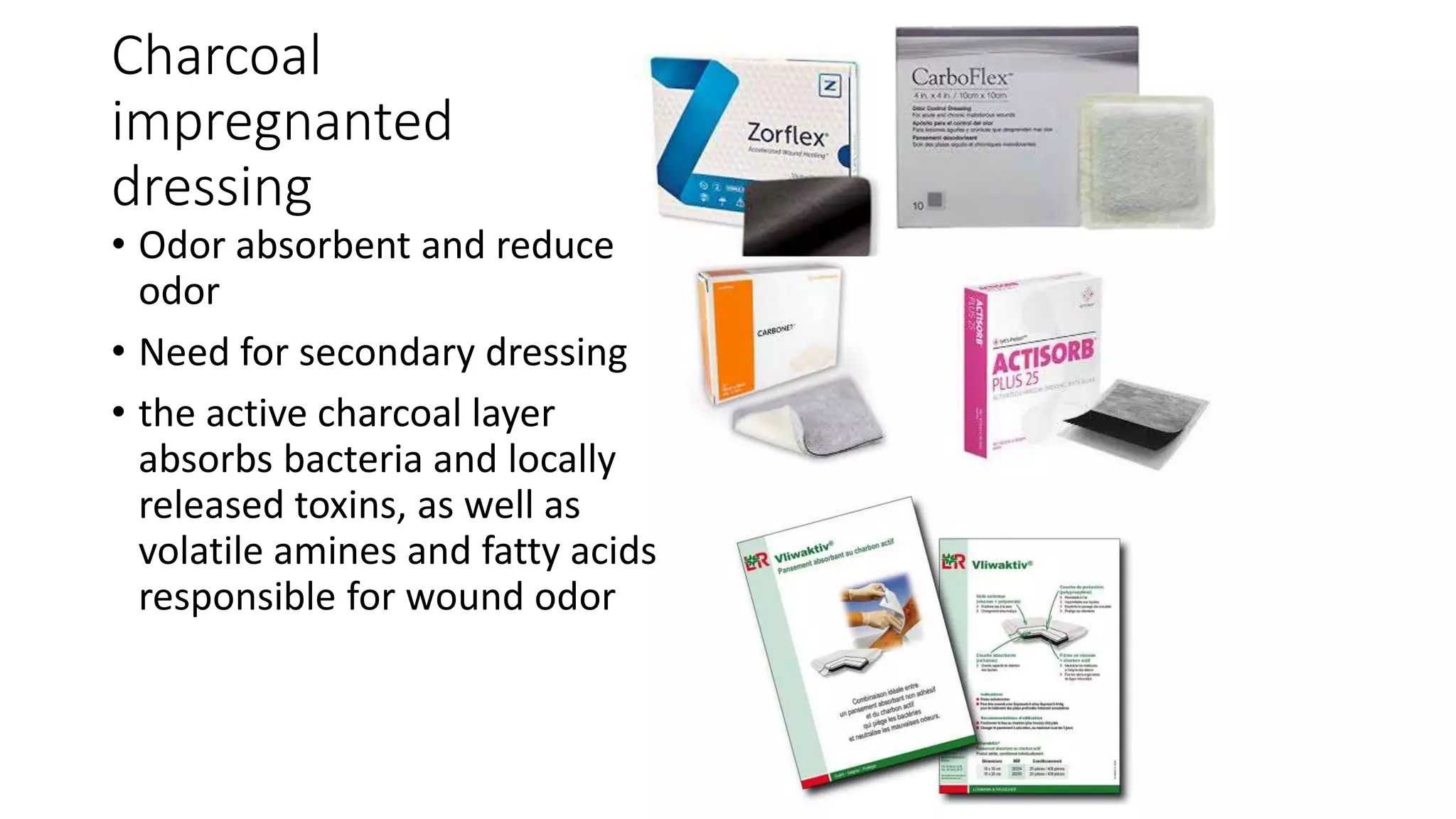
The document discusses principles of modern wound dressings, including ideal features and categories of dressings. It provides details on several specific advanced dressings types:
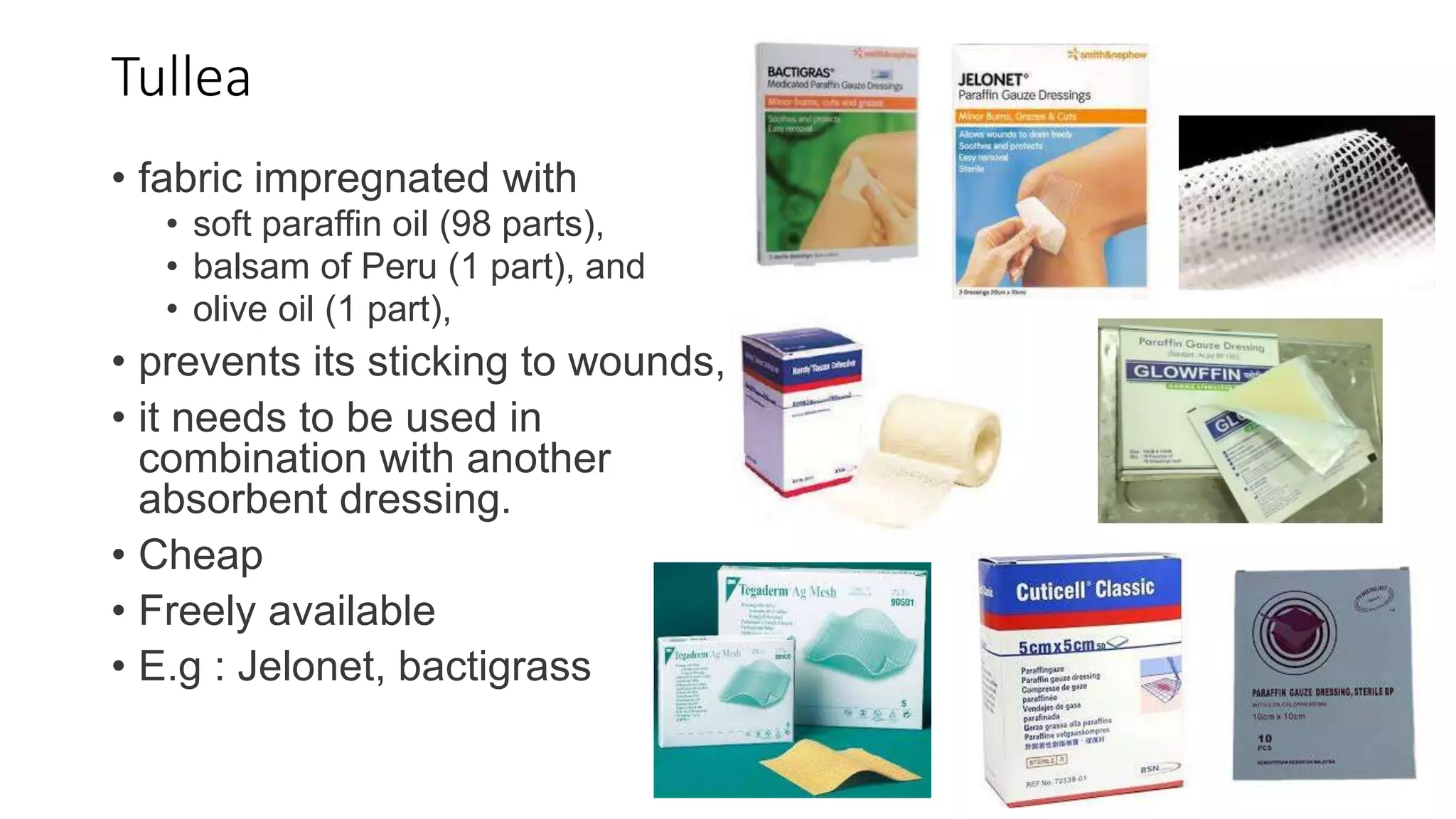
- Tullea dressings are fabric impregnated with oils to prevent sticking to wounds and are inexpensive and readily available.
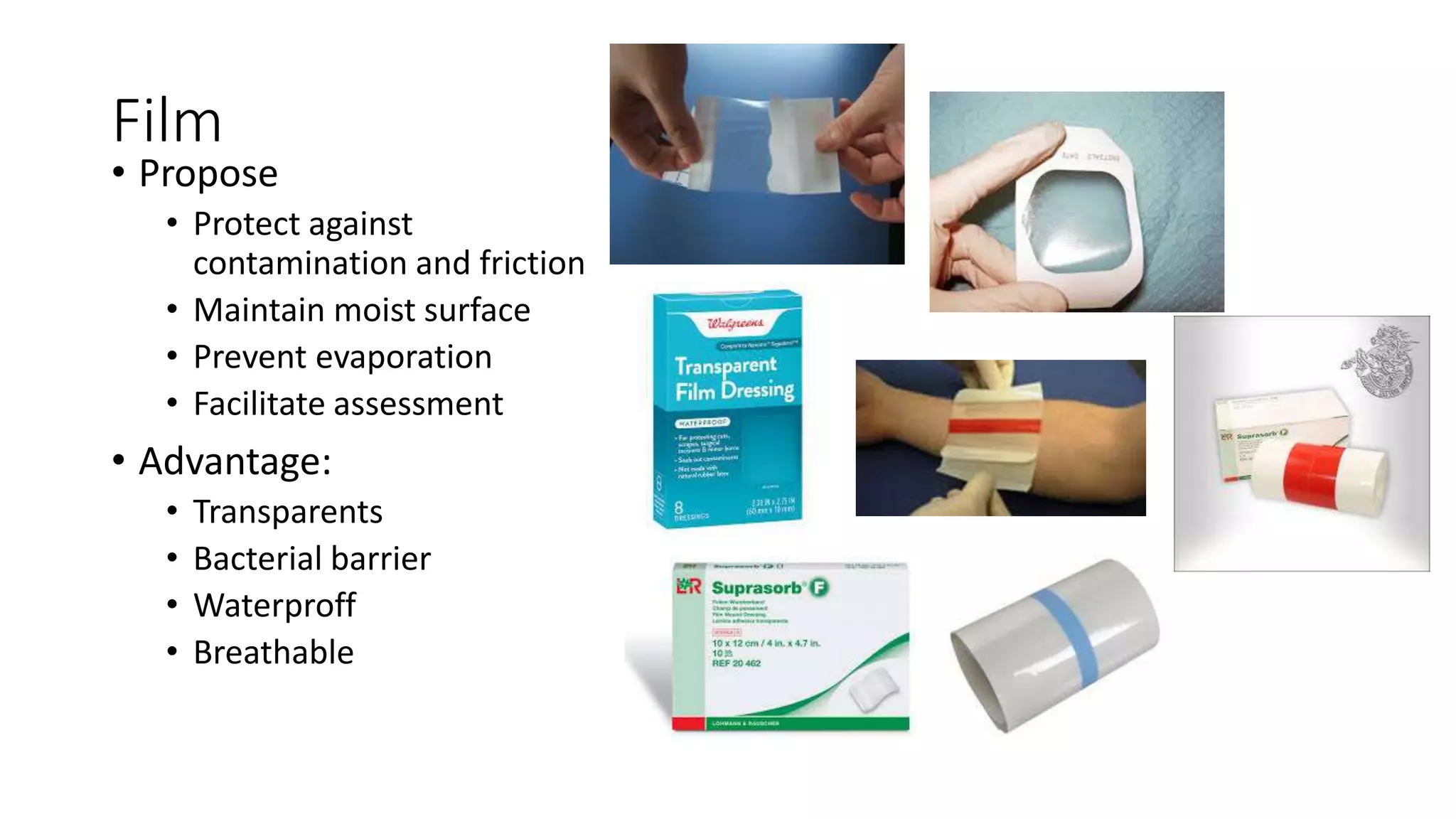
- Film dressings form a bacterial barrier and maintain a moist surface while allowing gaseous exchange.
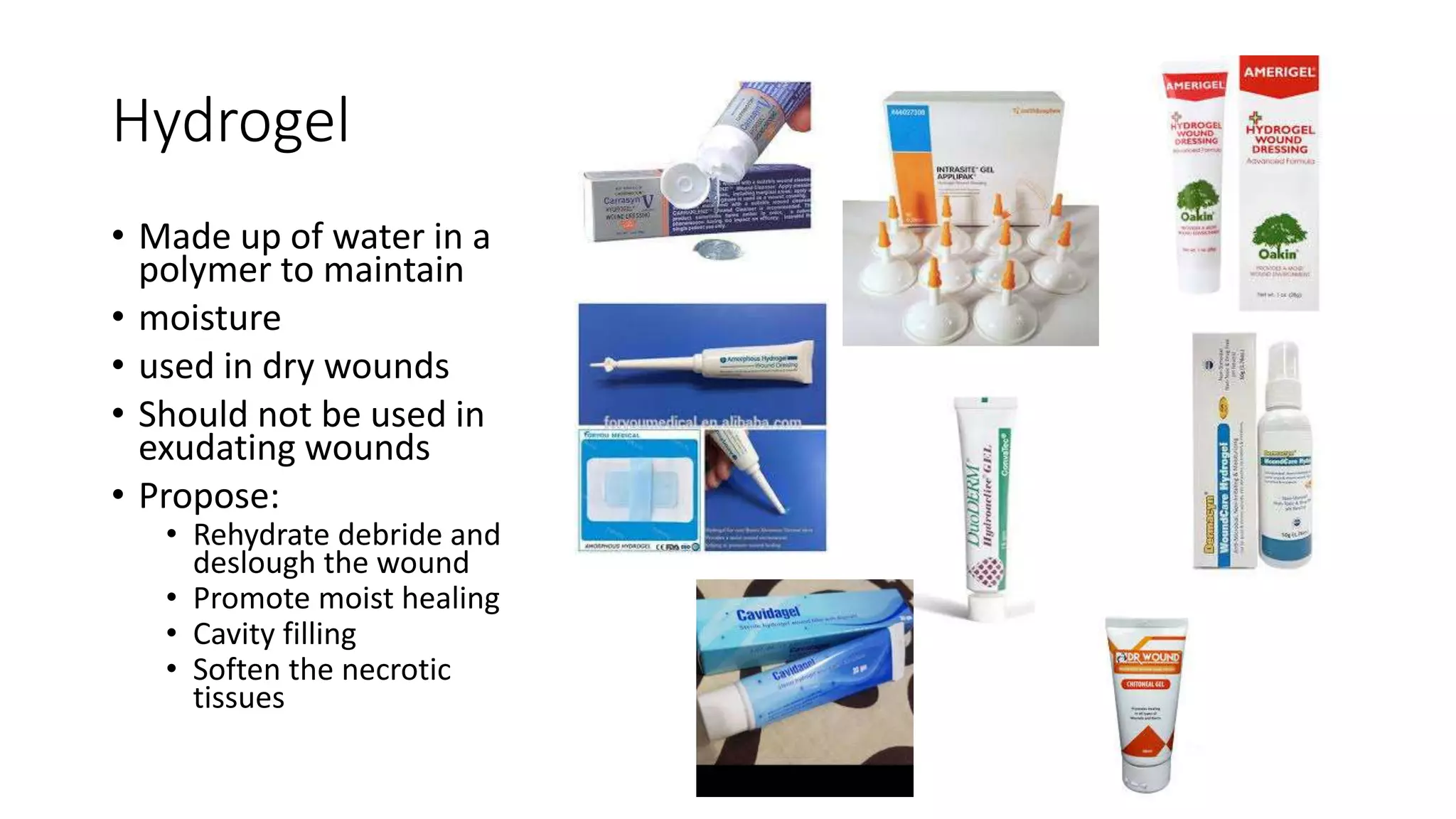
- Hydrogel dressings rehydrate wounds and promote moist healing by maintaining moisture in dry wounds.
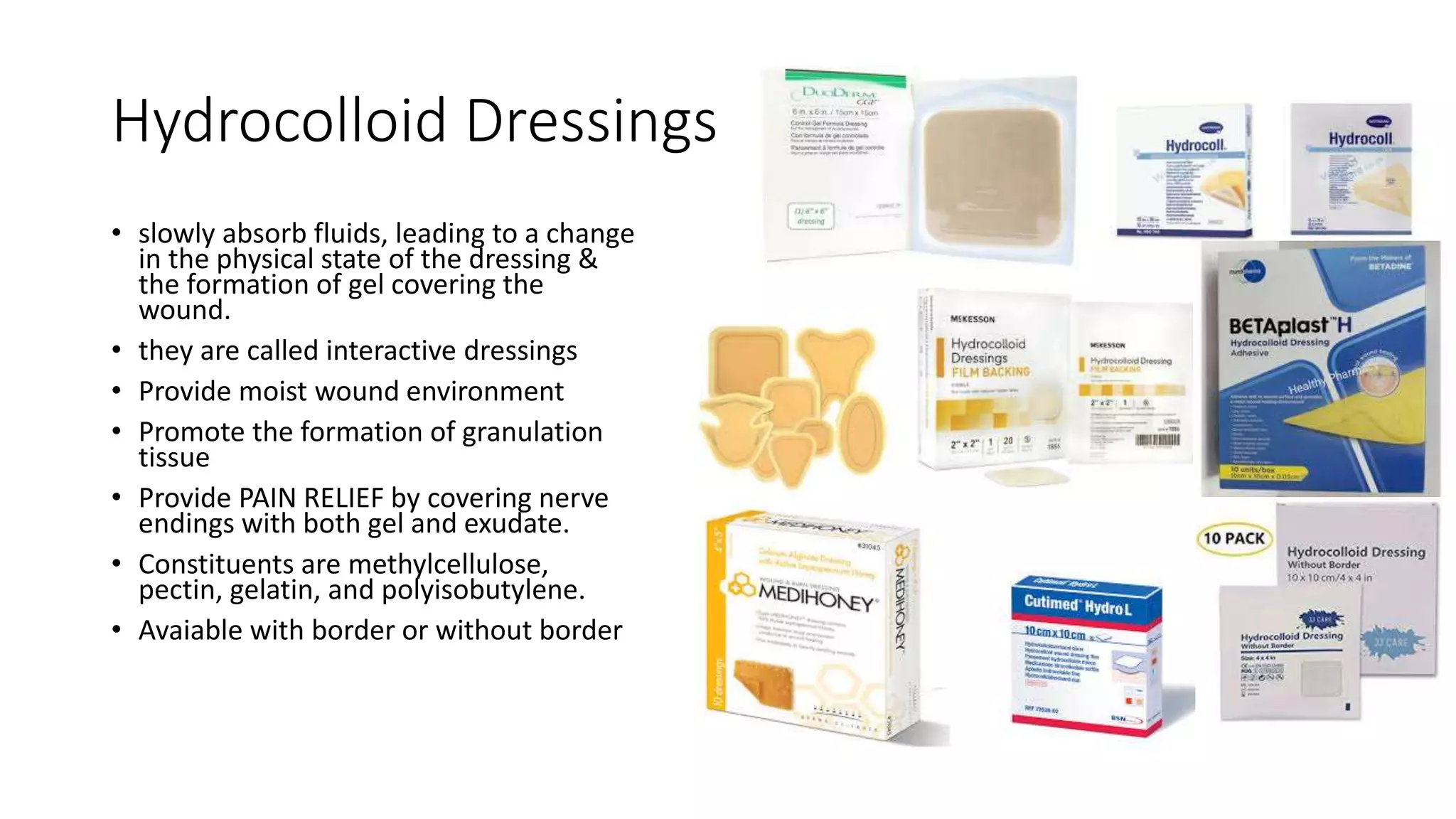
- Hydrocolloid dressings slowly absorb fluid to form a gel covering wounds, providing a moist environment and pain relief.
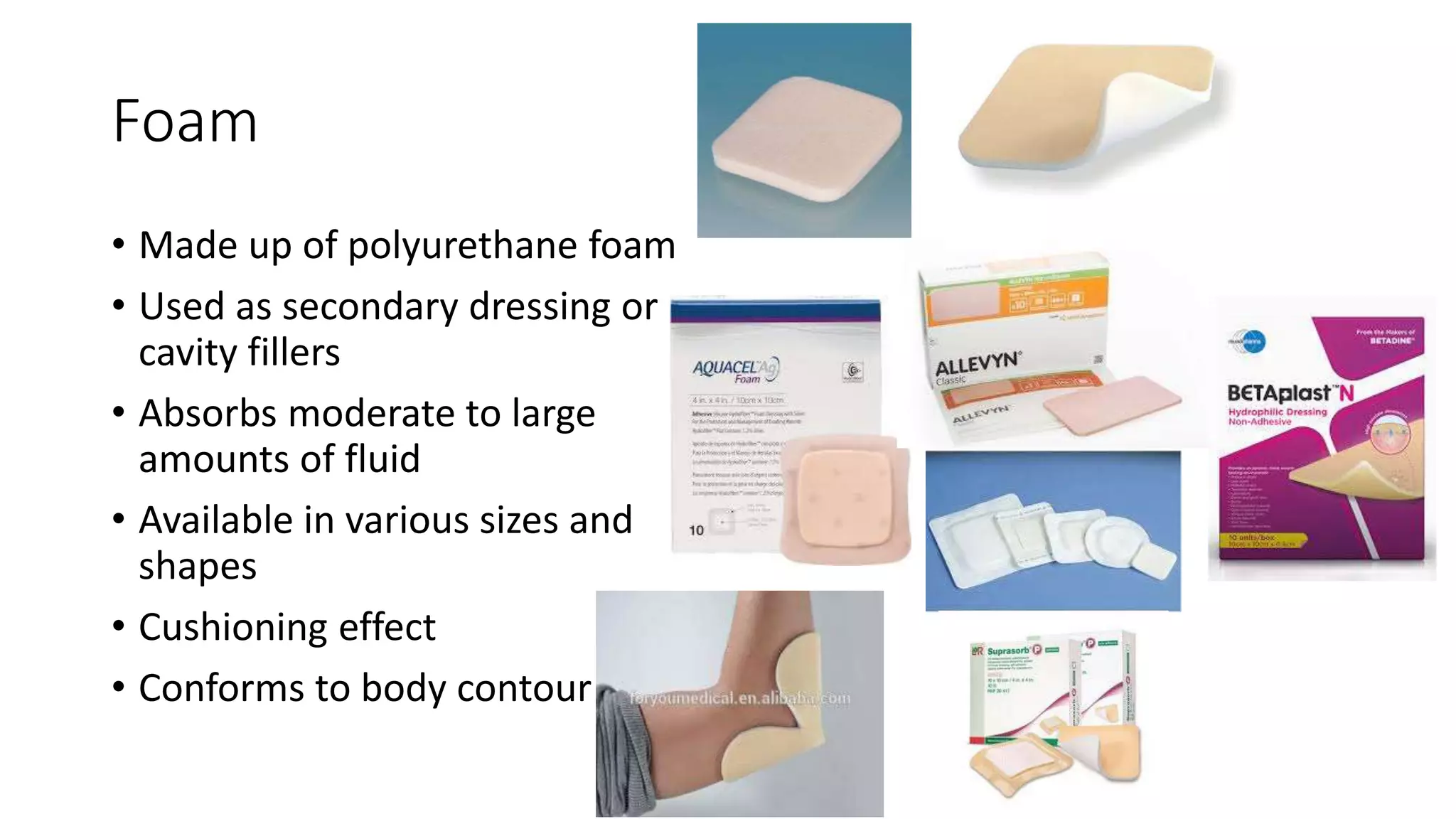
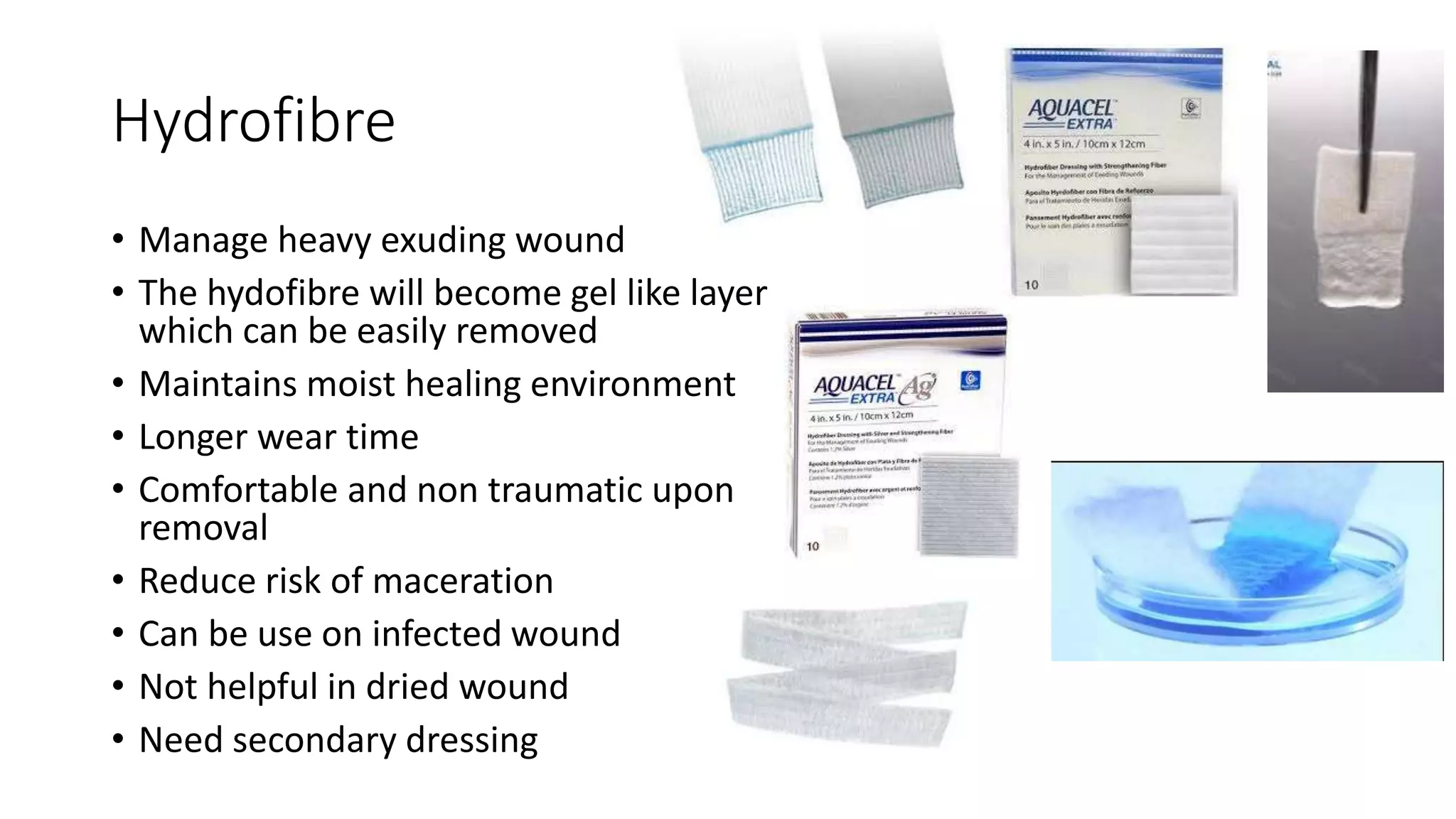
The document also discusses alginate, foam, hydrofibre, silver-impregn